Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in Current Affairs.
This section includes 7 InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your Current Affairs knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1. |
ZX Limited invited applications for issuing 5,00,000 Equity shares of Rs. 10 each at a premium of Rs. 10 each payable with Final call. Amount per share was payable as follows : {:(,"Rs."),("On Application",2),("On Allotment",3),("On First Call",2),("On Second and Final Call","Balance"):} Applications for 8,00,000 shares were received. Applications for 50,000 shares where rejected and the application money was refunded. Allotment was made to the remaining applicants as follows : {:("Category","Number of Shares Applied","Number of Shares Allotted"),("I","2,00,000","1,50,000"),("II","5,50,000","3,50,000"):} Excess application money received with applications was adjusted towards sums due on allotment. Balance, if any was adjusted towards future calls. Govind, a shareholder belonging to category I, to who 1,500 shares were allotted paid his entire share money with allotment. Manohar belonging to category II who had applied for 11,000 shares failed to pay 'Second & Final Call money'. Manohar's shares were forfeited after the final call. The forfeited sharses were reissued at Rs. 10 per share as fully paid up. Assuming that the company maintains ''Calls in Advance Account'' and ''Calls in Arrears Account'', pass necessary entries for the above transactions in the books of ZX Limited. |
Answer» SOLUTION : 
|
|
| 2. |
ZLtd. forfeited 1,000 equity shares of Rs. 100 each for the non-payment of first call of Rs. 20 per share and ssecond and final call of Rs. 25 per share. State : (i) Can these shares be re-issued ? (ii) If yes, state the minimum amount at which these shares can be re-issued. (iii) If these shares were re-issued at Rs. 50 per share fully paid up, what will be the amount of Capital Reserve ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) YES, these shares can be re-issued. (II) The minimum AMOUNT Rs. 45 per share. (iii) Amount transferred to Capital RESERVE Rs. 5,000. |
|
| 3. |
Zee Ltd. intends to issue 10,00,000 Equity Shares of Rs. 10 each to public for subscription. The management was suggested by the accountant Rahul that shares should be issued at 10% discount so that shares are subscribed in full. The management did not accept the suggestion of Rahul. What must be the reasonfor not accepting the suggestion? |
| Answer» Solution :The reason for not accepting the suggestion of ACCOUNTANT Rahul must have been that Section 53 of the Companies Act, 2013 does not permit issue of SHARES at DISCOUNT. | |
| 4. |
Zee Limited was registered with a capital of Rs. 20,00,000. divided into 80,000 shares of Rs. 25 each. The Company offered to the public for subscription 40,000 shares payable Rs. 7.50 per share on Application, Rs. 7.50 per share on allotment and the balance in two calls of equal amounts. The company received applications for 46,400 shares. Applications for 4,00 shares were rejected altogether and the application money was returned to the applicants. A person who applied for 4,000 shares wasallotted only 1,600 shares and the excess of his application money was carried forward rowards the payment to allotment and calls. Make Journal entries to record the above issue of shares. |
| Answer» Solution :AMOUNT received on ALLOTMENT RS. 2,88,000, on 1ST CALL Rs. 1,94,000, on Final Call Rs. 2,00,000. | |
| 5. |
