Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
How is equilibrium reached if there is excess demand at a price lower than equilibrium price? |
|
Answer» Solution :At any price lower than the equilibrium price, quantity DEMANDED of a commodity exceeds its quantity supplied. It is CALLED a situation of excess demand. It is not an equilibrium price because Quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied at equilibrium price only. Whenever there is excess demand, eqquilibrium will be achieved as explained under. At `OP_(1)`, there is excess demand equal to `M_(1)M_(2)`. Excess demand WOULD create competition among buyers which will push price up from `OP_(1)` to OP. As price rises there would be : extension in supply from B to E CONTRACTION in demand from C to E Hence, equilibrium will be achieved at point E when quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. 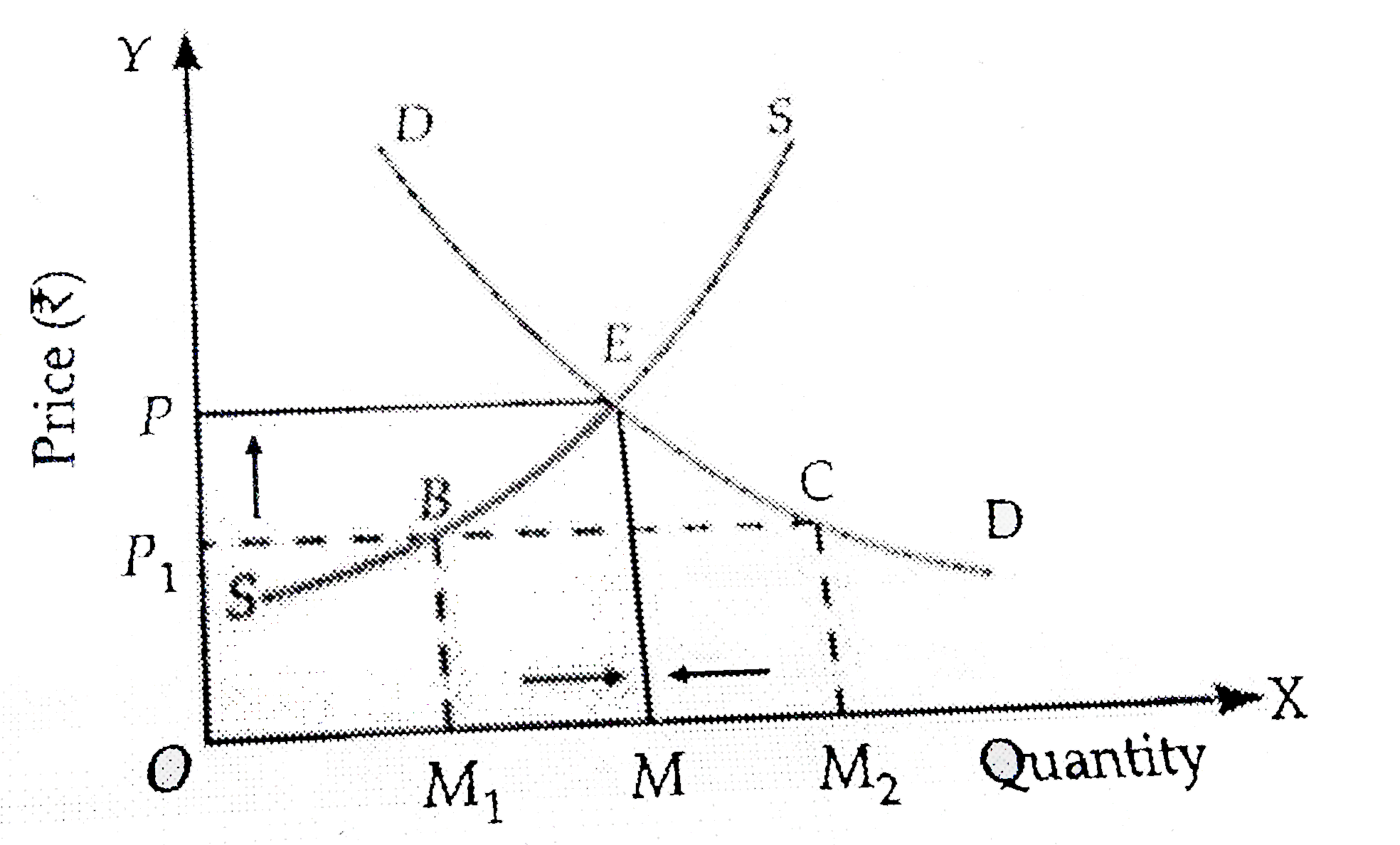
|
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Assumption of ordinal apporch
- Critical appraisal of methods of collection of data
- Different between microeconomics and macroeconomics
- What happense when ic slops downwards
- Implications of perfect competition in forms of market
- If price of mango rises demand will ?
- What is statistical table? Explain briefly tha main characteristics of a good statistical table.
- What is production possibility curve
- Explain any three factor which affect the supply of a commodity
- What do you understand by the increasing returns to scale