Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Question : Describe Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM Cycle). |
Answer» Solution :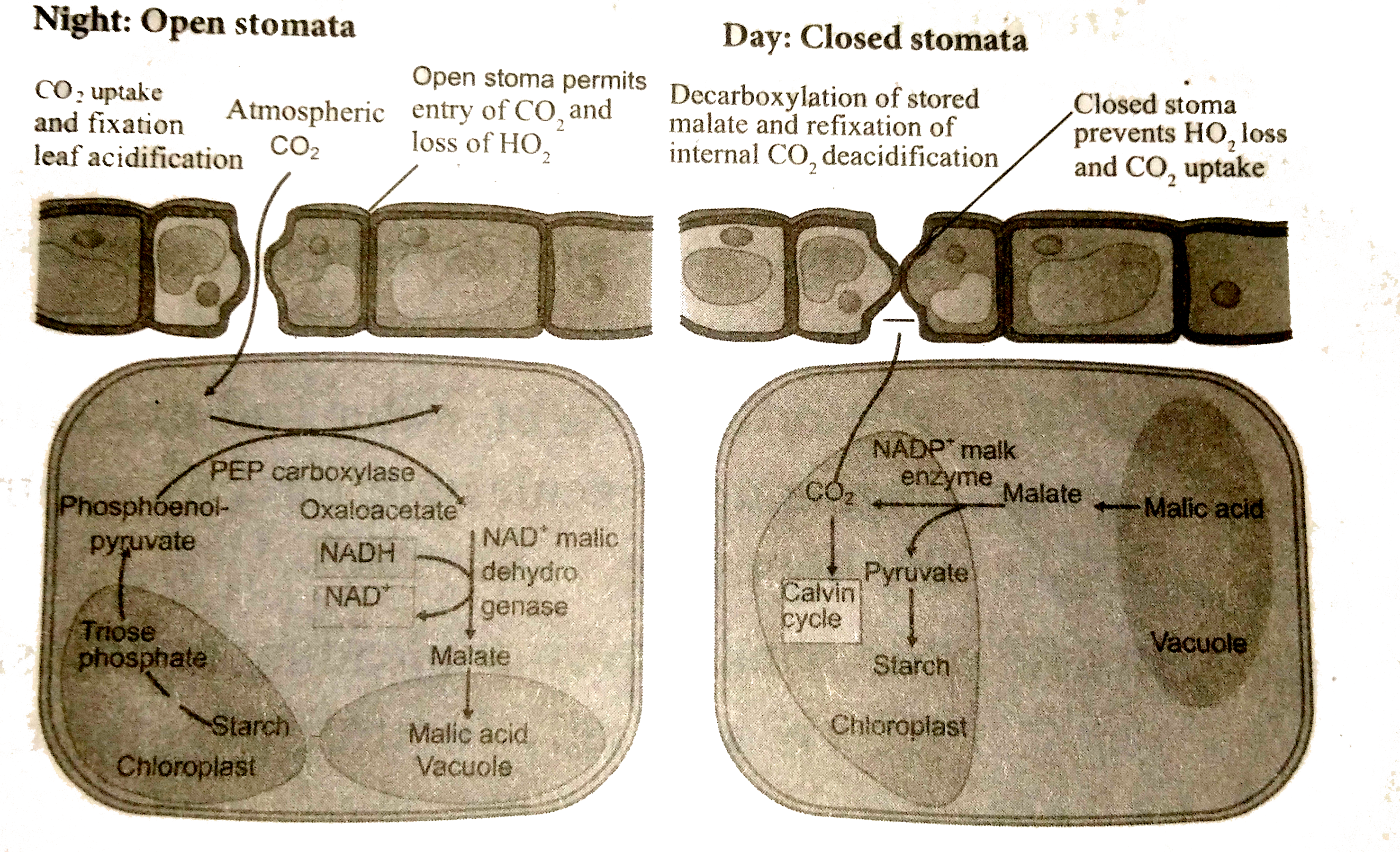 1. It is one of the carbon pathways identified in succulent plants growing in semi-arid or xerophytic condition. 2. First observed in Crassulaceae family plants like Bryophyllum, Sedum, Kalanchoe and is the reason behind the name of this cycle . 3 . Also noticed in plants from other families Eg.., Agave , Opuntia , Pineapple , Orchids , etc. 4 . The stomata are closed during day and are open during night ( Scotoactive) . This reverse stomatal rhythmhelps to CONSERVE water loss through transpiration and will stop the fixation of `CO_(2)` during the day time . 5. At night time CAM plants fix `CO_(2)` with the help of Phospho Enol Pyruvic acid (PEP) and produce OxaloAcetic Acid (OAA) . 5. Subsequently OAAis converted into Malic acid like `C_(4)` Cycle and gets accumulated in vacuole increasing the acidity . 6. During the day time stomata are closed and Malic acid is decarboxylated into Pyruvic acid resulting in the DECREASE of acidity . `CO_(2)` thus formed enters into Calvin Cycle and produces carbohydrates . Significance of CAM Cycle . 1It is advantageous for succulent plants to obtain `CO_(2)` from malic acid when stomata are closed. 2 During day time stomata are closed and `CO_(2)` is not taken but CONTINUE their photosynthesis . 3. Stomata closed during the day time and help the plants to avoid transpiration and water loss . |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- What is epidermal tissue system?
- Minimal coiling of chromosome
- Ncert question ch 16
- Ncert question of biology class 11
- What is phyllotaxy??????
- What is mycorrhizal one mark
- What is alternation of generation
- How is deuteromycetes different from other fungi?
- How can u classify leaves?
- Define nucleoplasm