Zavier, Yusuf and Zaman were partners in a firmsharing profits in the ratio of 4:3:2. On 1st April, 2014, their Balance Sheet was as folows: Yusuf had been suffering from ill health and thus gave notice of retirement from the firm. An agreement was, therefore, entered into as on 1st April, 2014, the terms of which were as follows, (i) That land and building be appreciated by 10% (ii) The provision for bad debts is no longer necessary. (iii) That stock be appreciated by 20% (iv) That goodwill of the firm be fixed at Rs 54,000. Yusuf's share fo the same be adjusted into Xavier's and Zaman's Capital Accounts, who are going to share future profits in the ratio 2:1. (v) The entire capital of the newly constituted firm be readjusted by bringing in or paying necessary cash so that the future capital of Xavire and Zaman will be in their profit sharing ratio. Prepare Revaluation Account and Partners' Capital Accounts. |
Answer» Solution : Woeking notes: 1. Calculation of Gaining Ratio, Xavier's Gain `=2/3-4/8=(18-12)/(27)=6/27'"Zaman's Gain"=1/3-2/9=(9-6)/(27)=3/27` Gaining Ratio `=6/27:3/27or2:1` 2. Yusuf's Share of Goodwill Rs 18,000 (i.e., Rs `54,000xx3//9`)will be contributed by Xavier and Zaman in their gaining ratio of `2:1.` 3. `{:("Calculation of Total CAPITAL of New Firm after Yousuf's Retirement,",Rs),("ADJUSTED Old Capital of Xavier Rs (1,20,000 + 11,400-12,000)","1,19,400"),("Adjusted Od Capital of Zaman Rs (60,000+5,700-6,000)","59,700"),("Total Capital of New Firm after Yusuf's Retirement",underline underline overline ("1,79,100")),("Calculation of cash to be brought in or paid off:",):}` 
|
|
| 6. |
Z Ltd. purchased machinery from K Ltd. Z Ltd. paid K Ltd. as follows: (i) By issuing 5,000 equity shares of Rs. 10 each at a premium of30%. (ii) By issuing 1,000, 8% Debentures of Rs. 100 each at a discount of 10%. (iii) Balance by giving a promissory note of Rs. 48,000 payable after two months. Pass necessary Journal entries for thepurchase of machinery and payment to K Ltd. in thebooks of Z Ltd. |
Answer» Solution :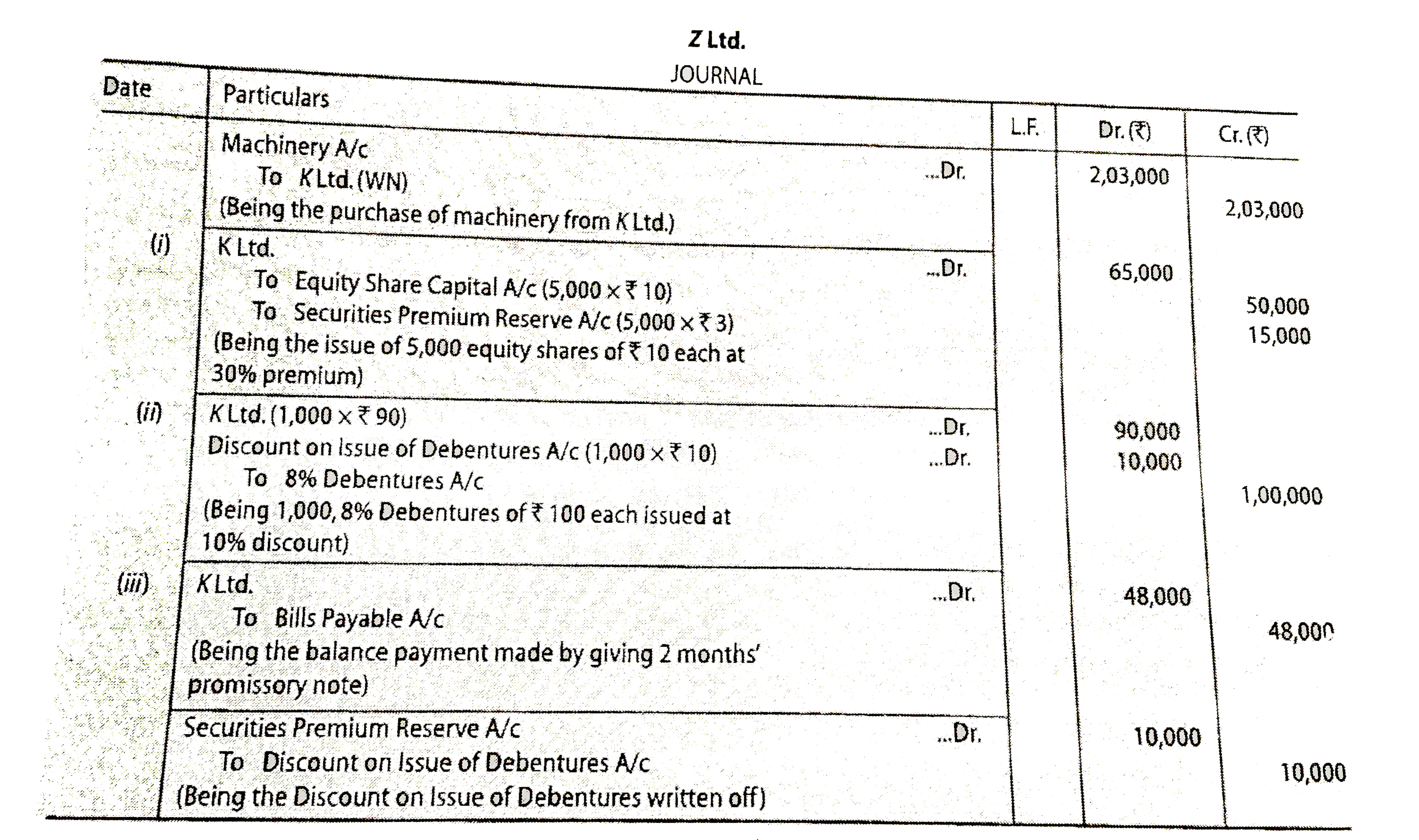 WORKING Note: PURCHASE CONSIDERATION = RS. 65,000 + Rs. 90,000 + Rs. 48,000 = Rs. 2,03,000. |
|
| 7. |
Zero Coupon Bonds are issued : |
|
Answer» At zero INTEREST Rate |
|
| 8. |
Z is admitted to a firm for 1/4th share in the profits for which be brings in RS.10,000 towards premium for goodwill. It will be taken by the old partners in |
|
Answer» the OLD profit-sharing RATIO. |
|
| 9. |
Z Ltd. Has a Current Ratio of 3.5 : 1 and Quick Ratio of 1.5 : 1. If the excess of current assets over quick assets as represented by stock is Rs. 60,000, calculate current assets and current liabilities. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :CURRENT ASSETS = RS. 1,05,000, Current LIABILITIES = Rs. 30,000. | |
| 10. |
Young India Ltd. Hasa Operating Profit Ratio of 20% . Tomaintain this ratio at 25% management may |
|
Answer» Increase selling PRICE of stock - in TRADE. |
|
| 11. |
You are given the Balance Sheet of Mohit, Sohan and Rahul who are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1, as on March 31, 2017. Sohan died on June 15, 2017. According to the Deed, his legal representatives are entitled to:(a) Balance in Capital Account, (b) Share of goodwill valued on the basis of thrice the average of the past 4 years’ profits.(c) Share in profits up to the date of death on the basis of average profits for the past 4 years. (d) Interest on capital account @ 12%p.a.Profits for the years ending on March 31 of 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017 respectively were Rs. 15,000, Rs. 17,000, Rs. 19,000 and Rs. 13,000.The firm had taken a Joint Life Policy of Rs. 1,25,000, the annual premium being charged to profit & loss account every year.Sohan’s legal representatives were to be paid the amount due. Mohit and Rahul continued as partner by taking over Sohan’s share equally. Work out the amount payable to Sohan’s legal representatives. |
