Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
What happens when ? (i) Cumene hydroperocide is treated with dilute (H_(2)SO_(4)). (ii) Phenol is distilled with C C l_(4) in presenceof aqueous NaOH. (iii) Phenol is distilled with phthalic anhydride in the presence of concentration H_(2)SO_(4). (iv) Benzenediazonium chloride is treated with alkaline ice-cold aqueous solution of phenol. (v) Phenol reacts with acetic anhydride in presence of sodium acetate. (vi) Phenol is heated with ammonia in presence of anhydrous ZnCl_(2) at 573K. (vii) Phenol is refluxed with con. H_(2)SO_(4) at 373K. (viii) Phenol condenses with excess of formaldehyde in presence of sodium hydroxide for a long period. (ix) 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol is heated with zinc dust. (x) Phenol reacts with benzoyl in presence of NaOH. (xi ) Phenol is treated with neutral FeCl_(3). (xii) Phenol is treated with bromine water. (xiii) Phenol is treated with conc. HNO_(30 in presence of conc. H_(2)SO_(4). (xiv) Phenol is treated with methyl chloride in presence of anhydrous AlCl_(3) (xv) Phenol is hydrogenated in presence of nickel catalyst at 473K-533K. |
Answer» Solution :[Hint] 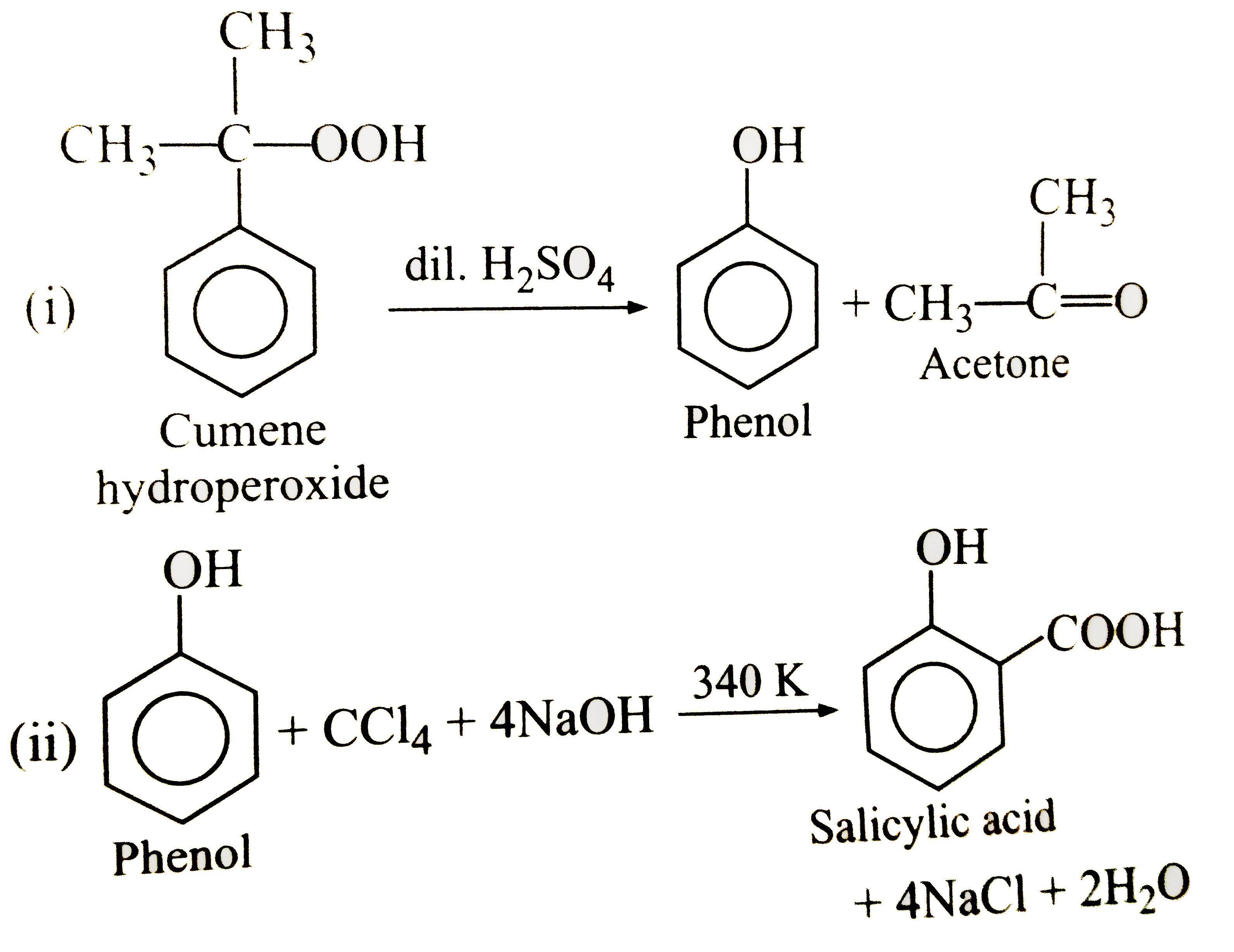 (iii) Phenolphthalein. (iv) p-Hydroxyazonbenzene (coupling reaction) (v) Phenyl ethanoate ( an ester ) . (VI) Aniline. (vii) 4-Hydroxybenzenesulphonic ACID. (viii) Bakelite (polymer) (ix) 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene (X) Phenylbenzoate. (xi) Violet coloured complex 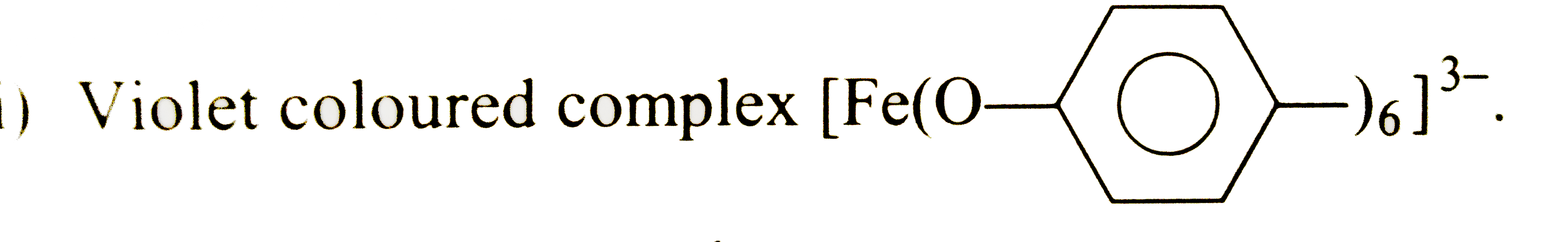 (xii) 2,4,6-Tribromophenol. (xiii) 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (PICRIC acid) (xiv) 4- Methylphenol (p-Cresol). (xv) Cyclohexanol (`C_(6)H_(11)OH)`. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?