Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
A series LCR circuit is connected to an ac source having voltage v=v_(m) sin omega t. Derive the expression for the instantaneous current I and its phase relationship to the applied voltage. (i)Maximum and (ii) minimum. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) (1) Equivalent impendance (Z) is LCR circuit: The effective resistance offered by a series LCR-circuit is called its impedance. It is DENOTED by Z. Suppose an inductance L, capacitance C and resistance R are connected in series to a source of alternating emf, `V=V_0` sin wt. Let, I be the instantaneous value of CURRENT in the series circuit. Then voltages across the three components are (i) `V_L=X_L I` It is ahead of current I in phase by `90^@`. (ii) `V_C=V_C I`. it lags BEHIND the current I in phase by `90^@`. (iii) `V_R=RI`. It is in phase with current I. 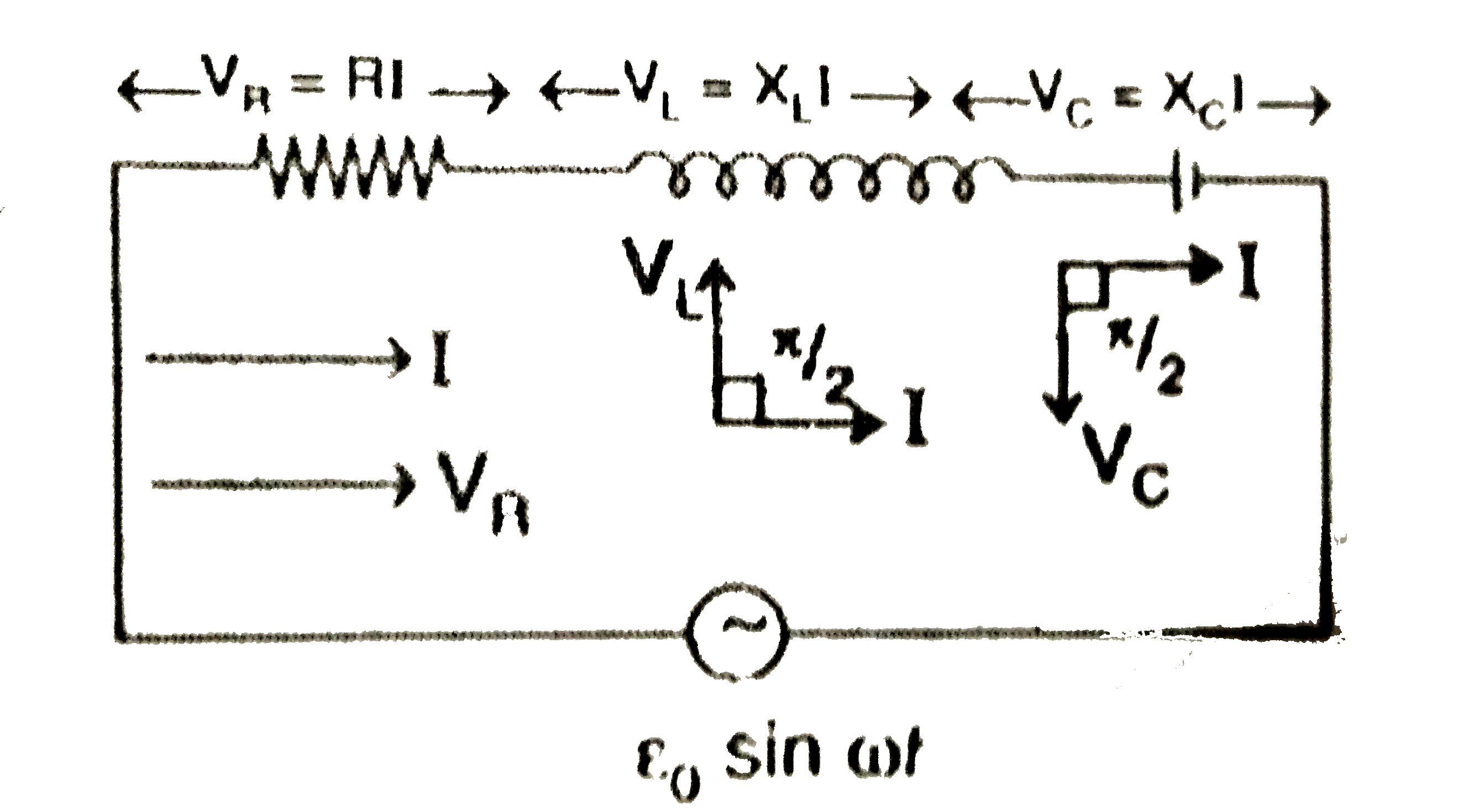 These voltages are shown in the phasor diagram given below : 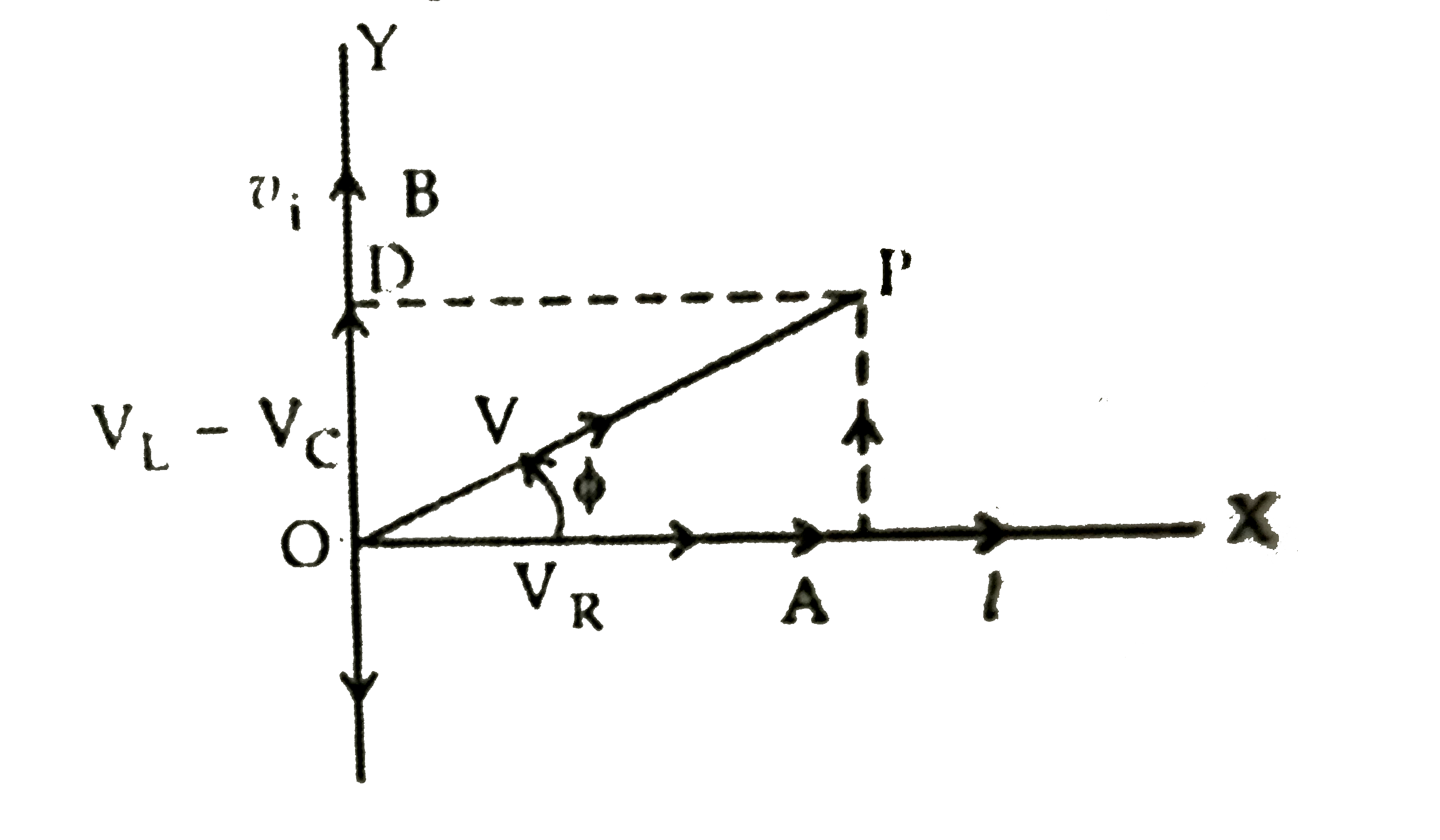 As ` V_L and L_C` are in opposite directions, their resultant is ` OD =V_L-V_C`, in the positive y-direction By paralllelogram law, the resultant voltage is ` V=OP` `=sqrt(OA^2+OD^2)=sqrt(V_(R)^(2)+(V_L-V_C)^2)` ` =sqrt(R^2I^2+(X_LI-X_CI)^2)=Isqrt(R^2+(X_L-X_C)^2)` ` therefore (V)/(I) =sqrt(R^2+(X_L-X_C)^2)`. Clear, `V//I` is the effective resistance of the series LCRcircuit and is called its impedance (Z). ` therefore Z=sqrt(R^2+(X_L-X_C)^2)=sqrt(R^2+(Omega L-(1)/(OmegaC))^2)[{:(because X_L=OmegaL),(X_C=1//OmegaC):}]` (2) When Z=R, then `X_1=X_C` ` therefore Omega