Answer» Solution : Working Notes 1. SOHAN's Share of Goodwill = Goodwill of the Firm `xx(2)/(5)` = Rs. 48,000 `xx(2)/(5)` = Rs. 19,200 Goodwill of the Firm `= 3 xx` Average Profit `= 3 xx (Rs. 64,000)/(4)` =Rs. 48,000 2. Profit and Loss (Share of Profit from the date of last Balance SHEET to the date of death) `2(1)/(2)`months. = `(Rs. 64,000)/(4)xx(2)/(5)xx(2.5)/(12)` `"= Rs. 1,333"` 3. JOINT Life Policy= Rs. 1,25,000 Sohan's share `= (2)/(5) xx` Rs. 1,25,000 `"= Rs. 50,000"` 4. Interest on Capital = Rs. 25,000 `xx(12)/(100) xx (2.5)/(12)` `"= Rs.625"` |
|
| 12. |
Y Ltd.' invited applications for issuing 15,000 Equity Shares of Rs. 10 each on which Rs. 6 per share were called-up, which were payable as follows: {:("On application",,-,,"Rs. 2 per share,"),("On allotment",,-,,"Rs. 1 per share,"),("On first call",,-,,"Rs. 3 per share."):} The issue was fully subscribed and the amount was received as follows: {:("On 10,000 shares",,-,,"Rs. 6 per share,"),("On 3,000 shares",,-,,"Rs. 3 per share,"),("On 2,000 shares",,-,,"Rs. 2 per share."):} The directors forfeited those shares on which less than Rs. 6 per share were received. The forfeited shares were reissued at Rs. 9 per share, as Rs. 6 per share paid-up. Pass necessary Journal entries for the above transactions in the books of thecompany. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Amount transferred to CAPITAL RESERVE RS. 13,000. | |
| 13. |
Young India Ltd. has a Operating Porfit Ratio of 20%. To maintain this ratio at 25%, management may |
|
Answer» Increase selling PRICE of Stock-in-trade |
|
| 14. |
You have shown interest paid of ₹ 514 lakhs under Cash Flow from Financing Activity, whereas you have shown interest received of₹ 10,759 lakhs under Cash Flow from Investing Activity. Why? |
| Answer» SOLUTION : Interest PAID of ₹ 514 lakhs is on borrowings of the company, i.e, Financing Activity WHEREAS interest received of₹ 10,759 lakhs is on account of investments made by the company, i.e., INVESTING Activity. | |
| 15. |
Y Ltd. forfeited 100 equity shares of Rs. 10 each for non-payment of first call of Rs. 2 per share. The final call of Rs. 2 per share was yet to be made. Calculate the maximum amount of discount at which these shares can be reissued. |
| Answer» Solution :MAXIMUM amount of discount which can be ALLOWED on reissue of 100 SHARES `= 100xx RS. 6 = Rs. 600` . | |
| 16. |
XYZ Ltdprovided the followinginformationcalculate NetCashFlow Finacing Activites: Additional Information: 1. Interest paidon debentures ₹ 19,000. 2. Divident paid on the year₹ 50,000. 3. Duringthe year, XYZ Ltd. issued bonus share in the ratio of 5:1by capialisingreserve. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 17. |
XYZ Ltd. Acquired a business and agreed to pay purchase consideration of ₹ 2,00,000. The assets taken over are ₹ 5,50,000 and liabilities assumed are ₹ 4,00,000 What is the amount that will be debitedto Goodwill Account or credited to Capital Reserve Account and why? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :GOODWILL Account will be DEBITED by ₹ 50,000 It is so because the amount paid, i.e., ₹ 2, 00,0000 is more then the value of NERT ASSETS acquired, i.e.,₹ 5,50,000(Assets) - ₹ 4, 00,000(Liabilities)= ₹ 1,50,000. | |
| 18. |
