Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Answer the following questions : (a) You have learnt that plane and convex mirrors produce virtual images of objects. Can they produce real images under some circumstances ? Explain. (b) A virtual image, we always say, cannot be caught on a screen. Yet when we 'see' a virtual image, we are obviously bringing it on to the 'screen' (i.e., the retina) of our eye. Is there a contradiction ? (c) A diver under water, looks obliquely at a fisherman standing on the bank of a lake. Would the fisherman look taller or shorter to the diver than what he actually is ? (d) Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely ? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease ? (e) The refractive index of diamond is much greater than that of ordinary glass. Is this fact of some use to a diamond cutter ? |
Answer» Solution :(a) We know that both plane and convex mirrors produce virtual images of real objects. They may produce real image of virtual objects i.e., when the incident light beam is highly convergent, converging towards a point O behind the mirror as shown in Fig. 9.05(a) for a plane mirror and Fig. 9.05(b) for a convex mirror respectively.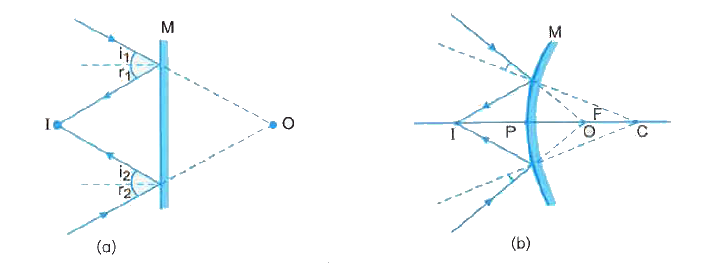 (b) A virtual image MEANS that the reflected/ refracted light rays form a divergent beam and HENCE it cannot be converged on a screen. However, when we .see. a virtual image, this virtual image acts as an object and the convex lens of eye converges it on the screen (the retina) of our eye. Therefore, there is no CONTRADICTION of any sort. (c) As shown in Fig. 9.06, when an object OO. situated in air is viewed from inside water its virtual, erect and magnified image II. is formed. It is on this account that to a diver under water a fisherman standing on the bank of lake appears to be taller than what he actually is. 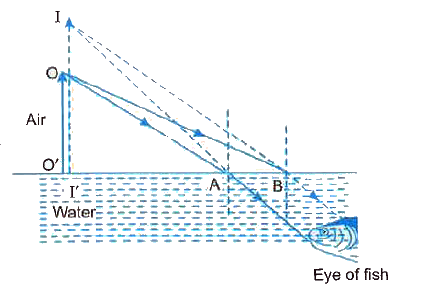 (d) The apparent depth decreases when a tank filled with water is viewed obliquely compared to the depth when SEEN near normally. (e) Refractive index of diamond is much greater than that of glass. In fact, it is 2.42 as compared to 1.5 of glass. Consequently, CRITICAL angle for diamond air interface is quite small (about 24°). Thus, a skilled diamond cutter has a large option to cut the diamond faces for any value of angle of incidence varying from 24° to 90°. It makes his work easy. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- A wire is bent to form a semicircle of the radius a. The wire rotates about its one end with angular velocity omega . Axis of rotation is perpendicular to the plane of the semicircle . In the space , a uniform magnetic field of induction B exists along the aixs of rotation as shown in the figure . Then -
- A massless non conducting rod AB of length 2l is placed in uniform time varying magnetic field confined in a cylindrical region of radius (R gt l) as shown in the figure. The center of the rod coincides with the centre of the cylin- drical region. The rod can freely rotate in the plane of the Figure about an axis coinciding with the axis of the cylinder. Two particles, each of mass m and charge q are attached to the ends A and B of the rod. The time varying magnetic field in this cylindrical region is given by B = B_(0) [1-(t)/(2)] where B_(0) is a constant. The field is switched on at time t = 0. Consider B_(0) = 100T, l = 4 cm(q)/(m) = (4pi)/(100) C//kg. Calculate the time in which the rod will reach position CD shown in the figure for th first time. Will end A be at C or D at this instant ?
- A concave lens with equal radius of curvature both sides has a focal length of 12 cm. The refractive index of the lens is 1.5. How will the focal length of the lens change if it is immersed in the liquid of refractive index 1.8 ?
- If the tempearture of black body is raised by 5%, the heat energy radiated would increases by :
- What are the co-ordinates of the image of S formed by a plane mirror as shown in figure?
- The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ in Fig. The direction in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4. Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
- What is meant by polarisation ?
- Two concentric coils each of radius equal to 2πcm are placed right angles to each other. If 3 A and 4 A are the currents flowing through the two coils respectively. The magnetic induction( in Wb m^(-2) )at the center of the coils will be
- Assertion: Out of ""_(1)He^(3) and ""_(7)He^(3), the binding energy of ""_(1)He^(3)is greater than ""_(2)He^(8). Reason: Inside the nucleus of""_(1)H^(3), there is more repulsion than inside the nucleus of ""_(2)He^(4).
- In which accelerated motion, K.E of the particle is constant