Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
A methyl glucoside can be converted to the _______ anhydride in the presence of pyridine. Identify the produce formed. |
|
Answer» tetramethyl 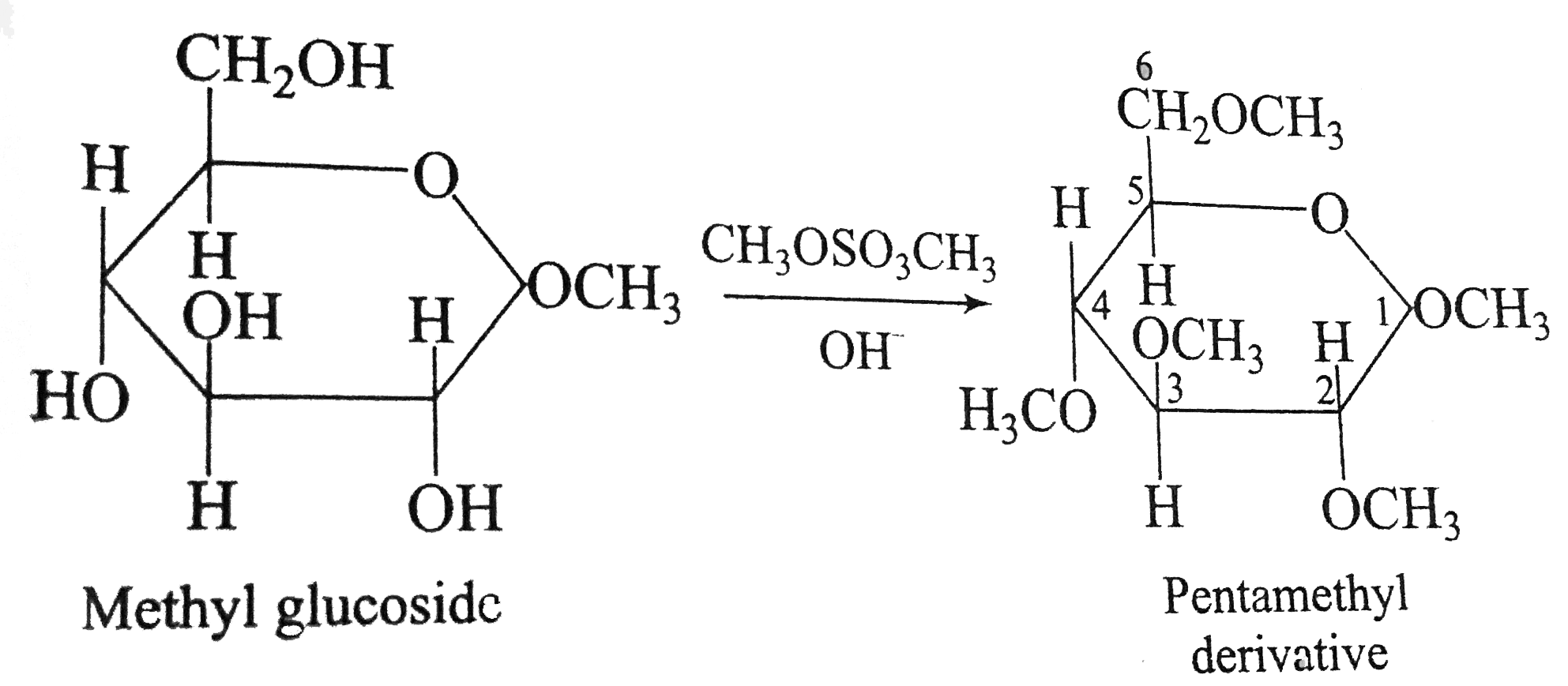 This reaction is just a multiple williamson synthesis. The hydroxyl groups of monosaccharides are more acidic than those of ordinary alcohols because the monosaccharides contains so many electronegative oxygen atoms, all of which exert electron-withdrawing inductive effects no nearby hydroxyl groups. In aqueous `NaOH`, the hydroxyl groups are CONVERTED to alkoxide ions, and each of these, in TURN reacts with dimethyl sulphate in an `S_(N)^(2)` reaction to yield a methyl ether. The process called exhaustive methylation. The methoxy groups at `C_(2), C_(3), C_(4)` and `C_(6)` of the pentmethyl derivative are ordinary ether groups. Consequently, these groups are stable in dilute aqueous acid (remember, to cleave ethers requires HEATING with come. `HBr` or `HI`). However, the methoxy group at `C1` is different from others because it is a part of an acetal linkage (it is GLYCOSIDIC). Therefore, treating the pentamethyl derivative with dilute aqueous acid causes hydrolysis of this glycosidic methoxy group and produces 2,3,4,6- teta `O`-methyl - `D-` glucose (The `O` in this name means that methyl groups are bonded to oxygen atoms). |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?