Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
State condition of consumer equilibrium in case of a single commodity . |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) When purchasing a unit of a commodity a consumer compares its price with the expanted utility from the utility obtained is the benefit, and the pricepayable is the cost , the consumer compares benefit and the cost. He will by the unit of commodity only if the benefit is is greater than or at latest equal to the cost. (ii) Equilibrium conditions for single commodity consumer Equilibrium . (a) Necessary Condition Marginal utility of MONEY = price `""...(1)` Or `(" Marginal Utility of a Product in Util " [MU_x])/("Marginal Utility of One Rupe "[MU_R]) " = Price of X"....(2)` In particular, the condition (1) saya that themarginal utility of a product in terms of Money should be equal to its price. Sometimes this is loosely stated as Marginal Utility is equal to price, i.e. ., MU = price . `"*"`If MU `gt`price `IMPLIES` As a rational consumer he willContinue to purchase an additional unit on a commodity as long as MU = price . `implies` MU `gt`Price impulse benefit is greater than cost and when ever benefit is greater than cost the consumer keeps on consuming additional unit of a commodity till MU = price . `implies` It is so because according to the law of DIMINISHING marginal utility MU falls moreis purchased . As MU falls it is bound to become equal to the price at some point of purchase. `"*"` If MU `lt`Price `implies` As a rational consumer he will have to reduce the consumption of a commodity as long as MU = price . `implies MU lt`price implies when benefit is less than cost , never benefit is less than cost the dressing the additional unit of a commodity till MU = price. `implies` It is so because according to the law of diminishing marginal utility, MU rises as less units are consumed. As MU rises , it is bound to become equal to the price at some point of purchase . (b) Sufficient condition: Total gain falls as more is purchased after equilibrium . it means that consumer continues to purchase so long as total gain is increasing or at least constant. (iii) It can be explained with the help of the following SCHEDULE : 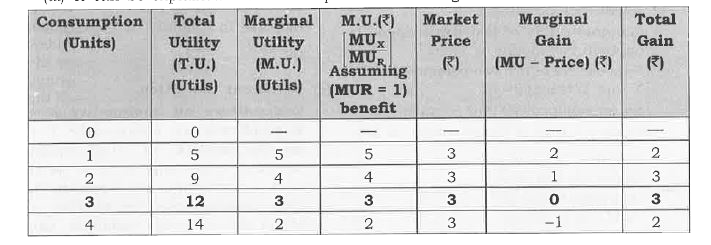 (a) Suppose , the price of commodity X in the market is Rs3 per unit .It means he has to pay Rs3 per unit for all the units he buys.Suppose, the unility obtained from the first unit is 5 utils(=Rs 5)The consumer will buy this unit because the utility of this unit is greater than the price and this process continues till Marginal utility = price as shown in the above schedule at quantity 3 . (b) Consumer will not buy the fourth unit utility of this unit is 2 unit because utility of this unit is 2 utils (= Rs 2)which is less than the price . It is not worth buying the fourth unit. The consumer will restrict his purchase to only 3 units. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Increase in stock of goods held by a consumer will contribute to capital formation.
- Explain the meaning of diminshing marginal rate of substitution with the help of a numercial example
- Explain the meaning of inflationary gap and deflationary gap . Explain any one measure by which these gaps can b e reduced.
- Distinguish between average propensity to consume and marginal propensity to consume. The value fo which of these two can be greater than oneand when ?
- Componenet of current account in BOP
- How are exports affected by depreciation of foreign currency ? Explain
- (a) State any two precautions that must be taken into consideration while estimating national income by value added method. In an economy following transcations took place. Calculate value of output value added by Firm B: (i) Firm A sold to firm B goods of 80 crore, to firm C 50 crore to household 30 crore and goods of value 10 crore remains unsold (iii) Firm B sold firm C goods of 70 crore, to firm D 40crore, goods of value 30 crore were exported and goods of value 5 crore was gold to government Or Differentiate betweeen National Current Places and National Income at Constant Prices. Which of the two presents a better view of the economic growth of economy and why?
- A firm gets maximum profits only if difference between average revenue and average cost is the maximum.
- Reserve repo rate is the rate at which Central Bank lends funds to banks.
- Commerical banksdo not contributeto quantumof moneysupplyin the economyas they do nothavenote- issuingauthority.