XY Ltd. Invited applications for issuing 50,000 equity shares of Rs. 10 each. The amount was payable as follows : On Application Rs. 3 per share On Allotment Rs. 4 per share On First and Final Call Rs. 3 per share Applications were received for 75,000 shares and pro-rata allotment was made as follows : Applicants for 40,000 shares were allotted 30,000 shares on pro-rat basis. Applicants for 35,000 shares were allotted 20,000 shares on pro-rata basis. Ramu, to whom 1,200 shares were allotted out of the group applying for 40,000 shares failed to pay the allotment money. His shares where forfeited immediately after allotment. Shamu, who had applied for 700 shares out of the group applying for 35,000 shares failed to pay the first and final call. His shares were also forfeited. Out of the forfeited shares 1,000 shares were re-issued @ 8 per share fully paid up. The re-issued included all the forfeited shares of Shamu. Pass necessary journal entries to record the above transactions. |
Answer» SOLUTION : 
|
|
| 19. |
X,Y,and Zare partners in a firmin theratioof 4:3:2Om firm'sDissoulationfirm's totalassets are Rs, 70,000 creditors are Rs, 15,000 RealisationexpensespaidRs, 2,100.AssetsRealised15% morethan thebook- value,Creditorswerepaid2%more.ForProfit/Loss on realisationY'scapitalaccountwillbedebitedcredited with : |
|
Answer» (a) CreditRs, 8,100 |
|
| 20. |
XY Ltd. invited applications for 5,00,000 Equity shares of Rs. 10 each, payable as Rs. 3 on application, Rs. 4 on allotment and the balance on first and final call. Applications were received for 12,00,000 shares and the shares and the shares were allotted on a prorata basis. The excess application money was to be adjusted against allotment only. R, a shareholder, who had applied for 6,000 shares, failed to pay the call money and his sharesd were accordingly forfeited and reissued at Rs. 9 per share as fully paid. Pass necessary journal entries. |
|
Answer» Solution :Amount RECEIVED on Ist & FINAL Call RS. 14,92,500, Capital Reserve Rs. 15,000. Hints : (i) SHARES allotted to R : 2,500. (ii) There would be no entry for receipt of allotment money. |
|
| 21. |
X,Y and Z were partners sharing profits in the ratio of 1/2,3/10and 1/5.X retired from the firm. Calculate the gaining ratio of the remaining partners. |
|
Answer» Solution :Profit-sharing Ratio of X,Y and Z `=1//2:3//10:1//5=5:3:2` GAINING Ratio of Y and Z = `3:2.` Note: Gaining Ratio of Y and Z will be same as the OLD ratio existed between them, i.e., `3:2,` SINCE Y and Z gain in their old rtio, unless agreed otherwise. |
|
| 22. |
X,Y and Z were partners sharing profits in ratio of 1/2,1/3 and 1/6. Y retired on 1st April, 2018 and he decided that: (i) Rs 20,000out of the due amount will be donated after one year to Uttrakhand Chief Minister's Fund as his donation to meet natural calamity faced by the state, and (ii) Balance to be paid to him after one year without interest. Identify the values involved. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 23. |
X,Y and Zenteredintopartnershipin 1stjuly ,2018to shareprofitand Lossesin theratioOf 3:2:1 X persnally intopartershipthatZ'sshareof profitafterchargingintereston capital@6%perannumWouldnot belessthanRs. 36,000p.athe capitalcontributed byX -Rs. 2,00,000 , T- Rs. 1,00,000and Z-Rs1,00,000 profitfot theyearendedon 31 st march, 2019was RS. 1,38,000 prepareprofitand LossAppropriation Account . |
