Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
(a) When a bright silver object is placed in the solution of gold chloride, it acquires a golden tings but nothing happens when it is placed in solution of copper chloride. Explain this behaviour of silver. [Given :E_(Cu^(2+//)Cu)^(@)=+0.34 V, E_(Ag^(+//)Ag)^(@) =+0.80 V, E_(Au^(3+//)Au)^(@) =+1.40V](b) Consider the figure given above and answer the following questions : (i) What is the direction of flow of electrons? (ii) Which is anode and which is cathode?(iii) What will happen if the salt bridge is removed ? (iv) How will concentration of Zn^(2+) and Ag^(+) ions be affected when the cell functions ? (v) How willconcentration of these ions be affected when the cell becomes dead ? |
Answer» Solution :(a) When a bright silver object is placed in gold chloride  `E_("Cell")^(@) = E_("cathode")^(@) - E_("anode")^(@)` `E_("cell")^(@) = E_(Au3+//Au)^(@)-E_(Ag+//Ag)^(@)` = 1.40 - 0.80 = 0.60V `E_("cell")^(@) = + 0.60V` When silver is palced in copper chloride solution 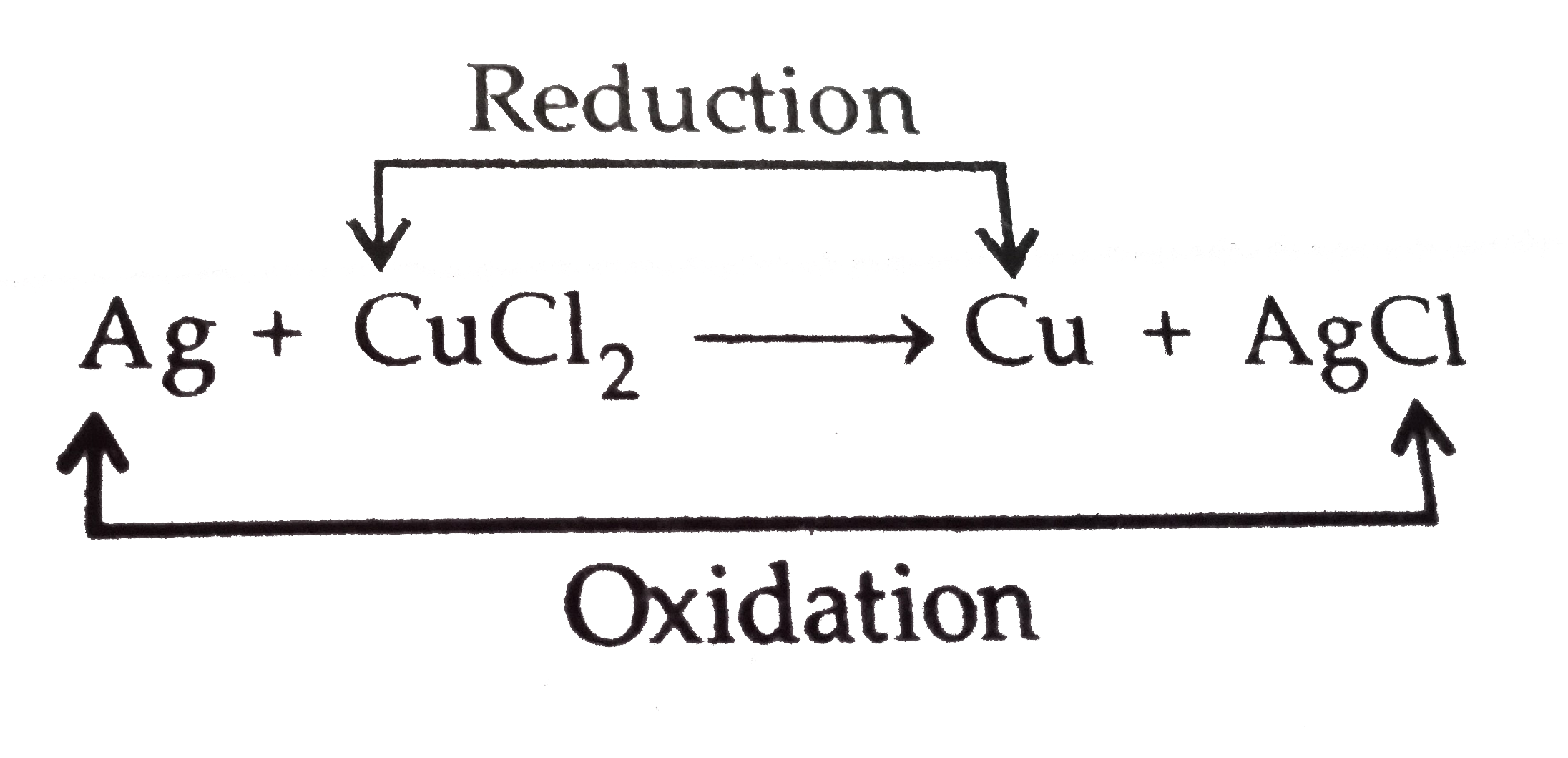 `E_("cell")^(@) = E_(C)^(@) - E_(A)^(@)` `=E_(Cu2+//Cu)^(@)-E_(Ag+//Ag)^(@) = 0.34 - 0.80` `E_("cell")^(@) = - 0.46V` As `E^(@)` cell is positive for gold chloride solution. Hence reaction is feasible and silver object acquires a GOLDEN tings but `E^(@)` cell is negative for copper chlrodie. Hence, nothing happens with it. (b) (i) Electrons flow from negative pole to positive pole (from left to right) i.e., from anode to cathode. (ii) The Zinc electrode at which oxidation takes place is anode and silver electrode WHERER reduction takes places is cathode. (iii) Circuit will not be completed, flow of electrons will stop and hence the current stops flowing. (iv) Concentration of `Zn^(2+)` decreases and `Ag^(+)` ions increases when the cell functions. (v) When E cell = 0, EQUILIBRIUM is reached and concentration of `Zn^(2+)` and `Ag^(+)` ions will not CHANGE. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?