Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in Current Affairs.
This section includes 7 InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your Current Affairs knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1. |
What is the reason for the twinkling of stars ? |
|
Answer» EXPLOSIONS occuringin the stars from TIME to time |
|
| 2. |
The change in magnetic field lines in a coil is the cause of induced electric current in it.Name the underlying phenomenon. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION. | |
| 3. |
Say True or False.The mass of the Earth is 6.4xx10^(6)kg. |
| Answer» Solution :False. MASS of the EARTH is `6xx10^(24)kg` | |
| 4. |
Whichof the follwing property of a proton can changewhileit moves freelyin a mageticfield ? (There may be more thanone correct answer). |
|
Answer» MASS |
|
| 5. |
When an object is placed infront of a spherical mirror at a distance 30 cm, the magnification is -1. Illustrate the conclusions. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 6. |
Does the frequency of sound waes depend on the medium in which it travels? |
|
Answer» Solution :YES. 1) We KNOW that frequency `upsilon = (" Speed of wave " (v))/(" Wavelength "( lambda))` 2) As speed of wave differs from MEDIUM to medium the frequency also CHANGES, keeping the wavelengths constant. |
|
| 7. |
The relation between N (no. of molecules), P,V. & T is ........... |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`N=(K_(B)T)/(PV)` | |
| 8. |
What is magnification of a lens ? |
|
Answer» Solution :MAGNIFICATION of a LENS is the ratio of the height of the image FORMED by lens to the actual height of object. If h is the height of the object and .h., the height of the image formed by lens, then magnification `m=(h.)/h` If U and v are the distances of object and image respectively from the OPTICAL centre, then `m=(h.)/h=v/u` |
|
| 9. |
A person is said to be colour blind if he/ she has deficiency of rod shaped cells in retina of his eyes. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :FALSE. A person is said to be colour blind if he/ she has deficiency of conical shaped cells RESPONDING to CERTAIN colours in retina of his eyes. |
|
| 10. |
"___________" prepares the 'Red List' that contains the names of endangered species from different countries. |
|
Answer» IUCN |
|
| 11. |
Ethylene has ………. Bond between two carbon atoms. |
|
Answer» a SINGLE |
|
| 12. |
…………. Is used as an anode during the electrolytic reduction of bauxite. |
|
Answer» SULPHUR |
|
| 13. |
One word is incorrect in the statement . Change it to make the statement correct : Herdmania has notochord in only tail region and hence it is called Hemichordate. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Herdmania has notochord in only tail REGION and hence it is CALLED Urochordate. | |
| 14. |
Anodes need to be replaced from time to time during the electrolysis of alumina. |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) During electrolysis of alumina, the oxygen liberated at the carbon anode REACTS with GRAPHITE rods (carbon anode) and forms carbon dioxide. (2) As the anodes gets oxidised during electrolysis of alumina, they are CONTINUOUSLY eroded. HENCE, it is necessary to replace anodes from TIME to time. |