Answer» Solution :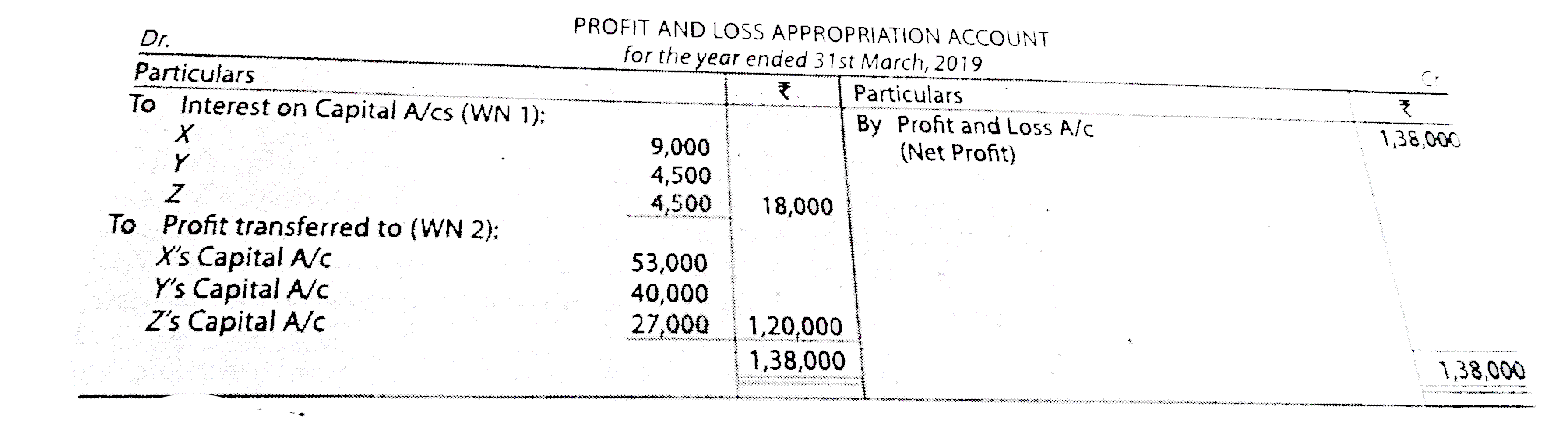 WorkingNotes : 1. Calculationof intereston capitalon : x'sCapital =Rs. 9,000 (i.e., Rs. 2,00,000 `xx` 6/10 `xx`9/12),Y'scapital=Rs. (i.e.,Rs. 1,00,000 `xx`6/100`xx` 9/12), Z'sCapital=Rs. 4,500 (i.e.,Rs. 1,00,000`xx`6/100``9/12) . 2. (i)Profitafterintereston capital=RS. 1,38,000 -Rs. 18,00=Rs.1,20,000 Profitos Rs. 1,20,000 will bedistributedbetweenX,Yand Z in THERATIO 3:2:1i.e.,X'sahareof profit=Rs. 60,000,Y 'sshareof profit= Rs. 40,000 and Z'sshareof profit=Rs. 20,000 (ii)z'sshareof profit=RS. 20,000,HOWEVER ,dueto guaranteeZ has to getminimumRs. 27,000* (i.e.,RS. 36,000 `xx`9/12 ) of profitbyX, X's shareof profitwill BERS. 53,000(i.e.,Rs. 60,000-Rs. 7,000) andZ's share =Rs. 20,000 +rs. 7,00=Rs, 27,000. |
|
| 24. |
X,Y and Z are sharing profits andlosses in the ratio of 5: 3: 2 .Theydecide to share futureprofitsequally w.e.f1st April, 2019.On the date,General Resrveshowed credit balance of ₹ 72,000. Instead ofdistributingthe General Reserve, it was decided to recond an adjustment entry reflecting the change in the profit-sharing ratio. Pass Journalentry to give effect to the same. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 25. |
X,Y and Z are partners sharng profits and losses in the ratio of 5 :3 :2, decided to share future profits and losses equally with effect from 1st April, 2019. On that date, the goodwill appeared in the books at ₹12,000. But it was revalued at ₹30,000. Pass Journal entries assuming that goodwill will not appear in the books of account. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 26. |
X,Y and Z are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 2:3:5. Goodwill is already appearing in their books at a value of Rs. 60,000. X retiresand Y and Zdecided to share future profits equally. Journal entry will be : |
|
Answer» `{:("Y's Capital A/c",,DR.,"12,000",),("To X's Capital A/c",,,,"12,000"):}` |
|
| 27. |
X,Y and Z are partners , Sharing profits in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1 , Y died on 30 th june , 2019 and profit for the accounting year 2018-19 was Rs. 36,000. How much shareof profit will be credited to Y, for the period 1st April , 2019 to 30th june , 2019? |
|
Answer» Rs.3,000 |
|
| 28. |
X,Y and Z are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 1/2, 2/5 and 1/10. Find the new ratio of remaining partners if Z retires. |
|
Answer» Solution :The RATIO of X, Y and Z is 1/2 : 1/2: 1/10 = `5:4:1.` THEREFORE, if Z retires, the NEW ratio between X and Y is `5:4.` |
|
| 29. |
X,Y and Z are partners sharingprofits in theraito of 5 :3:2. Calculate new profit -sharing ratio, sacrificing ratio, gaining ratioin eachof the followingcases: Case 1. If Zacquires1//5thshare from X. Case 2.If Z acquires 1//5th share equallyfrom X and Y. Case 3.If X,Y and Z decide to share equallyform X and Y. Case 4. IfZ acquire 1//5th share of Xand 1//6th Share of Y. |
|
Answer» Solution :Case.1 (A) Their existingshare (B) Share ACQUIRED by Z and X TheirNew Share (A+B) 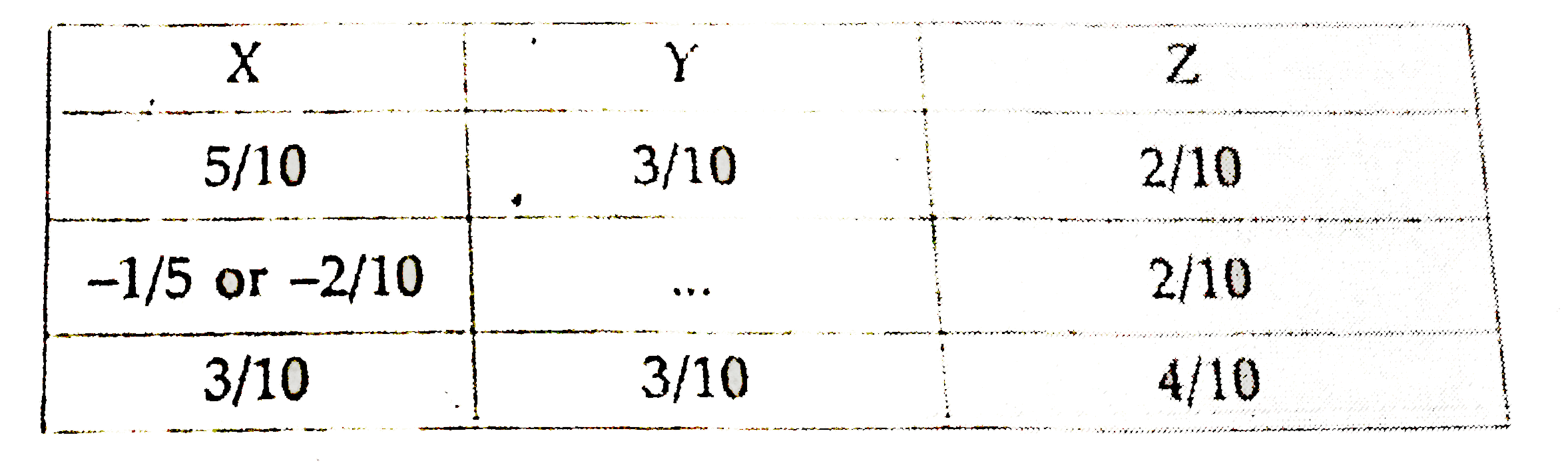 Thus, New Profits-sharing Ratio of X ,Y and Z `= (3)/(10): (3)/(10) : (4)/(10) = 3: 3:4,` Sacrifice of `X = 1//5, ` Gainof `Z = 1//5` Case 2. (A) Theirexisting share (B). Share acquired by Z form X and Y Their New Share (A + B) 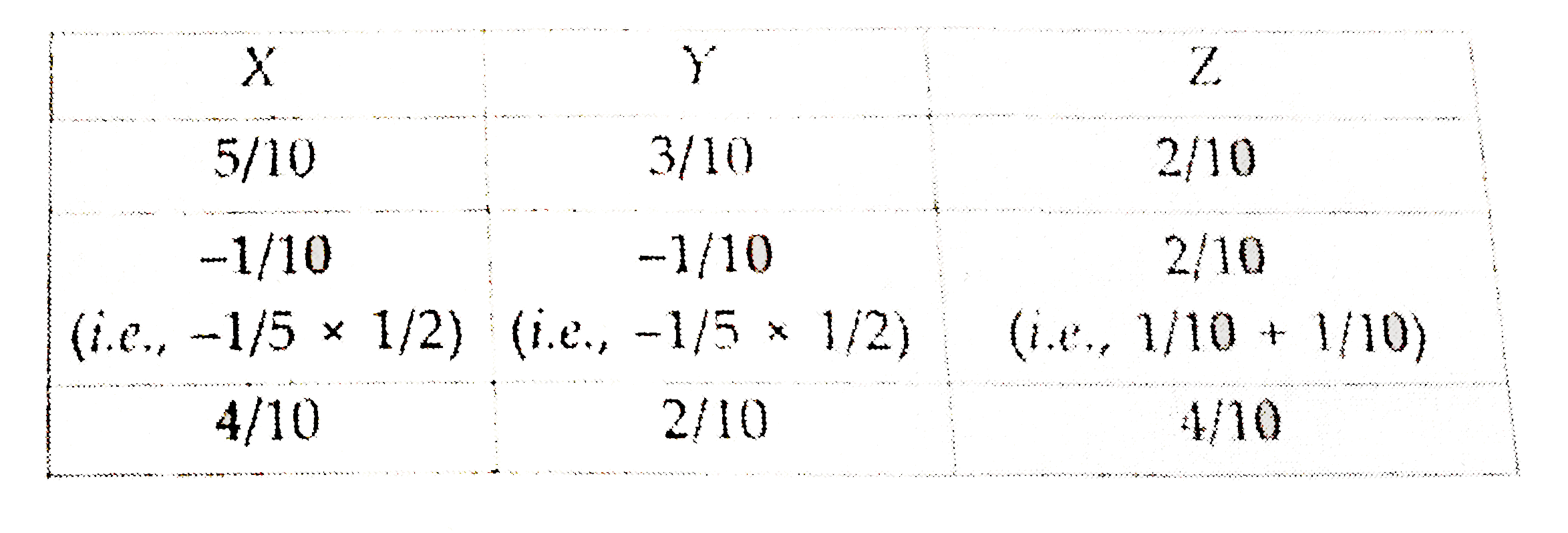 Thus, New Profit- SharingRatio of X,Y andZ `= (4)/(10): (2)/(10): (4)/(10) = 2:1:2,` Sarcrifing RatiobetweenX and Y`= 1//10 : 1/10 = 1:1,` Gain ofZ`= 2//10` Case 3.Sacrificing /(Gaining) Share = Old Share - New Share `{:(,,("X"),("Y"),("Z")),(("A") ,"Their existing(old)share",5//10,3//10,2//10),(("B"), "Their new share",1//3,1//3,1//3):}` `X = (5)/(10)- (1)/(3) = (15-10)/(30) =(5)/(30)("Sacrifice")` `Y = (3)/(10) - (1)/(3) = (9-1)/(30) = (1)/(30)`(beingnegative result, it is a gain) `Z = (2)/(10) - (1)/(3) =(6-10)/(30) = - (4)/(30)`(being negativeresult, it is