Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Question : Describethe process of transcription in protein synthesis. |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) Transcription is the process in whichall the TYPES of RNA moleculesare formed. It is the friststep in the protein synthesis . In this,m -RNAstrand is formed fromDNAtemplate. (2)Initiatingthe process of transcription requiredthe presence of an enzyme called DNAdependentRNApolymerase. Genticinformation fromDNAis copiedinto m-RNAduringthe step, (3) A transcription unithas a promoter,the structuralgeneand a terminator. Thistranscripitonunithelpsin thetranscription process. The DNAstrandwhich is used for thesynthesisof RNA is calledtemplatestrand or antisencestrand. Thisis oriented in ` 3' to 5'`direction . The otherstrandwhich is no involvedin RNAsynthesisis calledcodingstrandor sense strand . THS strandhas theorientation` 5' to 3'` . A smallDNAsequence is usedas a binding site for RNApolymerase.thisregionis calledpromoter. Promoteris presenttowards 5 end.Towardsthe 3' end there is anothersmall DNAsequence called terminator.5' endis calledupstreamwhilethe 3' endis called downstream. (4)structural gene is generallymonocistronicin eukaryotes and polycistronic in prokaryotes. This gene getstranscribed. In eukaryotes. the geneshaveintronsand exons. In theexons, DNAsequences are expressedin the mature or processedRNA. Duringtranscription , the enzyme RNApolymerase bindsto the promoter site.it initiates the process . Dueto thistwostrandsof DNAseparate . ComplementaryRNA nucleotides arejoined to form the m-RNAstrand. Thisprocess is calledelongation . (5)A smallpartof RNAremainsattached to theenzyme RNA polymerase.This partreaches the terminator region and then bothenzyme and NEWLY synthesized m-RNAfalloff.Thisis called terminationof the transcription. 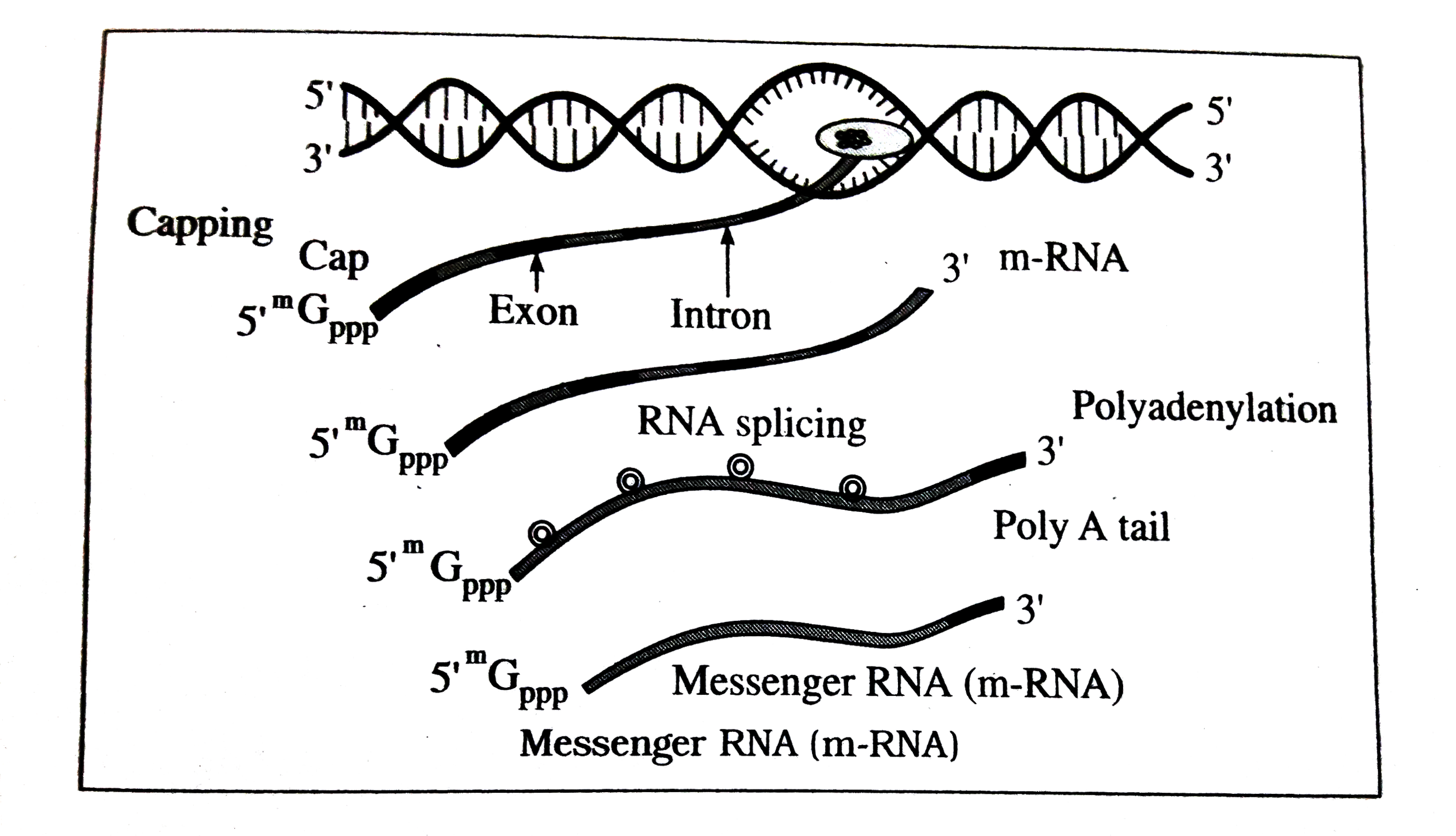 (6) Forthe process of transcription. initiation fator (` gamma` sigma) and temination factor(`rho` rho) are ESSENTIAL . In prokaryotesfurtherprocessingof RNAdoes notnot takeplacebut in eukaryotes , there is anelaborate process of RNAprocessing . Thereare three types of RNApolymeraseenzymesfor this purpoe. These are RNApolymerase I , II and III. (7) (i) r-RNAis formedis formedby RNApolymerase I. (ii) hn-RNA (het- eroncuclear RNA)is formedby RNApolymerase II and (iii) t-RNAand sn-RNA (small nuclear) are formedby RNApolymerase III. (8)The RNAformedby transcriptioon is non functionalin eukaryotes. It undergoesfurther processing for becoming active. Thisprocess consistsof splicing, cappingand TAILING (9) Suchhn-RNA whichundergoessplicing , cappingand tailingnow becomes m-RNA. In eukaryotic cellsthe m-RNA molecular leavesnucleusand goes toribosomes to carryout the further process of protein synthesis. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Question : Which is the most common mechanism of genetic variation in the population of a sexually reproducing organism?
- Question : Which is the most common methods of fossilization? Explain how it occurs.
- Question : Which is the most common mechanism of genetic variation in the population of a sexually reproducing organism ?
- Question : Which is the microscopic parasitic animal ?
- Question : Which is the method of temporary birth control that reduces the chances of pregnancy by 80%? Write the fact on which this method is based.
- Question : Which is the main cause to convert water bodies into land ?
- Question : Which is the lowest level of ecological organisation ?
- Question : Which is the longest cell of the human body ?
- Question : Which is the longest bone of the body ?
- Question : Which is the link between glycolysis and Krebs cycle·?