Saved Bookmarks
Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in Current Affairs.
This section includes 7 InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your Current Affairs knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1. |
Which rivers are called perennial? |
| Answer» Solution :PERENNIAL rivers are the ONES which have water THROUGHOUT the YEAR. These rivers receive water from rain as well as from melted snow from the lofty mountains. | |
| 2. |
What kind of soils are needed for natural vegetation? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The sandy soils of deserts SUPPORT cactus and thorny bushes while WET, marshy deltaic regions support mangroves and deltaic VEGETATION and hill SLOPES with some depth soil have conical trees. | |
| 3. |
Which hills are called 'Purvanchal' ? |
| Answer» Solution :The PURVANCHAL comprises the Patkai HILLS, the Naga Hills, Manipur, the Mizo hills, Garo, Khasi and JAINTIA hills. | |
| 4. |
Which river is the largest Peninsular river? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The GODAVARI, its LENGTH is about 1500 KM. | |
| 5. |
Why do mostof the peninsular states have moderate population? |
| Answer» Solution :Most of the PENINSULAR states have MODERATE population because of hilly, dissected and ROCKY nature of the terrain, moderate to LOW rainfall, shallow and less FERTILE soils. | |
| 6. |
Why are forests important for human beings? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Forests are renewable resources and play a major role in enhancing the QUALITY of the environment. (ii) They modify the local climate and control soil erosion. (iii) They regulate the flow of streams and support a variety of industries like the rubber industry. (iv) Forests also provide a LIVELIHOOD for MANY communities. (v) They also offer PANORAMIC or scenic view for recreation. (vi) They control the wind force and temperature and cause rainfall. (vii) They provide humus to the soil and shelter to WILDLIFE. |
|
| 7. |
Where are the Sundarbans located? |
| Answer» Solution :West Bengal | |
| 8. |
Writeon the following. The Indian Desert |
| Answer» Solution :The Indian desert LIES towards the WESTERN margins of the Aravalli Hills. It is an undulating sandy plain covered with sand dunes called .barchans.. This region receives very low rainfall below 150 mm per YEAR (15 cm). It has arid climate with low vegetation cover. Streams appear during the rainy season. Soon after, they disappear into the sand as they do not have enough water to reach the sea. Luni is the only LARGE RIVER in this region. | |
| 9. |
Which one of the following bio-reserves of India is not included in the world network of bioreserve? |
|
Answer» MANAS |
|
| 10. |
Which region is called "Terai Region'? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :SOUTH of bhabar, the streams and rivers re-emerge and create a wet SWAMPY & marshy region known as Terai. | |
| 11. |
Which of the following positions does India occupy in the world with regard to plant diversity? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Tenth | |
| 12. |
What steps have been taken by the government to protect the flora and fauna of the country? |
|
Answer» Solution :Steps taken by the GOVERNMENT to protect the flora and fauna are as follows: (i) About fourteen biosphere reserves have been set up in the COUNTRY to protect both flora and fauna. Four out of these—the Sundarbans (West Bengal), Nanda Devi (UTTARAKHAND), Gulf of Mannar (Tamil Nadu) and Nilgiri (Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu) have been included in the world network of Biosphere Reserves. (ii) Since 1992, financial and technical assistance is being provided to many botanical gardens by the government. (iii) Project Tiger, Project Rhino, Project Great Indian Bustard and many other eco developmental PROJECTS have been introduced. (iv) About 103 national parks, 535 wildlife sanctuaries and zoological gardens have been set up to take care of the natural HERITAGE. |
|
| 13. |
Which are the major physiographic divisions of India? Contrast the relief of the Himalayan region with that of the Peninsular Plateau. |
|
Answer» Solution :The major PHYSIOGRAPHIC divisions of India are: (i) The Himalayan Mountains (II) The Northern Plains (III) The Peninsular Plateau (iv) The Indian Desert (V)The Coastal Plains (VI) The Islands 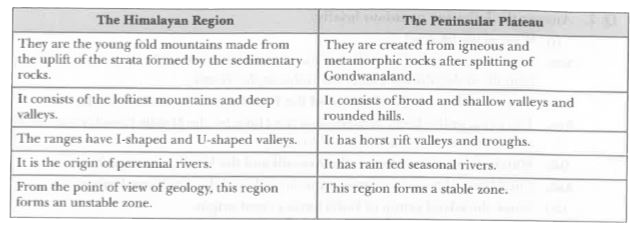
|
|
| 14. |
Where do the rivers Indus and Ganga have their origin? |
| Answer» Solution :The Indus RIVER has its origin in TIBET near the Mansarovar Lake while the Ganga River has its origin in Gangotri Glacier in UTTARANCHAL. | |
