Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
896 mL vapour of a hydrocarbon 'A' having carbon 87.80% and hydrogen 12.19% weighs 3.28 g at STP. Hydrotion of 'A' gives 2-methylpentane . Also 'A' on hydration in the presnce of H_(2)SO_(4) andHgSO_(4) gives a katone 'B' having molecular formula C_(6)H_(12)O. The ketone 'B' gives a positive iodoform test. Find the structure of 'A' and give the reactions involved. |
|
Answer» Solution :To DETERMINE the molecular mass of hydrocarbon (A) 896 mL vapour of `C_(x)H_(y)` (A) weighs `3.28`g at STP 22700 mL vapour of `C_(x)H_(y)` (A) weighs `(328xx22700)/(896)g//`"mol at" STP = `83.1g//mol` Hence , molecular mass of `C_(x)H_(y)` (A) =`83.1g mol^(-)` To determine the empirical formula of hydrocarbon (A) `{:("Elament" ,%,"Atomic mass","Relative ratio","Relative no. of atoms","Somplest ratio"),(C,87.8,12,7.31,1,3),(H,12.19,1,12.19,1.66,4.98~~5):}` Thus, Empirical formula of A si `C_(3)H_(5)` . `:.` Empirical formul mass = 36 + 5 = 41. `n = ("Molecular mass")/("Emprirical formula mass")= 83.1/41 = 2.02~~ 2` Molecular mass is double of empirical formula mass. `:.` Molecular formula is `C_(6)H_(10)` To determine the structure of compounds (A) and (B) 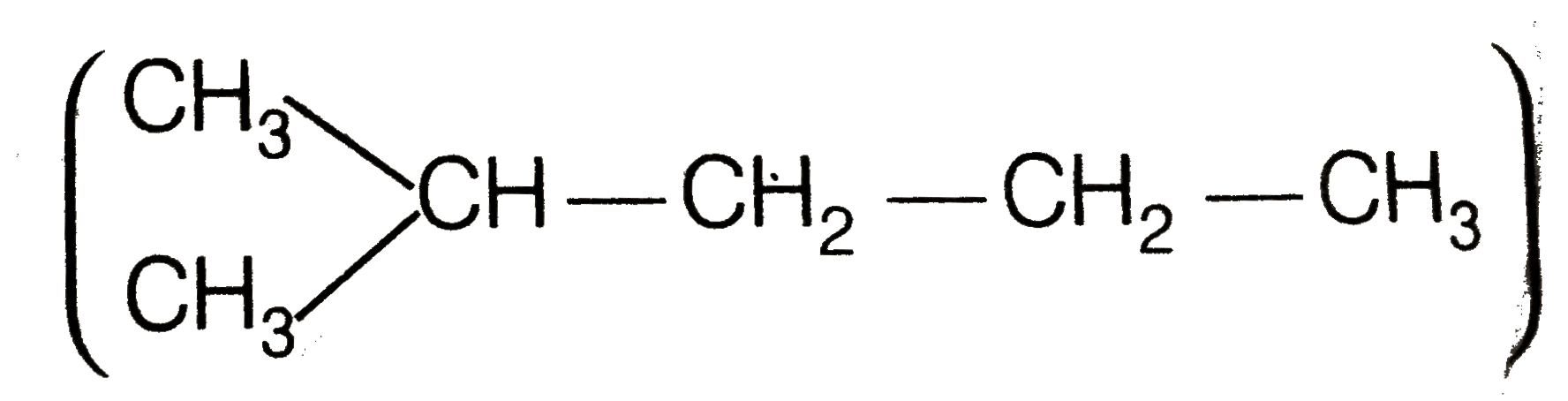 Hence, hydrogenation of hydrocarbon (A) requires 2 moles of hydrogen to form 2-methylpentane. Therefor, hyrocarbon (A) is an alkyne having five carbon atoms in a staight chain and a methyl substituent at position 2. Thus the possible structures for the alkyne (A) are I and II. 