a gain.) Thus, Y GAINS `1//30th` share Zgain by `4//30th` (Share of Yand Z haveincreased) and X scarifices by `5//30th` share. Gaining Ratio betweenY and Z `= (1)/(30) : (4)/(30) =1:4` Case. 4 `{:(,,("X"),("Y"),("Z")),((A),"Their existing(old)share",5//10,3//10,2//10),((B), "Share acquired by Z from",,,):}` ` X = (5)/(10) xx (1)/(5) xx (1)/(10), Y = (3)/(10) xx (10)/(6) = (1)/(20)` (C) Total share acquired by `Z = (1)/(10)+ (1)/(20) =(3)/(20)` Calculationof NewProfit-sharingRatio and Sacrifing Ratio :  Thus, New Profit-SharingRatio of X,Y and Z `= (8)/(20):(5)/(20) : (7)/(20) = 8 :5:7` Gainof `Z = (3)/(20),` SacrficingbetweenX and Y= 2 : 1. |
|
| 30. |
X,Y and Z are partners ina frim sharingprofits in 3:3:2 ratio. Theydecide to showsthe credit balance of ₹60,000. They decide that Profitand Loss Account will remain asit is.You are required to fill up the following Journalentry. |
Answer» Solution :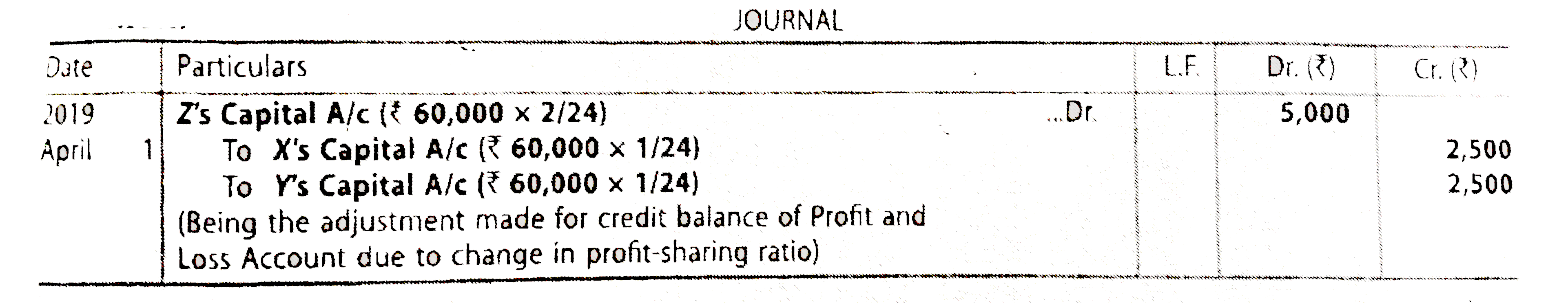 `{:(,,"X","Y","X"),(("i"), "Their Old Shares",3//8,3//8,2//8),(("II"),"Their New Shares", 1//3,1//,1//3),(("iii"),"SACRIFICE /(GAIN) (i)-(ii)",3//8-1//3= 1//24,,3//8-1//3=-1//24,2//8-1//3= 2//24),(,,"Sacrifice","Sacrifice","(Gain)"):}` |
|
| 31. |
X,Y and Zare partnersin a firm,Theirprofit - sharingratio is 5:3:2.Zis guaranteed aminimumprofitof Rs.10,000 every yearAny defifciencyarisingis tobemetby Ythe profitsfor thetwoyearended31stMarch, 2018and 2019wereRs. 40,000and 60,000Respectivelyprepaneprofitand LossAppropriationAccountof thetwoyears . |
Answer» SOLUTION : NOTE: Z 's sharein profitis morethantheminimum guaranteedamountSO threeis noneedforany ADJUSTMENT . |
|
| 32. |
X.Y and Z arepartnerssharingprofitand lossesequally as perpartnershipDeed ,Zis entitedto acommissionof 10%on thenetprofitafter chargingsuchcommissionthenetprofitbeforechargingcommissionis Rs. 2,20,000 . Determinetheamountofcommissionpayableto Z. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :COMMISSION PAYABLETO Z -Rs.20,000 | |
| 33. |
XL Ltd. invited applications for issuing 1,00,000 equity shares of Rs. 10 each at par. The amount was payable as follows : On Applicantion Rs. 3 per share. On Allottment Rs. 4 per share. On First and Final Call Rs. 3 per share. The issue was over-subscribed by three times. Applications for 20% shares were rejected and the money refunded. Allotment was made to the remaining applicants as follows. {:("Category","Number of Shares Applied","Number of Shares Allotted"),("I","1,60,000","80,000"),("II","80,000","20,000"):} Excess money received with applications was adjusted towards sums due on allotment and first and final call. All calls were made and were duly received except the final call by a shareholder belonging to Category I who has applied for 320 shares. His shares were forfeited. The forfeited shares were re-issued at Rs. 15 per share fully paid up. Pass necessary Journal entries for the above transactions in the book of XL Ltd. Open calls in-arrears and calls in advance account whenever required. |
Answer» SOLUTION : 
|
|
| 34. |
Xansa Ltd. Offered 22,000 equity shares of Rs. 100 each to the public at a premium of Rs. 20 per share. The amount per share was payable as Rs. 30 on application, Rs. 50 (including premium) on allotment, and the balance on first and final call. 20,000 shares were subscribed bythe public. All calls were made. A shareholder holding 1,000 shares failed to pay the first and final call money. His shares were forfeited. Show 'Share Capital' in the Balance Sheet of Xansa Ltd. Also, prepare 'Note to Accounts'. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 35. |
