Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Question : What is dark reaction of photosynthesis ? Describe C_(3) pathway ? |
|
Answer» Solution :1. Dark reaction of pohotosynthesis : The lilght independent reaction of photosynthesis that occurs in stroma of chloroplast is called dark reaction of photosynthesis. 2. `C_(3)` Pathway : (1) Dr Melvin Calvin in the year 1954 discovered the path of carbon in photosynthesis, i.e.,sequence of reactions of `CO_(2)` fixation and synthesis of glucose from it using tracer technique, chromatography and autoradiography. (2) The sequence of reactions of `CO_(2)` fixation into glucose is called Calvin cycle. (3) Calvin and his co-worker Dr Bensen worked on Chlorella and Senedesmus (unicellular algae using `C^(14)` radioactive isotope of carbon) as tracer. (4) The first product in Calvin cycle of photosynthesis is a 3-carbon compound, i.e., PGA (phosphoglyceric acid). Therefore, this pathway of photosynthesis is called `C_(3)` pathway. (5) Calvin demonstrated and proved that the initial acceptor of carbon dioxide, i.e., RuBP is regenerated simultaneously with the synthesis of glucose. Calvin and his co-worker Dr Bensen where awarded a Nobel prize for this work in 1961. (6) The various steps of Calvin cycle are as follows : (i) Carboxylation : RuBP (Ribulose-1,-5 biphosphate) accepts atomospheric `CO_(2)` in the presence of the enzyme RuBP carboxylase (RUBISCO) and forms a 6-carbon unstable compound which soon splits into two molecules of 3-carbon compound called PGA (phosphoglyceric acid) in the presence of the same enzyme enzyme as shown under : `underset((5C))("RuBP")+underset((1C))(CO_(2)) overset(Mg^(+))underset("RuBISCO")to underset((6C))("unstable compound (i)")` `underset((6C))underset("compound")("Unstable")+H_(2)O overset(Mg^(++))underset("RuBISCO")to underset((3C))("2 molecules of 3-PGA")` (II) REDUCTION of PGA : The PGA thus formed undergoes photo-phosphorylation using ATP to form 1. 3-disphosphoglyceric acid which is reduced to PGAL (phospho-glyceraldehyde) by `NADPH_(2)` with the release of iP (inorganic phosphate). The reduction of PGA to PGAL can be SUMMARIZED as follows: `3PGA +ATPto 1`, 3 diphospohoglyceric acid `+`ADP 1, 3 diphosphoglycericacid `+ NADPH_(2) to 3PGAL + NADP + iP` Some molecules of PGAL undergo isomerization and form DHAP (dihydroxyacetone phosphate). This isomerization reaction is catalysed by the enzyme triose phosphate isomerase. 