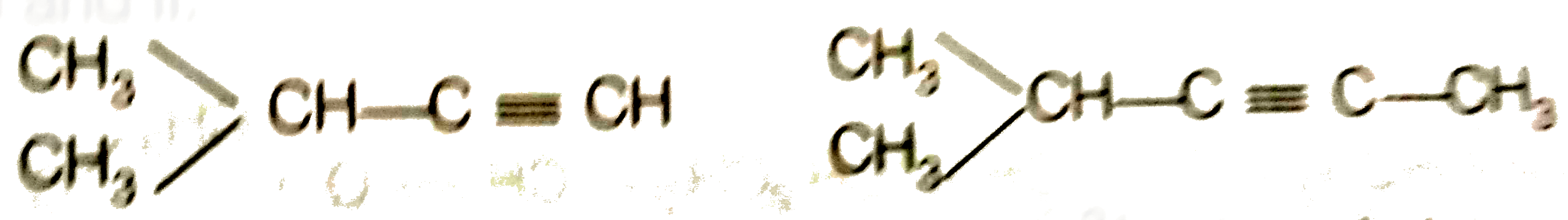 Since, addition of `H_(2)O` to alkyne (A) in presence of `Hg^(2+)` , give a ketong which gives positive iodoform test, therefore, therefore, ketone (B) must be a methyl katon , i.e., it must contain a `COOH_(3)` GROUP. Now addition of `H_(2)O` to alkyne (II) should give a MIXTURE of two ketones in which 2- methyl pentan -3 one (minor) and 4- methylpentan -2-one ketone (B) (which shows `+ve` iodoform test) PREDOMINATES. 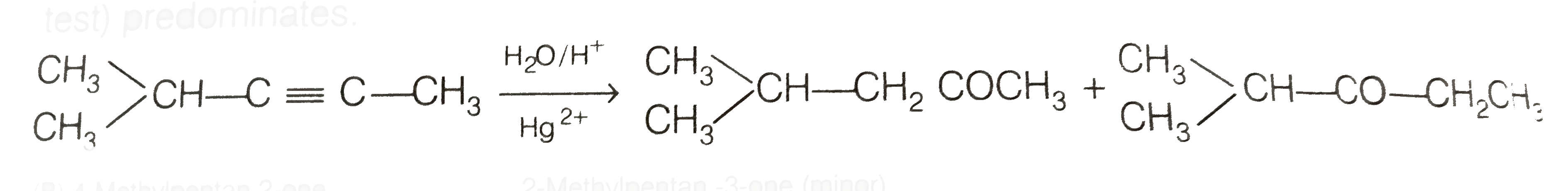 In contrast, addition of `H_(2)O` to alkyne (I) will give only one ketone, i.e., 4-methylpentan-2- one which gives iodoform test. 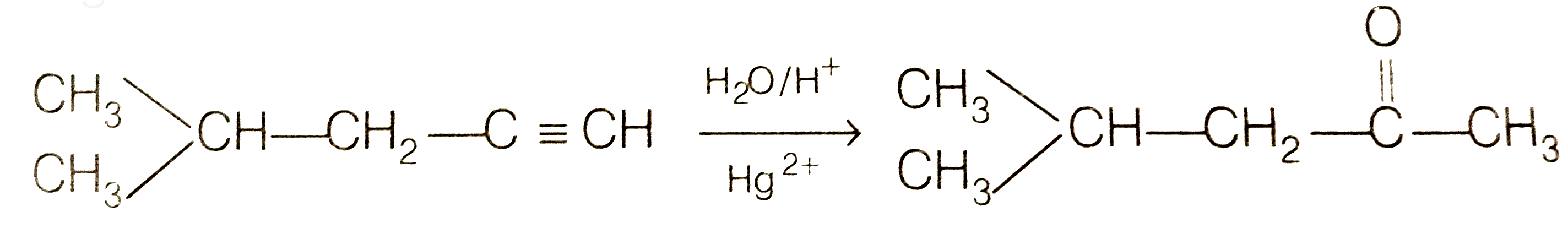 Thus, hydrocabon `C_(x)H_(y)` (A) is 4-methylpent -1-yne. 4-methylpentan -2 one (gives + ve iodoform test) |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- The weight of one molecule of compound C60H122 is
- Le
- Some important compounds of sodium, notes
- find the position of Zn30 in periodic table
- How to solve ion electron method
- Calculate the amount of water produced by the combustion of 16 g of methane
- Some MCQ between chapter 1and2
- Define reciprocal proportion
- What is the spectrum of hydrogen????
- I am not able to understand ch4 piz help me