L=(1)/(OmegaC) rArr Omega^2LC =1 rArr Omega =(1)/(sqrt(LC))` (3) , From phasor diagram, it follows that in LCR series circuit, V leads I `(X_Lgt L_C)` by phase angle `phi` then `tan phi= (AP)/(OA) =(V_L-V_C)/(V_R)` `tan phi=(IX_L-IX_C)/(IR)rArr tan phi =(X_L-X_C)/(R)` `tan phi =("Reactive Impedance")/("Resistance")` `thereforephi =tan^-1 [("Reactive Impedance ")/("Resistance")]` `because " Impedance " Z=sqrt(R^2+(X_L-X_C)^2)` For resonance, `X_L=X_C therefore Z=sqrt(R^2)rArr Z=R` Hence, for the CONDITION of resonance, impedance is equal to resistance. Power factor : Power factor is defined as the ratio of true power to apparent power. it is denoted by `cos phi`. `therefore "Power factor"cos phi= (R)/(sqrt(R^2+(X_L-X_C)^2))` (i) Power factor is maximum when the circuit contains only R. (ii) Power factor is minimum for purely inductive or capacitive circuit. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- A wire is bent to form a semicircle of the radius a. The wire rotates about its one end with angular velocity omega . Axis of rotation is perpendicular to the plane of the semicircle . In the space , a uniform magnetic field of induction B exists along the aixs of rotation as shown in the figure . Then -
- A massless non conducting rod AB of length 2l is placed in uniform time varying magnetic field confined in a cylindrical region of radius (R gt l) as shown in the figure. The center of the rod coincides with the centre of the cylin- drical region. The rod can freely rotate in the plane of the Figure about an axis coinciding with the axis of the cylinder. Two particles, each