Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Write notes on (a) Bond Angle (b) Bond Enthalpy (c)Bond length and (d) Bond order. |
|
Answer» Solution :a) Bond angle : The angle between the orbitals containing bonding electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule, COMPLEX ION is called bond angle. Bond angle is expressed in degrees. i) Bond angle depends on the presence of lone pair electrons with increase in the number oflone pairs the bond angle decreases. eg. in the molecules which contain four electron pairs the bond angles are follows. 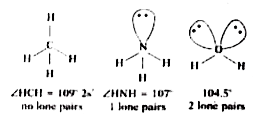 ii) Bond angle decreases with increase in the electronegativity with increase in the electronegativity of central atom. eg. 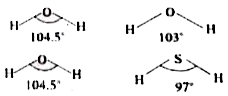 iii) Bond angle depends on the hybridisation.  b) Bond enthalpy : The AMOUNT of energy required to break one mole of bonds of a particular type between two at atoms in a gaseous state is called bond enthalpy. More is the bond enthalpy, stronger the bond and more is the STABILITY of the molecule. In the case of poly atomic molecules the bond enthalpy is the average of the similar bond ENTHALPIES is taken. eg. in `H_(2)O` to break the two O - H bonds is not same. The energy required for breaking first bond is 502 kJ `mol^(-1)` and for the second bond is 427 kJ `mol^(-1)`. So the average value 464.5 kJ `mol^(-1)` is considered as the bond enthalphy. c) Bond length : It is defined as the equilibrium distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond length is equal to the sum of the covalent radii of two similar atom in the bond. In hetero atomic molecules the bond length can be calculated using the formula. `d_(AB)=r_(A)+r_(B)+c(X_(A)-X_(B)). " Where " X_(A) " and " X_(B)` are the electronegativities of atom A and B. The value of C depends on the nature of atoms participating in the bond. Bond lengths depend on the number of bonds between atoms, type of hybridisation etc. d) Bond order : It is defined as the number of bonds between the two atoms in a molecule. Eg : Bond orders in `H_(2)` is 1, `O_(2)` =2 and `N_(2)` = 3. In the resonance hybrid the bond order `="No. of bonds around the central atom"/"No. of atoms around the central atom"` In cyclic compounds, the bond order is `="No. of bonds in the ring"/"No. of atoms forming the ring"` Isoelectronic molecules and ions have identical bond orders. e.g. `F_(2) " and " O_(2)^(2-)` have bond order 1. `N_(2)`, CO and `NO^(+)` have bond order 3. More the bond order more is the bond enthalpy, lesser the bond length, more the stability. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?