|
| 15. |
Define electric potential difference. State the formula for it. Name and define the SI unit of potential difference. |
|
Answer» Solution :Definition of electric potential difference : The electric potential difference (p.d.) between any two points A and B in an electric FIELD is the work DONE to move a unit positive charge (+ 1 C) from one point A to the another point B against the electric force due to the electric field. Potential difference (V) between two points `=("Work done (W)")/("Charge (Q)")` If potential at point A is `V_A` and that at point B is `V_B`. electric potential difference between points A and B is `({:("Potential at"),("Final Point B"):})-({:("Potential at"),("Initial Point A"):})=W/Q` `i.e., V_B - V_A = W/Q`.......(12.3) If `V_B - V_A` is denoted by V, `V = W/Q` Electric potential difference (p.d.) is also known as voltage. The SI unit of p.d. is volt or JOULE / COULOMB. Definition of the volt: The potential difference between two points in an electric field is said to be 1 volt if 1J of work is done to move a charge of 1c from one point to another point. `(1V = (1J)/(1C))` |
|
| 16. |
Mention any three differences between reflection and refraction of light. |
| Answer» Solution :`{:("REFLECTION","Refraction"),("Reflection refers to BOUNCING back of light RAYS to the same medium on striking a polished or SHINY surface.","Refraction refers to bending of light rays as they travel from one medium to another."),("This phenomenon USUALLY occurs in mirrors.","This phenomenon usually occurs in lenses, prisms, glass slabs, etc and not in mirrors."),("The light entering a medium returns to the same medium.","The light entering a medium travels to another medium."),("There is no change in the speed of light rays.","Speed of light rays changes according to the medium."),("The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.","The angle of incidence is not equal to the angle of reflection."):}` | |
| 17. |
Red colour is scattered in a greater amount than blue and violet colour. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 18. |
A positively charged rod is brought near an uncharged conductor. If the rod is then suddenly withdrawn, the charge left on the conductor will be |
| Answer» Solution :zero | |
| 19. |
When a ray of light passes thorugh a glass slab how many times does it change its path and why ? |
|
Answer» Solution :The ray of light bends TWICE. RIGHT TIME when it enters from air to the glass SLAB, it bends towards te normal, i.e., fromrarer medium to denser medium. Second time, when the ray moves out fromthe glass slab to air, it bends away from the normal, i.e.,it moves from denser medium to RARER medium. |
|
| 21. |
What is meant by resistance of conductor? Name and define its Sl unit. List the factors by which the resistance of a wire is affected. What happens if i] its length is doubled ii] its radius is doubled? |
|
