Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Write short notes on the following (i) Hoffmann's bromide reaction (ii) Ammonolysis (iii) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis (iv) Schoten-Baumann reaction v. Carbylamine reaction vi. Mustard oil reaction vii. Couplingreaction viii. Diazotisation ix. Gomberg reaction. |
|
Answer» Solution :i. Hoffmann.s bromide reaction: When Amides are treated with bromine in the presence of aqueous or ethanolic solution of KOH, primary amines with one carbon atom less than parent amides are obtained. `UNDERSET("amide")(R-)overset(O)overset(||)(C)-NH_(2)overset(Br_(2)//KOH)(to) underset("Primary amine")(R-NH_(2)+K_(2))CO_(3)+KBr+H_(2)O` R=Alkyl (or) Aryl (ii) Amkonolysis: When Alkyl halides (or) benzylhalides are heated with alcoholic ammonia in a sealed tuber MIXTURES of `1^(@), 2^(@)` and `3^(@)` amines and quanternary ammonium salts are obtained. `CH_(3)-Brunderset(Delta)overset(overset(..)(N)H_(3))(to) underset(1^(@)-"amine")(CH_(3)-overset(..)(N)H_(2))overset(CH_(3)-Br)(to) underset(2^(@)-"amine")((CH_(3))_(2)overset(..)(N)H)overset(CH_(3)Br)(to) underset(3^(@)-"amine")((CH_(3))_(3)overset(..)(N))overset(CH_(3)Br)(to) underset("Quarternary ammonium bromide")((CH_(3))_(4)overset(+)(N)Br^(-))` (iii) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis Gabriel synthesis is used for the preparation of Aliphatic amines. Phthalimide on treatment with ethanolic KOH forms potassium salt of phthalimide which on heating with alkyl halide followed by ALKALINE hydrolysis gives primary amine. 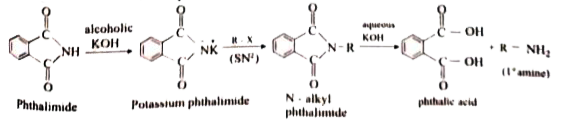 (iv). Schotten- Baumann reaction: Aniline reacts with benzoylchloride `(C_(6)H_(5)COCl)` in the presence of NaOH to give acylation and benzoylation are nucleophilic substitutions. `underset(("Aniline"))(C_(6)H_(5)-NH_(2))+underset(("Benzoylchloride"))(C_(6)H_(5)-overset(O)overset(||)(C)-Cl)overset(NaOH)(to) underset((N-"phenyl benzamide"))(C_(6)H_(5)-NH-overset(O)overset(||)(C)-C_(6)H_(5))+HCl` v. Carbylamine reaction: Aliphatic (or) aromatic primary amines react with chloroform and a alcoholic KOH to give isocyanides (CARBYLAMINES), which has an unpleasant smell. This reaction is knwon as carbylamines test. This test used to identify the primary amines. `underset("Ethylamine")(C_(2)H_(5))-NH_(2)+underset("Chloroform")(CHCl_(3))+3KOH to underset("Ethylisocyanide")(C_(2)H_(5)-3KCl)+3H_(2)O` (vi.) Mustard oil reaction: When primary amines are treated wtih carbon disulphide (`CS_(2))`, N- alkyldithip carbonic acid is formed which on SUBSEQUENT treatment with `HgCl_(2)`, give an alkyl isothiocyanate. `underset("Methylamine")underset(H)underset(|)(CH_(3)-N-H+)overset(S)overset(||)(C)=Stounderset("N-Methyl dithiocarbamic acid")(CH_(3)-NH-overset(S)overset(||)(C)-SH)overset(HgCl_(2))(to) underset("Methyl isothiocyanate" ("Mustard oil smell")) (CH_(3)-N=C=S)+HgS+2HCl` vii. Coupling reaction: Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with electron rich aromatic compounds like phenol, aniline to form brightly cooured azo compounds. Coupling generally occurs at the para position. If para position is occupied then coupling occurs as the ortho position. Coupling tendency is enhanced if an electron donating group is present at the para position to `-overset(+)(N_(2))Cl^(-)` group. This is an electrophilic substitutio. 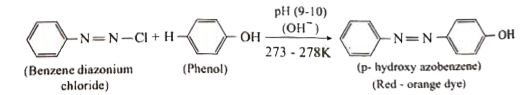 viii. Diazotisation: Aniline reacts with nitrous acid at low temperature (273-278K) to give benzene diazonium chloride which is stable for a short time and slowly decompose seven at low temperatures. This reaction is known as diazotization. 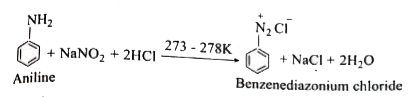 ix. Gomberg reaction Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with benzene in the presence of sodium hydroxide to give biphenyl. This reaction in known as the Gomberg reaction. 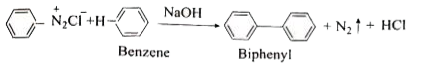
|
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?