| 15. |
Which are the main west flowing rivers of Western Ghats? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :SABARMATI, MAHI, Bharatpuja and PERIYAR. | |
| 16. |
Why are the Shivalik ranges prone to landslide and earthquakes? |
| Answer» Solution :The Shivalik ranges are still in the process of folding. This is the youngest range of the Himalayas formed by unconsolidated ROCK MATERIAL. THEREFORE, these ranges are PRONE to EARTHQUAKES and landslides. | |
| 17. |
Write down the differences between a delta and an estuary. |
|
Answer» Solution :DELTA (i) It is a triangular-shaped piece of land, formed at the mouth of a river, where it meets the sea. (ii) With the continuous deposition of silt on its bed, a river GOES on splitting itself into channels or distributaries. They CARRY river water into the sea. (iii) Delta shows an extension of land into sea. It is continuously growing seawards. (iv) The sea is shallow. Tidal currents are not strong enough to remove deposits effectively. (v) The world.s largest and the fastest growing delta is the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta known as the Sundarban delta. Peninsular rivers like the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri also form big deltas. Estuary (i) An estuary is an inlet formed generally by the submergence of the mouth of a river. (ii) It has a single mouth or channel. It has steep banks or slopes. Where an estuary is formed, sea is deep. (iii) Strong tidal waves carry away the little amount of SEDIMENTS deposited by a river. (iv) Estuaries produce an indented coastline and PROVIDE sites of natural harbours. They create conditions for better navigation. (v) The mouths of rivers Narmada and Tapi present good examples of stuaries. |
|
| 18. |
Who are Adolescents? |
| Answer» Solution :ADOLESCENTS are generally grouped in the age group of 10 to 19 YEARS. | |
| 19. |
Writeon the following. The Island groups of India |
|
Answer» SOLUTION : India consists of 2 main island GROUPS, namely Lakshadweep and Andaman and Nicobar island. The Lakshadweep consists of many small islands located opposite the Kerala coast in the Arabian Sea. The islands of this group are FORMED of coral deposits CALLED .atolls in MALAYALAM which refer to their ring or .horse-shoc. shape. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands, on the other hand, are larger in size. They are more in number and more widely scattered. |
|
| 20. |
What significant improvements have been noticed in the health status of our population? |
|
Answer» Solution :Following improvements have been made in the health status of our population: (i) Diseases like SMALL pox and PLAGUE have been eradicated. (ii) Inoculationand vaccinations are provided to control dengue fever, leprosy, TB and polio, etc. (iii) The infant mortalityrate has also SUBSTANTIALLY reduced. (iv) Improvement has been shown in sex ratio also in some STATES of India. v.Good pujblic health facilities are provided to prevent spread of diseases and periodically information is imparted to the public to take precautions. |
|
| 22. |
Which are the most widespread forests of India? Mention any two characteristic features of these forests. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The Tropical Deciduous forests are the most WIDESPREAD forests in India-found in areas receiving 70 to 200 cms of rainfall. (i) Trees of this type of forests shed their leaves for about six to eight weeks during the DRY season. (ii) The forests are further subdivided into moist and dry deciduous DEPENDING on the AVAILABILITY of water. |
|
| 23. |
Which river is known as 'Dakshin Ganga? State any two characteristics of it. |
|
Answer» Solution : (i) The Godavari is the largest peninsular RIVER. (II) Its length is about 1500 km. Its drainage basin is also the largest amongst the peninsular rivers. (iii) The basin covers the parts of Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha and Andhra Pradesh. (iv) The Godavari is joined by a number of tributaries such as the Purna, the Wardha, the Pranhita, the Manjra, the Wainganga and the Penganga. (v) The last THREE tributaries are very large. Because of its length and the area it covers, it is also KNOWN as .DAKSHIN Ganga.. |
|
| 24. |
Why are rivers important for the country's economy? |
|