Answer» Solution :RESISTANCE is the property of the CONDUCTOR to resist the flow of current. Sl UNIT of Resistance is Ohm. Resistance of a conductor DIRECTLY depends upon Length of the wire L Inversely depends upon Area of Cross section of the conductor I/A Nature of material used. Therefore, `R=(rhoL)/A` Length of the conductor is double, means you are stretching that given length to double it. As a RESULT, the wire becomes thin due to stretching. So its area of cross section will be halved [since the volume remains constant]. So new resistance `R_(N)=(rho2L)/(A/2)=(4rhoL)/A=4R` Hence the new resistance will increase will become one-fourth. |
|
| 22. |
When an objects is thrown upward, the force of gravity_____________. |
|
Answer» is OPPOSITE to the direction of MOTION |
|
| 23. |
Observe the diagram given and answer the question asked. b. What is the cause of this defect? |
|
Answer» Solution :The cause of this defect are: i. The curvature of cornea and eye LENS increases. ii. The converging power of lens REMAINS LARGE due to decreased focal length. iii. The distance between the lens and retina INCREASE due to elongation of eye ball. ltbr. iv. The far point of the eye is not at infinity but has SHIFTED closer to the eye. |
|
| 24. |
(a) What will happen if slow moving neutrons are made to strike the atoms of a heavy element ._(92)^(235)U?What is the name of this process ? (b) Write a nuclear equation to represent the process which takes place.(c ) Name one installation where such a process is utilised. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 25. |
Assertion (A) : Ethanoic acid is also known as glacial acetic acid.Reason (R) : The melting point of pure ethanoic acid is 290 K and hence it often freezes during winters in cold climates. |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are TRUE and (R) is CORRECT explanation of the ASSERTION. |
|
| 26. |
{:("Column- A ","Column - B "),("A] Commutator","i] detects the presence of electric current in a circuit."),("B] Fuse","ii] converts mechanical energy into electrical energy"),("C] Galvanometer","iii] measures the potential difference"),("D] Electric generator","iv] shows the direction of the motion of the conductor"),(,"v] protects the electrical appliances"),(,"vi] reverses the direction of current"),(,"viii] converts electrical energy into mechanical energy"):} |
| Answer» Solution :`{:("COLUMN - A" ,"Column - A"),("A] COMMUTATOR","vi] reverses the DIRECTION of current"),("B] FUSE", "v] protects the electrical appliances"),("C] Galvanometer" ,"i] DETECTS the presence of electric current in a circuit" ),("D] Electric generator", "ii] converts mechanical energy into electrical elergy"):}` | |
| 27. |
The hot air ballon rises because it is |
|
Answer» denser |
|
| 28. |
The length and breadth of a rectangular sheet are 16.2 cm and 10.1 cm, respectively. The area of the sheet in appropriate significant figures and error is |
|
Answer» `164+-3cm^(2)` |
|
| 29. |
PV/nT =a constant is called as equation of state. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :It is CALLED the COMBINED LAW of GASES. | |
| 30. |
Give the characteristics and uses of Xanthan gum: |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) Xanthomonas species is used to make Xanthan gum by FERMENTATION of STARCH and molasses. (2) It is useful DUE to properties LIKE solubility in hot and cold water and its high density. (3) It is used in the PRODUCTION of pigments, fertilizers, weedicides, textile pigments, tooth pastes, high quality paper, etc. (4) It is also used in ice creams, pudding, chocolates, milk shakes, instant soups for bringing thickness. |
