Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Two planets revolve with same angular velocity about a star. The radius of orbit of outer planet is twice the radius of orbit of the inner planet. If T is time period of the revolution of outer planet, find the time in which inner planet will fall into the star. If it was suddenly stopped. |
|
Answer» `sqrt((23gR)/11)` CONSIDER an imaginary comet moving along an ELLIPSE. The extreme POINTS of this ellipse are located on orbit of inner planet and the star, sem-major axis of orbit of such comet will be half of the semi-major axis of theinner planet's orbit. ACCORDING to Kepler's law. if `T'` is the time period of the comet. `(T'^(2))/((r//4)^(3))=(T_(1)^(2))/((r//2)^(3))` `T'^(2)=8/64T_(1)^(2)=(T_(0)^(2))/32( :' T_(1)=T_(0)//2)` `T'=T/(4sqrt(2))` `(T'//2)` represents time in which inner planet will FALL into star. `((T')/2)=T/(8sqrt(2))=(Tsqrt(2))/16` 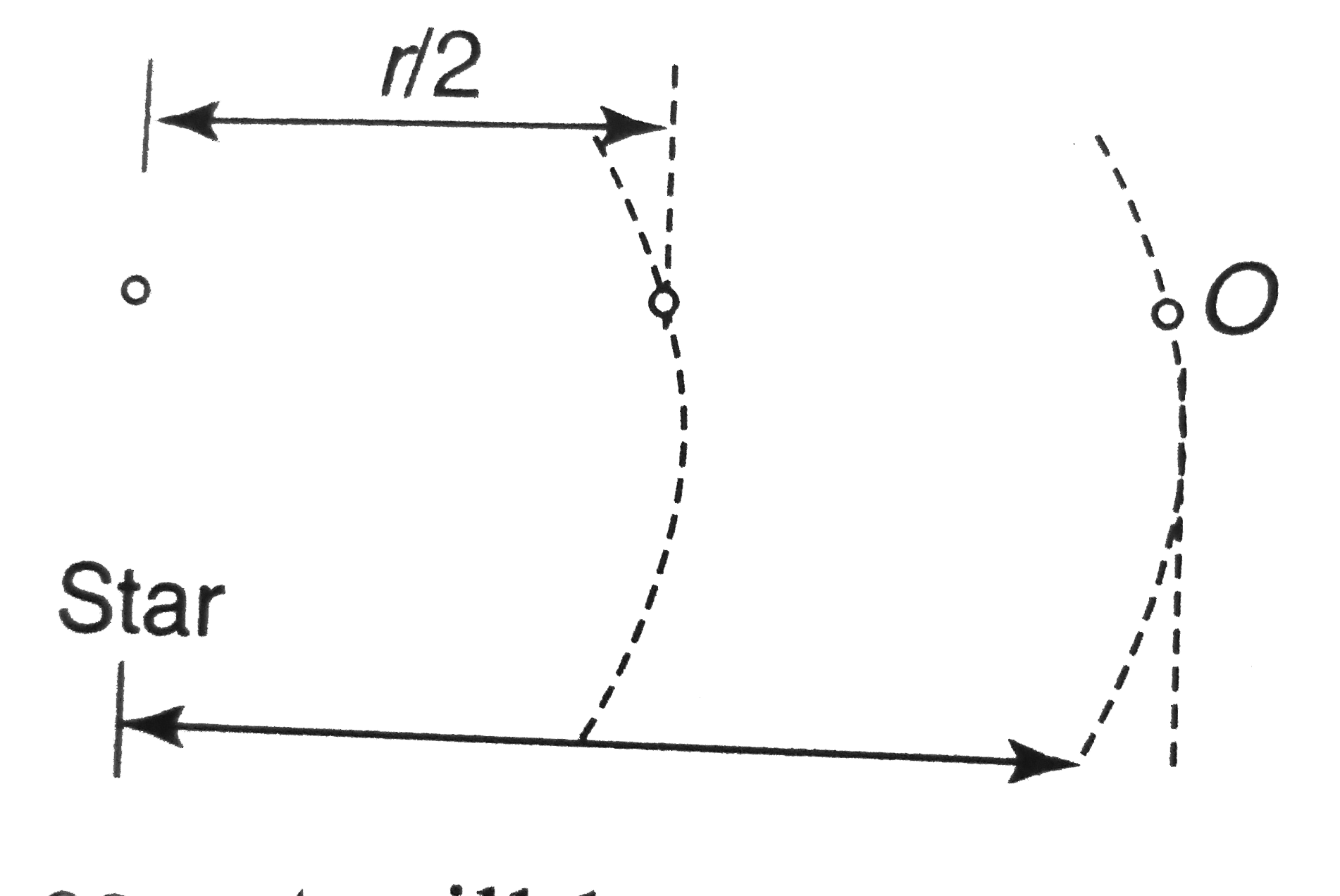
|
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- What is uniform velocity
- Derive the speed time equation by calculas method
- 9×2y - 24x^2 +16y^3.factorise?
- Give me tips for preparation of physics??
- Advantage of friction
- Derivation of equation of Newton\'s Second Law of Motion that is F=ma
- Equation of projectile?
- Unit of Permeability
- Difference between vectr and scalar
- what is centripetal force ?