of mass m and charge q are attached to the ends A and B of the rod. The time varying magnetic field in this cylindrical region is given by B = B_(0) [1-(t)/(2)] where B_(0) is a constant. The field is switched on at time t = 0. Consider B_(0) = 100T, l = 4 cm(q)/(m) = (4pi)/(100) C//kg. Calculate the time in which the rod will reach position CD shown in the figure for th first time. Will end A be at C or D at this instant ?
- A concave lens with equal radius of curvature both sides has a focal length of 12 cm. The refractive index of the lens is 1.5. How will the focal length of the lens change if it is immersed in the liquid of refractive index 1.8 ?
- If the tempearture of black body is raised by 5%, the heat energy radiated would increases by :
- What are the co-ordinates of the image of S formed by a plane mirror as shown in figure?
- The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ in Fig. The direction in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4. Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray?
- What is meant by polarisation ?
- Two concentric coils each of radius equal to 2πcm are placed right angles to each other. If 3 A and 4 A are the currents flowing through the two coils respectively. The magnetic induction( in Wb m^(-2) )at the center of the coils will be
- Assertion: Out of ""_(1)He^(3) and ""_(7)He^(3), the binding energy of ""_(1)He^(3)is greater than ""_(2)He^(8). Reason: Inside the nucleus of""_(1)H^(3), there is more repulsion than inside the nucleus of ""_(2)He^(4).
- In which accelerated motion, K.E of the particle is constant