|
| 31. |
Mention the phenomena responsible for the following. Formation of rainbow. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 32. |
Partial reflection and Total internal reflection. |
Answer» SOLUTION :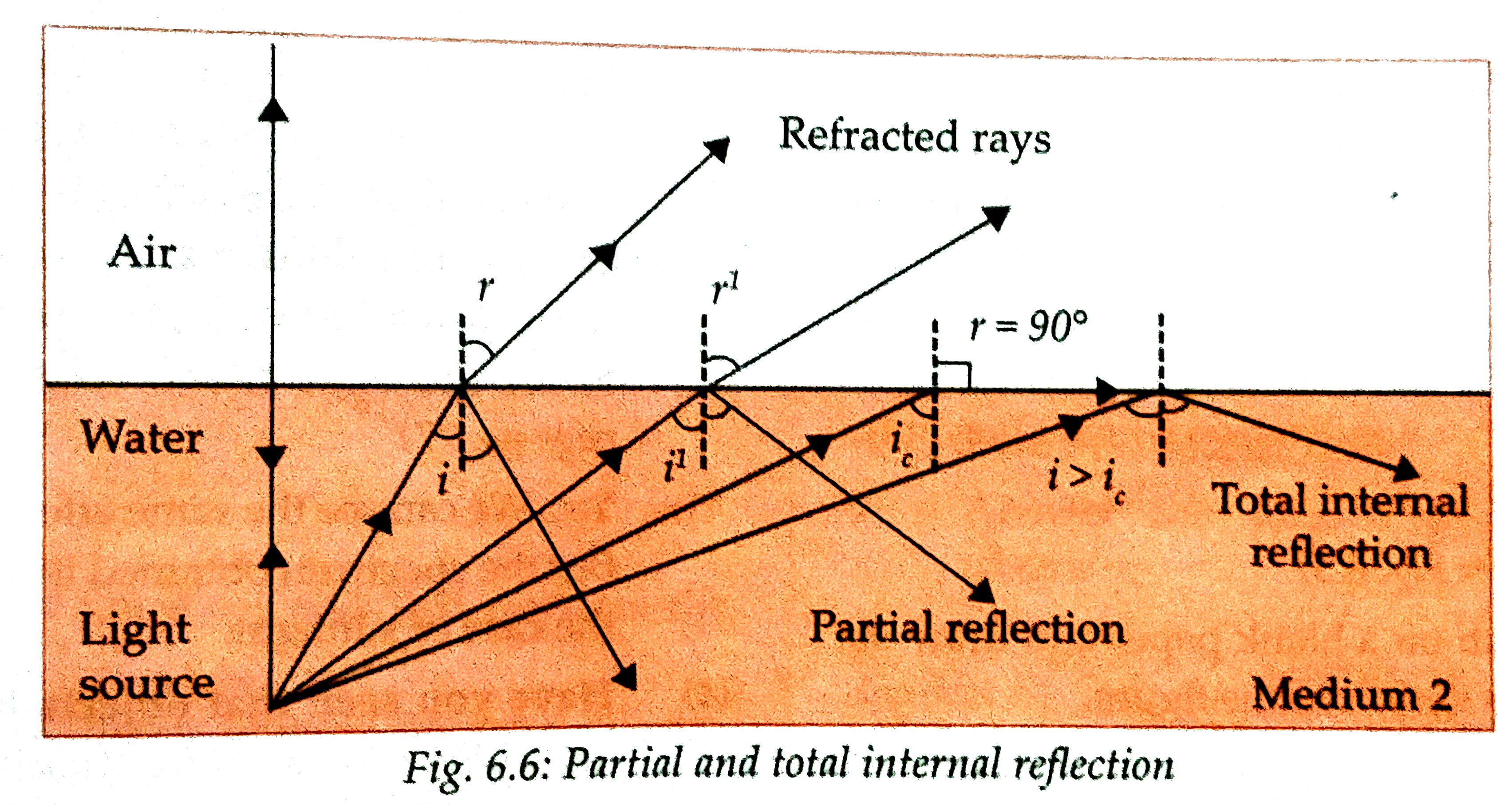
|
|
| 33. |
Derive an expression for the equivalent resistance of three resistors R_(1) R_(2) and R_(3) connected inseries. |
|
Answer» Solution :Total potential difference across a combination of resistors in series is equal to the sum of potential difference across the individual resistors. `V=V_(1)+V_(2)+V_(3)` Let I be the current in the CIRCUIT The current through each resistor is also I. It is POSSIBLE to replace the THREE resistors joined ir, series by an equivalent resistor of resistance R. Applying Ohm.s law, V = IR On applying Ohm.s law to the three resistors RESPECTIVELY we further have `V_(1)=IR_(1)` `V_(2) =IR_(2)` `V_(3)=IR_(3)` 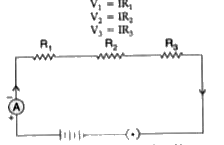 But `"" V =V_(1)+V_(2)+V_(3)` `IR =IR_(1)+IR_(2)+IR_(3)`, `R=R_(1)+R_(2)+R_(3)` |
|
| 34. |
(i) Define dispersion of light (ii) Name the colour that deviates least and the one which deviates most while passing through a glass prism. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) DISPERSION : BREAKING up of WHITE light into COMPONENT colours. (ii) Red colour deviates the least and violet deviates the most. |
|
| 35. |
How can we get the rrequired amount of energy by connection solar panels? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) In solar panel, many solar cells are CONNECTED in series and parallel combinations to generate the required current and potential difference. (ii) In series combination of solar cells the potential difference is the addition of the potential difference of individual solar cells while the current id equal to the current from an individual cell. (IV) Many such solar panels are then connected in series to from a solar string and many such solar strings are further conected in parallel to form a solar ARRAY. (v) Thus by CONNECTING many solar panels in series and in parallel combinations , the required amount of energy can be GENERATED. |
|
| 36. |
Arrange the following common substances in the increasing order of refractive indices, ice, Kerosene, Glass, Diamond, Alcohol, Water. |
|
Answer» Solution :Order of INCREASING REFRACTIVE INDICES: ICE, Water , Alcohol, Kerosene, Glass, DIAMOND. |
|
| 37. |
Biotechnology is |
| Answer» Solution :Technology that brings about artificial genetic CHANGES and HYBRIDIZATION in ORGANISMS for HUMAN welfare is called BIOTECHNOLOGY. | |
| 38. |
Can you obtain the nature, position and relative size of images formed by a lens by drawing the ray diagrams ? If yes, draw neat ray diagrams to find different types of images formed by a convex lens. |
|
Answer» Solution :We can easily obtain the NATURE, position and relative size of image formed by a lens by drawing the RAY diagram using rays WHOSE refracted path can be drawn easily. A CONVEX lens may form six different types of IMAGES depending upon the position of the object relative to the lens. Ray diagrams for these have been drawn in Figure. 