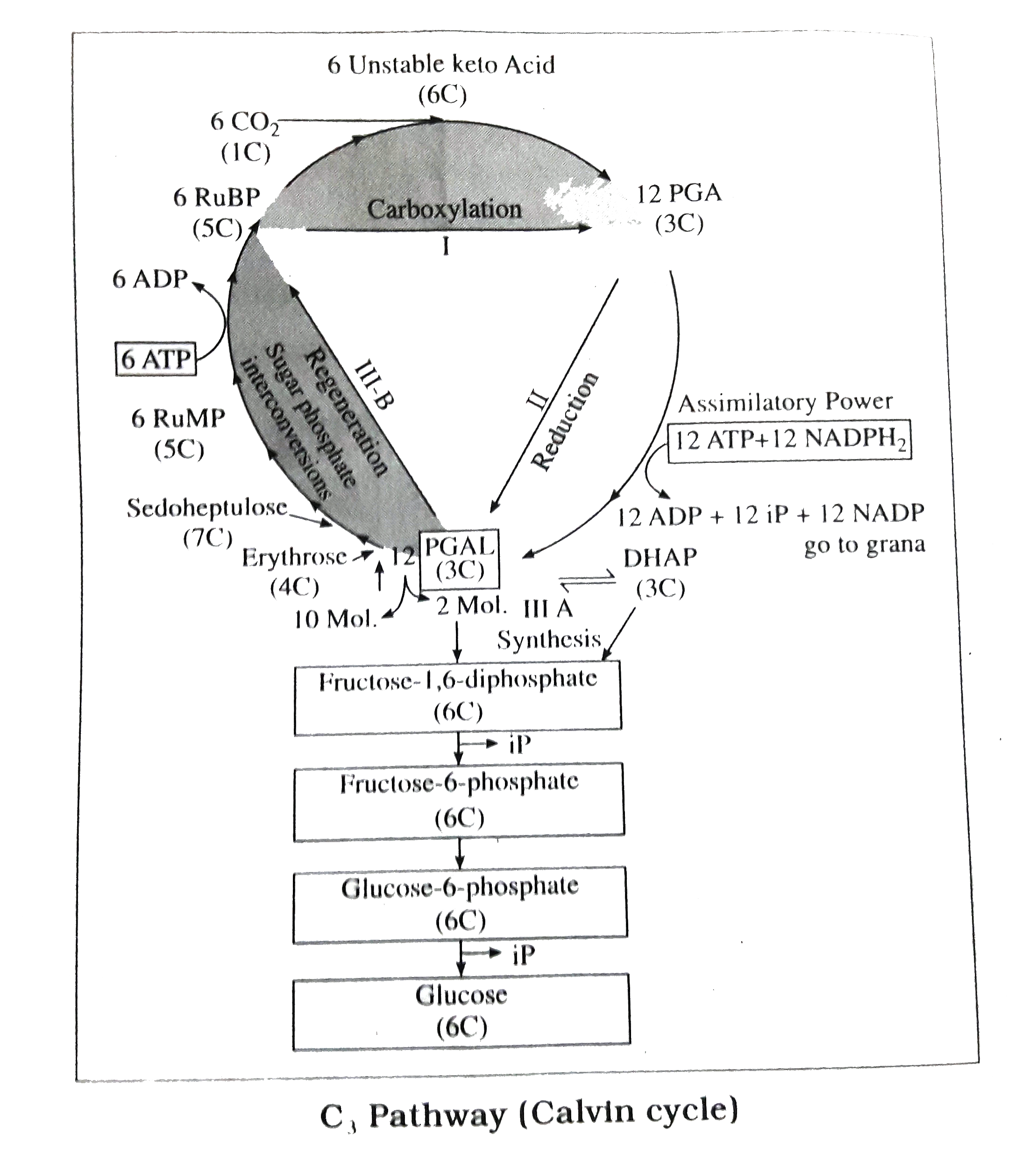 (iii) Synthesis of sugar : For the synthesis of one molecule of glucose six molecules of RuBP and six molecules of `CO_(2)`or 6 turns of Calvin cycle ar required. This shows that six turns of Calvin cycle are required for the synthesis of one molecule of glucose. Out of 12 molecules 2 molecules 2 molecules i.e., 1/6 part of PAGAL are utilized for thesynthesisof glucose. One molecule of PGAL and one molcecule of DHAP combine witheach other to form one molecule of fructose 1, 6-diphosphate as shown below : `underset((3C))(3PGAL)+underset((3C))(DHAP) tounderset((6C))("Fructose 1, 6-diphosphate")` Fructose 1, 6-diphosphate undergoes dephosphorylation to form fgructose-6-phosphate which on isomerization forms glucose-6-phosphate. Glucose-6-phosphate undergoes dephosphorylation to form glucose. Glucose thus formed is either utilized or stored as STARCH. (iv) Regeneration of RuBP : RuBP is regenerated through biochemical reactions called sugar phosphate interconversions. All the intermediate compounds, for example, erythrose-4-phosphate, xylulose-5-phosphate, ribose-5-phosphate, sedoheptulose-7-phosphate, etc. that arew formed during these reactions are sugar phosphates. Out of 12 molecules of PGAL 10 molecules are utilized for the regeneration of 6 molecules of RuMP (ribulose monophosphate) which on pohosphorylation form RuBP as shown below : ` "12 PGAL "to" 6 RuMP" ` ...(1) `"6 RuMP" + "6 ATP" to "RuBP" ` ...(2) Thus RuBPwhich is necessary for the reduction of `CO_(2)` is regenerated to keep the process going. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Question : Which is the most common mechanism of genetic variation in the population of a sexually reproducing organism?
- Question : Which is the most common methods of fossilization? Explain how it occurs.
- Question : Which is the most common mechanism of genetic variation in the population of a sexually reproducing organism ?
- Question : Which is the microscopic parasitic animal ?
- Question : Which is the method of temporary birth control that reduces the chances of pregnancy by 80%? Write the fact on which this method is based.
- Question : Which is the main cause to convert water bodies into land ?
- Question : Which is the lowest level of ecological organisation ?
- Question : Which is the longest cell of the human body ?
- Question : Which is the longest bone of the body ?
- Question : Which is the link between glycolysis and Krebs cycle·?