X ,Y and Z who are presently sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 5:3:2 decide to share future profits and losses in the ratio of 2 :3:5. Give the Journal entry to distribute Workmen Compensation Reserve of₹1,20,000 at the time of change in profit-sharing ratio, when there is a claim of₹80,000 against it. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 36. |
X, Yand Z who are sharing profits in the ratio of 5:3:2, decide to share profits in the ratio of 2:3 5 with effect from 1st April, 2019.Workmen Compensation Reserve appears at ₹1,20,000 in the Balance Sheet as at 31st March, 2019 and Workmen Compensation Claim is estimated at ₹1,50,000. Pass Journal entries for the accounting treatment of Workmen Compensation Reserve. |
|
Answer» Cr. PROVISIONFOR Workmen CompensationClaimA/c -₹1,50,000. (b) Dr. X's capitalA/c - ₹15,000; Y's CapitalA/c - ₹ 9,000 and Z's CAPITAL A/c - ₹ 6,000;Cr. Revalation A/c -₹ 30,000 |
|
| 37. |
X, Y and Z were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3:2:1. X retired and the new profit sharing ratio between Y and Z will be 5:4. On X's retirement the goodwill of the firm was valued at Rs. 54,000. Journal entry will be: |
|
Answer» `{:("Y's CAPITAL A/C",,DR.,"24,000",),("Z's Capital A/c",,Dr.,"30,000",),("To X's Capital A/c",,,,"54,000"):}` |
|
| 38. |
X, Y and Z share profits asd 5:3:2. Theydecide to sharetheirfuture profitsas 4:3:3 with effect from1st April, 2019. On thisdate the followingrevalutions havetaken place: Pass necessary adjustmententry to bemade because of the above changein thevalues of assetsandliabilities. However,old values will continue in the books. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39. |
X, Y and Z have been sharing profits in the ratio of 4:2:1 Z retires. X and Y take Z's share equally. New profit sharing ratio will be: |
|
Answer» `5:2` |
|
| 40. |
X ,Y and Zenteredintopartnershipon 1stOctober , 2018 to shat to shareprofitsin theratioof 4:3:3 X,PersonallygurantedthatthatZ'sshareof profitchargingintereston capital210%p.a Wouldnot be lessthan Rs.80,000in a yearcapitalcontributionswere:X- Rs. 3,00,000,y-Rs. 2,00,000andZ- rs, 1,50,000 profitfor theyear ended31st MArch2019wasRs. 1,60,000prepare profitand lossappropriationAccount. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Nett profit-RS. 1,27,500 ,share of profit, X- RS. 51,000-rs. 1,750 )= rs. 49,250 y- Rs. 1,27,500 `XX`3/10=rs. 38,250 + rs. 1,750 =Rs. 40,000 . |
|
| 41. |
X, Y and Z are sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 5:3:2. With effect from 1st April, 2019, they decide to share profits and losses in the ratio of 5:2:3. Calculate each partner's gain or sacrifice due to the change in ratio. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42. |
X ,Y and Z are partnres in a firm sharingprofits in theratio of 2:2:1fixedcapitals thatinterest wereX Rs. 5,00,000 ,Y 5,00,000 and Z Rs. 2,50,000 respctively thepartnershipDeedProvidesthatinterestoncapitalis tobe allowed@ 10%p.aZisis tobe alloweda salay ofRs. 2,000per month . profitof thefirm for theyear ended31st March, 2018afterdebitingZ's salary wasRs. 4,00,000PRepaneprofitand lossapppration Account |
|
Answer» |
|
| 43. |
X ,Y andZ arepartnersthey have omittedinterestintereston capital@ 10% p.a for three yearsended 31 stMarch ,2019theirfixed capitalson whichinterestwasto bebe calculated throughoutwere :X-Rs. 10,000 Y- Rs. 8,000and Z -Rs. 7,000 theirprofits - sharing ratioswere: 2017-1:2:2, 2018 -5:3:3,2019 -4:5:1 thefirmearned profitof Rs. 2,500IN eachYearpassNecessaryadjustmentJournal entry. |