|
|
| 40. |
A 100 watt bulb is used for 5 hours daily and four 60 watt bulbs are used for 5 hours daily. Calculate the energy consumed (in kWh) in the month of January. |
|
Answer» Solution :100 w = 100 joules PER second 1 watt hours = 3600 joules The electric bulb is lighted for 5 hours daily, `:.100Wxx5=500` watt hours 500 watt hours = 1800000 joules 1 kWh = 3600000 joules Units CONSUMED per DAY `=(1800000)/(3600000)=0.5` units Untis consumed in month `=0.5xx31=15.5` units.. . . . (1) Now, Sum of power of four 60 watt bulbs = 240 W 240 `Wxx5` hours = 1200 watt hours 1200 watt hours = 4320000 joules Energy consumed per day `= (4320000)/(3600000)=1.2` units Energy consumed in a month `=1.2xx31=37.2` units. . . . (2) Total energy consumed in a month `=15.5+37.2` `""=52.7` units 1 unit = 1 kWh The energy consumed in the month of January `=52.7` kWh |
|
| 41. |
What happens to the resistance of a conductor when its aru of cross-section is increased ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :RESISTANCE is DECREASED. | |
| 42. |
a) Write the differences between potential energy and kinetic energy. Compare and differentiate between political energy and kinetic energy. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 43. |
If objects ·of equal masses are given equal heat, their final temperature will be different. This is due to difference in their ……….. |
|
Answer» SHAPES |
|
| 44. |
Which of the following mirrors forms an image which is virtual and smaller in size? |
|
Answer» CONVEX |
|
| 45. |
What will be the change in the resistivity of a resistance wire. When its length is doubled by stretching it uniformly ? |
|
Answer» Will be doubled |
|
| 46. |
An electric bulb is rated 220 V and 100 W. When it is operated on 110 V, the power consumed will be : |
|
Answer» |
|
| 47. |
