Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Question : Describeany twosteps of formationof polypeptidechain. |
|
Answer» Solution :Formation of the polypeptidechain : This is the actual processof translationand it takes part in theresteps. Viz. initiation ,elongationand termination. (a)Initiation : (1) Duringthe process of initiation , there is formation of initiationcomplex. This requires the m-RNAhaving codons for the formationof polypeptideand twosubunitsof ribosomes, viz, 30S and50S.Initial AA-t-RNAcomplex and ATP, GTP as source of energy. (2)Initiation factors are alsonecessary for this process. In prokaryotes, the first AA-t-RNAcomplexhasaminoacid,N-formylmethionine (or f-met). n eukaryotesit ismethionine (met).Theprocess starts withbindingof m-RNAin the smallersubunitof 30S onribosome . (3) AUGis the start codon, whichis positioned properly. 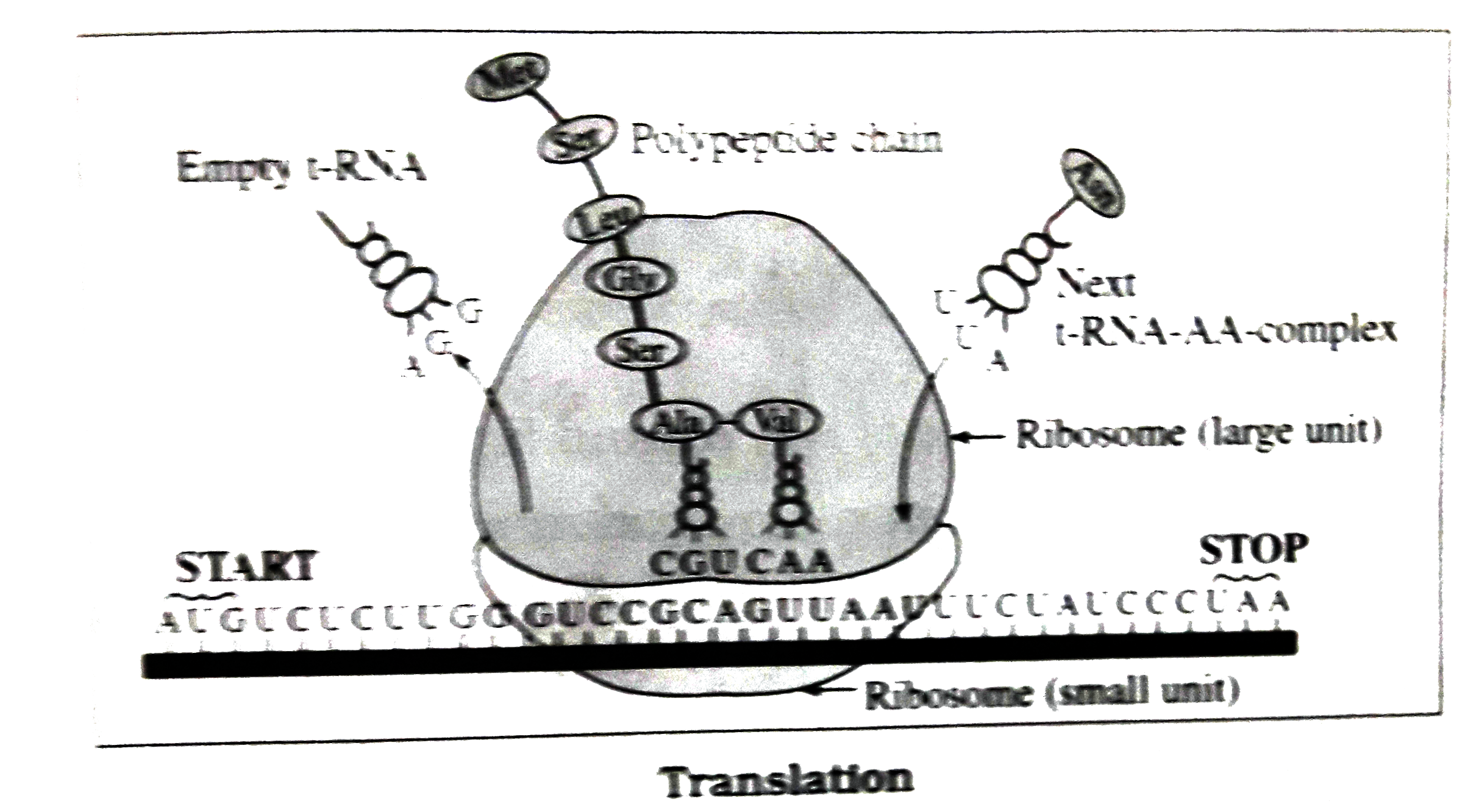 (4)TheAA-tRNA complex (f-met-RNA complex) then getsattachedto thestart codonat the P site of SMALLER subunit of ribosome. This is DONE by anticodon, UAC of t-RNA. Thensmall and large subunitsof ribosomes join and form 70Sribosome . (5)The ribosome has three sites,viz.aminoacyl site (A) , peptidylsite (P) and exit site (E).Aftertranslation is OVERTHE empty t-RNAleaves from E site. The AA -t-RNA complex binds at P sitedirectly. The otherincomingt-RNAcomplexesgetattached first at A site and then they are shiftedto P site. Polypeptidechainwhich is beingformed is releasedfrom P site. (b) Elongation : (1)Theprocessof elongationstarts afterinitiaion. This is doneby the formationof peptidelinkages betweenthe successiveaminoacidmolecules. Thisactivityis catalyzedby an enzyme. Peptidyl transferase. (2) Each t-RNAcomplexbrings a specificamino acid.The anticodonsand condons arecomplementaryto eachother. Due to thisappropriate aminoacidsare placedin theirproperposition. For the elongation, elongation factors are needed. (3) The ribosomes movealongthe m-RNAin step wisemannerfrom startto stopcodon in 5-3direction. Thismovement is calledtransclocation. The movement of m-RNA is onecondon ahead each time and therefore oneamino acid is added in the polypeptide CHAIN causingsystematic elongation. (c)Termination : (1)Elongation continuestill the last amino acid is added whichhas been coded by m-RNA. when m-RNAreaches EITHER UAA, UAG orUGA whichare termination codons then thetermination processbeings. (2) The termination factors R1 , R2 and S playan importantrolein indetifying the stopor ermination codon and releasingthe polypeptide chain. (3) Once the terminationis done, the smaller (30S) and larger (50S) subunits of ribosomes are freed from each other .The entireprocessof proteinsynthesis requires energywhichis suppliedby ATP and GTP. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Question : Which is the most common mechanism of genetic variation in the population of a sexually reproducing organism?
- Question : Which is the most common methods of fossilization? Explain how it occurs.
- Question : Which is the most common mechanism of genetic variation in the population of a sexually reproducing organism ?
- Question : Which is the microscopic parasitic animal ?
- Question : Which is the method of temporary birth control that reduces the chances of pregnancy by 80%? Write the fact on which this method is based.
- Question : Which is the main cause to convert water bodies into land ?
- Question : Which is the lowest level of ecological organisation ?
- Question : Which is the longest cell of the human body ?
- Question : Which is the longest bone of the body ?
- Question : Which is the link between glycolysis and Krebs cycle·?