Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Show that the coefficient of area expansions, (DeltaA//A)//DeltaT, of a rectangular sheet of the solid is twice its linear expansively, alpha_(l).(alpha_(l)=10^(-5)K^(-1)) |
Answer» Solution :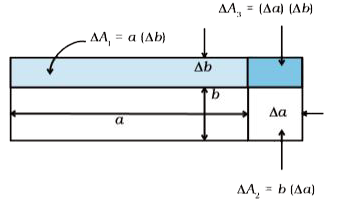 Consider a RECTANGULAR sheet of the solid material of length a and BREADTH b (Fig. 11.8). When the TEMPERATURE INCREASES by`Delta T, a `Increases by `Delta a = alpha_(1) a Delta T` andbincreases by `Delta b = alpha_(1), b Detla T`. From Fig. 11.8, the increase in area `Delta A = DeltaA_(1) + DeltaA_(2) + DeltaA_(3)` `DeltaA = a Deltab + b Delta a + (Delta a) (Deltab)` ` = a alpha_(1) b DeltaT + b alpha_(1) a DeltaT + (alpha_(1))^(2) AB (Delta T)^(2)` ` = alpha_(1) ab DeltaT (2 +alpha_(1) DeltaT) = alpha_(1) A DeltaT (2 + alpha_(1) DeltaT)` Since `alpha_(1) approx 10^(-5) K^(-1)`,from Table 11.1 , the product `alpha_(1) Delta T ` for fractional temperature is small in comparision with 2 and may be neglected. Hence, `((Delta A)/A) 1/(Delta T) approx 2alpha_(l) ` |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- What is uniform velocity
- Derive the speed time equation by calculas method
- 9×2y - 24x^2 +16y^3.factorise?
- Give me tips for preparation of physics??
- Advantage of friction
- Derivation of equation of Newton\'s Second Law of Motion that is F=ma
- Equation of projectile?
- Unit of Permeability
- Difference between vectr and scalar
- what is centripetal force ?