Answer» Solution :The rivers are important for the country.s economy due to the FOLLOWING reasons - • It is an important source of natural freshwater, which is required for the survival of most of the animals including HUMAN. • River water is USED for various purposes like domestic, industrial, agriculture. • The presence of rivers BOOSTS trade and commerce by HELPING in the easy transport of goods. They are also a potential source of energy. • River water is also used in running the hydro-electric dams. • It is also used for navigation and transport, thus, important for commercial activities. • It also provides fishing and great scenic and recreational value. Thus, serve as good tourist spots. |
|
| 25. |
Which river is called 'Dakshin Ganga'? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :GODAVARI is called .DAKSHIN Ganga. because of its LENGTH and the AREA it covers. | |
| 26. |
Which of the following was not a part of the ancient landmass of Gondwana land? |
|
Answer» EUROPE |
|
| 27. |
Write any three characteristics of the Central Highlands. |
|
Answer» Solution :The part of the Peninsular plateau LYING to the NORTH of the Narmada river, covering a major area of the MALWA plateau is known as the Central HIGHLANDS.. Its three characteristics are: (i) They stretch from the north-west with the Aravallis, further merging with the sandy and ROCKY desert of Rajasthan. (ii) They are wider in the west but narrower in the east. (iii) The eastward extension of this plateau is locally known as .Bundelkhand. and .Baghelkhand.. The Chotanagpur plateau. is the easternmost part of this plateau, which is drained by the river Damodar. |
|
| 28. |
Which plateau lies between the Aravalli and the Vindhyan ranges? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The Malwa PLATEAU LIES between the Aravalli and the Vindhyan Ranges. | |
| 29. |
Which animals are found in Tropical Rain Forests? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Common ANIMALS found in these forests are ELEPHANTS, monkeys, LEMURS and deer and one horned RHINOCEROS. | |
| 30. |
Which are the main tributaries of river Indus? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The SATLUJ, the Beas, the Ravi, the Chenab and the Jhelum are the MAIN TRIBUTARIES of river Indus. | |
| 32. |
Where is Himalayan range 'Himachal located? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The RANGE lying to the south of the Himadri FORMS the most rugged mountain system and is known as HIMACHAL or LESSER Himalaya. | |
| 33. |
What kind of land is suitable for natural vegetation? |
| Answer» Solution :The undulating and rough terrains are areas where grasslands and woodlands DEVELOP and GIVE shelter to a variety of WILD LIFE. | |
| 34. |
Who is a literate person according to the Census 2011? Why is literacy considered important for the quality of the population? |
|
Answer» Solution :According to the CENSUS 2011 data, a person aged 7 years and above who can read and write with UNDERSTANDING in any language is treated as literate. Literacyis considered very IMPORTANT for the quality of a population because of the following: (i) Only a well informed and EDUCATED citizen can make intelligent choice and UNDERTAKE research and development projects. (ii) Low levels of literacy are a serious obstacle for economic improvement. |
|
| 35. |
What types of lakes are found in India? Give suitable examples. |
|
Answer» Solution :India has many lakes. They differ in size and other characteristics. Most lakes are permanent, whereas some contain water only during the rainy season. There are lakes which are formed by the action of glaciers and ice sheets, while the others have been formed by HUMAN activities. (i) Salt water lakes: Spit and bars form LAGOONS or salt water lakes in the coastal areas like the Chilika lake, Pulicat lake and the Kolleru lake. Sometimes, salt water lakes are formed with island drainage like Sambhar lake in Rajasthan. Its water is used for producing salt. (ii) Freshwater lakes: Most of these are in the Himalayan region. They are of glacier origin. They are formed when glaciers dug out a basin, which was later filled with snow melt. The Wular lake in Jammu and Kashmir is the largest freshwater lake in India. Other freshwaterlakes are the Dal, Bhimtal, Nainital, Loktak and Barapani. (iii) Man-made lakes: The DAMMING of the rivers for the generation of HYDEL power has also led to the formation of lakes. These lakes are formed to drain excessive water of the river during floods and adding water to the rivers during the dry season. Such lakes are the Guru Gobind Sagar (Bhakra NANGAL Project), Nizain Sagar, Nagarjuna Sagar, Rana Pratap Sagar, etc. |
|
| 36. |