What is meant by short circuit ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) When a live wire comes in contact with a neutral wire, it causes a . short CIRCUIT.. (ii) This happens when the insulation of the wires get damaged due to temperature changes or some EXTERNAL FORCE. (iii) Due to a short circuit, the effective resistance in the circuit becomes very small, which leads to the flow of a large current through the wires. (iv) This result in heating of wires to such an extent that a fire may be CAUSED in the building. |
|
| 48. |
What is the role of the split ring in an electric motor? |
| Answer» Solution :In an electric motor, the split ring ACTS as a commutator. Due to its action, the direction of current FLOWING in motor COIL reverses after EVERY half turn, giving rise to a continuous rotation of the coil and the axle. | |
| 49. |
(a) Write the electron dot structurefor calciumand oxygen. The atomic numbers of calcium and oxygen are 20 and 8 respectively. (b) Show the formation of calcium oxideby the transfer of electrons. (c) Ionic compounds are high melting solids. Give reason. |
Answer» SOLUTION :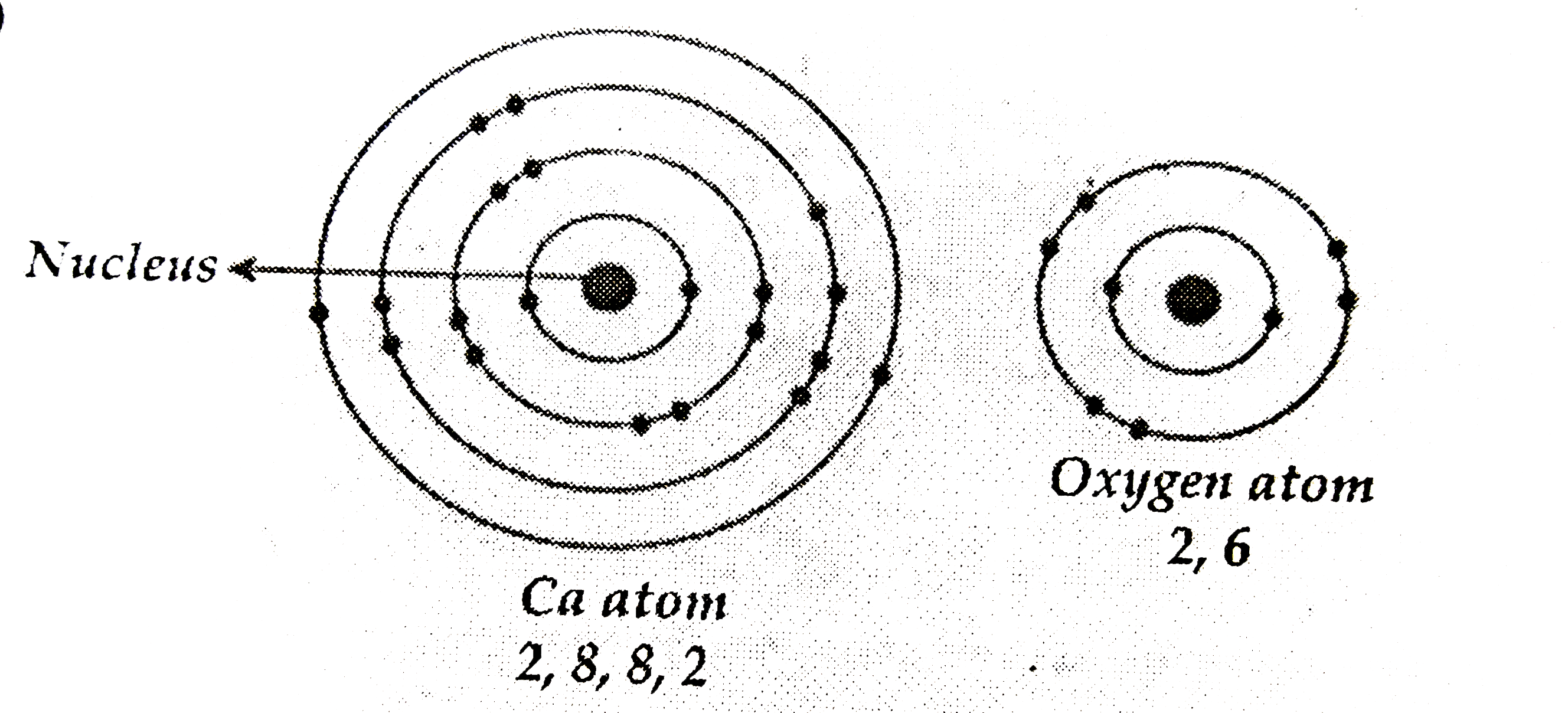 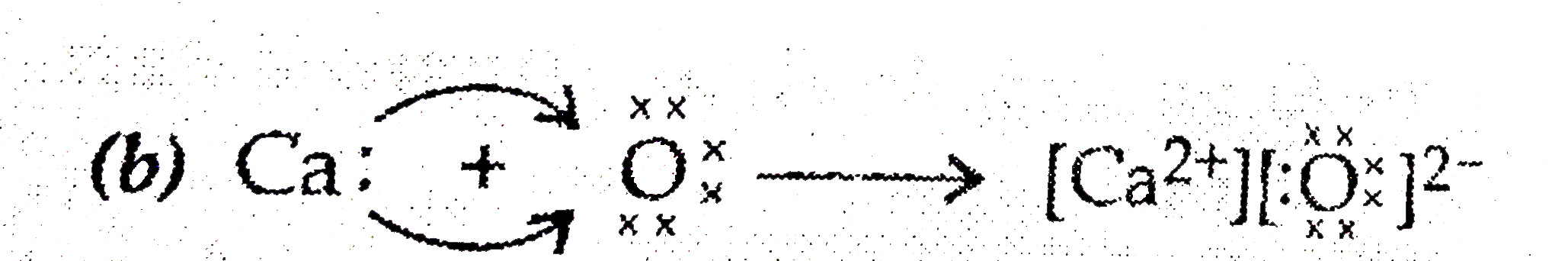 (c)Ionic compounds have high meltingpoint, as their oppositely charged ions are strongly held together by STRONG electrostatic FORCE of ATTRACTION. |
|
| 50. |
State the significance of the following devices in domestic circuits : (i) Main switch(ii) Main fuse(iii) Electricity meter |
|
Answer» Solution :i] In case of any mishaps such as accidental fire, electric shock, etc., or when some electrical work is being done at home,main switch can be switched off to cut off electricitysupply to all appliances. Thisprevents furtherdamage and avoids the possibilityof electric shock. II] If a high current flows due to lightning, suddenincrease in supply voltage, short circuit,overloading, faulty appliance, etc., the main FUSE burns off and cuts the electricitysupplyto the home . This protects all the appliances and linewires fromgetting burnt or damaged. iii] Electricity meter is INSTALLED in every home to measure the AMOUNT of electrical energyconsumed. Its main purpose is to help the electricity- supply board in BILLING. |
|