Answer» SOLUTION :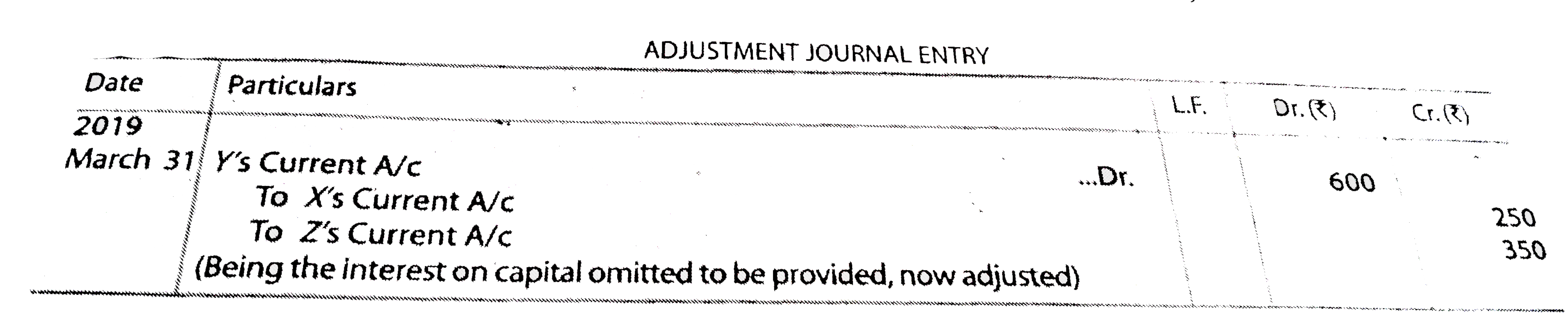 wokingNotes:1. INTERESTON capital @ 10%p.aX-Rs. 1,000 , Rs. 800andZ-Rs, 700, theaboveintereston capital Rs. 2,500 (i.e., Rs. 1,000 +rs.800+Rs. 800+Rs, 700) HASNOT beencredited to thepartnersNowis it to be creditedto thepartner'sCurrent ACCOUNTS resulting in alossof Rs. 2,500to thefirm WHICHIS toto bedebitedto thepartnersintheir- sharringratio .  Note : sincecapitalsof thepartnersarefixedadjustmententrywillbe passedthroughthrough partners' Cuttent Accounts. |
|
| 44. |
X ,Y and Z are sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 5 :3:2.With effect from 1st April, 2019. they decide to share profits and losses equally Calculate each partner's gain or saurifice due to the changes in the ratio. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 45. |
X Y and Z are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 5 : 3:2. They decide to share future profitin the ratio of 2 : 3 :5 with effect from 1st April, 2019. They also decide to record the effectfollowing revaluations without affecting the book values of assets and liabilities, by passingan adjusting entry: The necessaryadjustmentenrtywill be |
|
Answer» DR. Z and CR. X by ₹27,000 |
|
| 46. |
X, Y and Z are partners sharing profits in the ratio of5:3 :2 . They decide to share future profits in the ratio of2 : 2 : 5 with effect from 1st April , 2019 . They also decide to record the effect of following revaluations without affectig the book values of assets and liabilities , by passing adjustment entry :{:(,"""Book Value (Rs.)","""Revised Value (Rs.)",),("Land and Building","""3,00,000","""4,50,000",),("Plant and Machinery","""4,50,000","""4,20,000",),("Trade Creditors","""1,50,000","""1,35,000",),("Outstanding Rent","""1,35,000","""1,80,000",):}The necessery adjustment entry will be : |
|
Answer» DR. Z'sCapital A/c and CR,X's CAPITAL A/cbyRs. 27,000. |
|
| 47. |
X, Y and Zare partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 7:5:4. Their Balance Sheet as at 31st March, 2019 stood as : Partners decided that effect from 1st April, 2019, they will share profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2:1. For this purpose, goodwill of the firm was valued at ₹ 1,50,000. The partners neither want to record the goodwill nor want to distribute the General Reserve and profits. Pass a Journal entry to record the change and prepare Balance Sheet of the constituted firm. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 48. |
X, Y and Z are partners, sharing profits in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1, Y died on 30th June, 2019 and profit for the accounting year 2018-19 was Rs 36,000. How much share of profit will be credited to Y, for the period 1st April, 2019 to 30th June, 2019 ? |
|
Answer» RS 3,000 |
|
| 49. |
X, Y and Z are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 5:3:2.From 1st April, 2018, they decided to share profits and losses equally. The Partnership Deed provides that in the event of any change in the pront-sharing ratio, the goodwill should be valued at two years' purchase of the average profit of thepreceding five years. The profts and losses of the preceding years ended 31st March. are You are required to calculate goodwill and pass Journal entry. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 50. |
X, Yand Z are partners sharing profits and losses in the rat io 5:3:2,They decide to share the future profits in the ratio 3:2:1, Workmen compensation reserve appering in the balance sheet on the date if on information is available for the same will be : |
|
Answer» DISTRIBUTED to the partners in old profit sharing ratio |
|