Why is Peninsular Plateau of India known as storehouse of minerals? Explain. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Peninsular PLATEAU known as storehouse of Minerals: (i) The Peninsular Plateau is formed by igneous and metamorphic rocks due to volcanic activities. (II) Major metallic minerals like iron-ore and coal deposits are abundantly found in this Plateau. (iii) other Non-metallic minerals like Mica is also found in this region, MAKING it storehouse of minerals of INDIA. |
|
| 37. |
When was Indus water Treaty signed? |
|
Answer» 1960 |
|
| 39. |
Where are The Central Highlands located? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The part of the Peninsular Plateau lying to the NORTH of the NARMADA river COVERING a major area of the Malwa Plateau is known as Central HIGHLANDS. | |
| 40. |
Which famous valleys are located in 'Himachal'? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The FAMOUS valleys of Kashmir, the Kangra and KULLU are LOCATED in .HIMACHAL.. | |
| 41. |
Why has the rate of population growth in India been declining since 1981? |
| Answer» Solution :DUE to greater use of birth control measure the RATE of POPULATION growth has been DECLINING. | |
| 42. |
Write a few lines on Deccan Trap of the Peninsular Plateau. What do you know about the distinct features of the peninsular plateau called the Deccan Trap? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) The BLACK soil area in the peninsular plateau is called the Deccan Trap. (ii) This is formed by volcanic activities, so the ROCKS are igneous. (iii) These rocks have been denuded over time and are responsible for the formation of the black soil. Due to continuous flow of lava an EXTENSIVE lava plateau has been formed known as Deccan Trap. (iv) The ARAVALLIS lie on the western and north-western margins of the peninsular plateau. (v) These are highly eroded hills and are found as broken hills. |
|
| 43. |
Which of the following ranges of the Himalayas are composed of unconsolidated sediments brought down by rivers. |
|
Answer» The SHIVALIKS |
|
| 44. |
Why do Himalayan rivers get flooded every year? What are its advantage? |
|
Answer» Solution :Himalayan RIVERS get FLOODED every year due to excessive melting of the snow due to global warming and excessive rains too. Advantage: (i) They enable the enriching of the SOIL in entire northern plains by providing ALLUVIAL silt to it. (ii) Various FOOD and cash crops are grown in it and due to irrigational facilities and green revolution, certain crops have bumper crops. |
|
| 45. |
Why has India a rich heritage of flora and fauna? |
|
Answer» Solution :India has a rich heritage of flora and fauna due to FOLLOWING reasons: • India is a diverse country with various relief features (i.e. mountains, plateaus, plains, etc.) These regions consist of different types of vegetation which support different types of animals. • There is availability of different types of soil which facilitates base for different types of vegetation. • There is variation in the climatic conditions of India (temperature, HUMIDITY, etc.). It differs from north to south and east to west. Thus, supporting LARGE variety of flora and fauna. • India has a monsoon TYPE of climate where rainfall varies from 20 cms to 300 cms distributed THROUGHOUT the year supporting large amount of flora and fauna. • Variation in the duration of sunlight at different places due to difference in the latitude and altitude. |
|
| 46. |
Which two peninsular rivers flow through trough? |
| Answer» Solution :The TWO RIVERS that flow through TROUGHS are Narmada and Tapi. They FORM estuaries while ENTERING the sea. | |
| 47. |
When was the Wildlife Protection Act implemented in India? Name any four protected species of animals found in India. |
|
Answer» Solution :First Wildlife Protection Act was PASSED and IMPLEMENTED in 1972. Four protected species are: (i) Lion (ii) Tiger (III) One-horned Rhinoceros (iv) Great Indian Bustard. |
|
| 48. |
Which is the outer most range of Himalayas? |
| Answer» Solution : The OUTERMOST RANGE of Himalayas is CALLED the .Shivaliks.. | |
| 49. |
Where are elephants and one-horned rhinoceros mainly found and why? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) The ELEPHANTS are the most MAJESTIC animals among the mammals. They are found in the hot wet forests of Assam, Karnataka and Kerala. They prefer forested hilly areas, providing plenty of food and water for them throughout the YEAR. (ii) One-horned rhinoceros live in swampy and marshy lands of Assam and WEST Bengal. |
|
| 50. |
Which forest is also known as Monsoon forest? |
| Answer» Solution :Tropical Deciduous | |
Previous
Next