Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Account for the following: (i) Aniline does not undergo Friedel -crafts reaction: ii. Diazonium slats of aromatic amines are more stable than those of aliphatic amines iii. pK_(b) of aniline is more tan that of methylamine iv. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is preferred for synthesising primary amines. v. Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is not vi. Amines are more basic than amides vii. Although amino group is o- and p- directing in aromatic electrophilic susbtitution reactions, aniline on nitration gives a susbstantial amount of m-nitroaniline. |
Answer» Solution :(i) Aniline does not undergo Friedel -Crafts reaction: 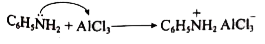 Due to presence of a positive charge on N-atom in the salt the group `overset(+)(N)H_(2)AlCl_(3)^(-)` ACTS as a strongly deactivating group. As a result, it reduces the electron density inteh benzene ring and which inhibits the electrophilic substitution reaction. Therefore, aniline does not under go Friedel-Crafts reaction. (ii) Diazonium salts of aromatic amines are more stable than those of aliphatic amines due to dispersal of the positive charge on the benzene ring as shown below: 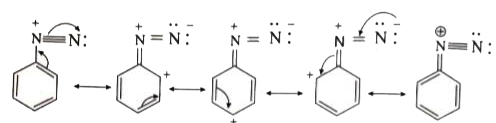 (iii) `pK_(b)` of aniline is more than that of methylamine: In aniline, the lone pair of electrons on the N-atom is decolized over the benzene ring. AS a result electron density on the nitrogen decreases. In contract in `CH_(3)NH_(2),+I` effect of `CH_(3)` increases the electron density on the N-atom. Therefore, aniline is a weaker base then methylamine and hence its `pK_(b)` value is more than that of methylamine. (iv) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is preferred for synthesising primary amines: Gabriel phthalimide reaction gives pure `1^(@)`- amine without any contamination of `2^(@)` and `3^(@)-` amines. Threfore it is preferred for synthesisting priamry amines. 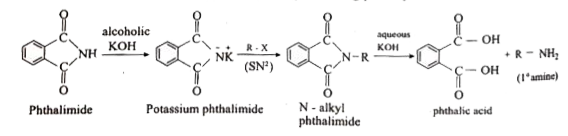 v. Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is not: Ethylamine when added to water forms intermolecular H-bonds with water. And therefore it is soluble in water. But aniline does not form H-bond with water to a very large extent due to the presence of a large hydrophobic `-C_(6)H_(5)` group. Hence, aniline is insoluble in water. 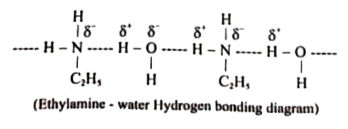 (vi). Amines are more basic than amides: In simple amines, the lone pair of electrons in on nitrogen and hence available for protonation. In amides on the other hand, the electron pair on nitrogen is delocalised to the carboxyl oxygen through resonance and thus, it is not available for protonation. so amines are more basic than amides. 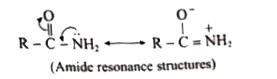 (vii) Although amino group is o- and p- directing in aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions, aniline on nitration gives a substantial amount of m- nitroaniline. Nitration is usually carried out with mixture of conc `HNO_(3)` and CON `H_(2)SO_(4)`.IN the presence of these ACIDS, most of aniline gets protonated to form anilium ion. Therefore, in the presence of acids, the reaction mixture consists of aniline and anilinium ion. Now `-NH_(2)` group in aniline is `O_(2)` P- directing and ACTIVATING while the `-NH_(3)` group is anilinium ion ismeta- directing and deactivating. Whereas nitration of anilien (due to steric hindrance at o- position) mainly gives p-nitroaniline, the nitration of anilinium ion gives m-nitro aniline. In actual practice, APPROXIMATELY a 1:1 mixture of P and m- nitroaniline is formed. 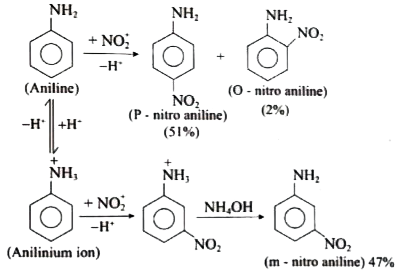
|
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?