Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Compound (A) on reaction with iodine in the solvent diglyme gives a hydride (B) and hydrogen gas. The product (B) is instantly hydrolysed by water or aqueous alkali forming compound ( C) and liberating hydrogen gas. The compound ( C) in aqueous solution behaves as a week mono basic acid. But in presence of certain organic polyhydroxy compound behaves as a strong monobasic acid. The hydride (B) in air catches fire spontaneously forming oxide which gives coloured beads with transition metal compounds. Which of the following statement is correct for the product (C)? |
|
Answer» It is an odd electron molecule. `B(OH)_(3)+H_(2)O to [B(OH)_(4)]^(-)+H^(+)` In the solid state, the `B(OH)_(3)` UNITS are hydrogen bonded TOGETHER in to two dimensional sheets with almost hexagonal SYMMETRY. The layered are quite a large distance apart `(3.18 A)` and thus the crystal breaks quite EASILY into very FINE particles. 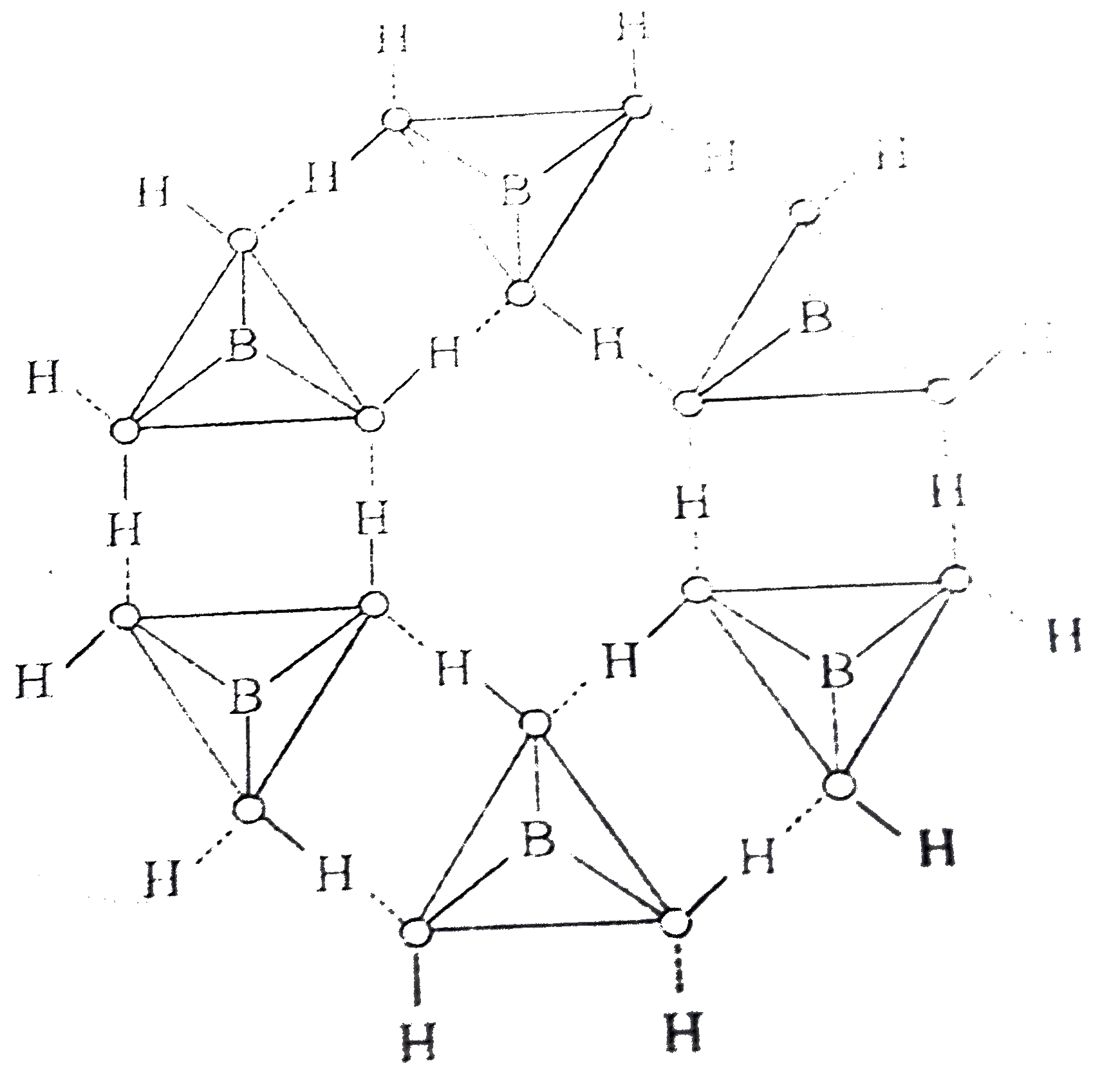 Reactions involved `(A)2Na[BH_(4)](A)+I_(2)underset("solution")overset("in diglyme")to B_(2)H_(6) , (B)+H_(2)+2NaI` `B_(2)H_(6)+6H_(2)Oto2H_(3)BO_(3)( C)+3H_(2)` `B(OH)_(3)+2H_(2)O hArrH_(3)O^(+) + [B(OH)_(4)]^(-) , pK=9.25` 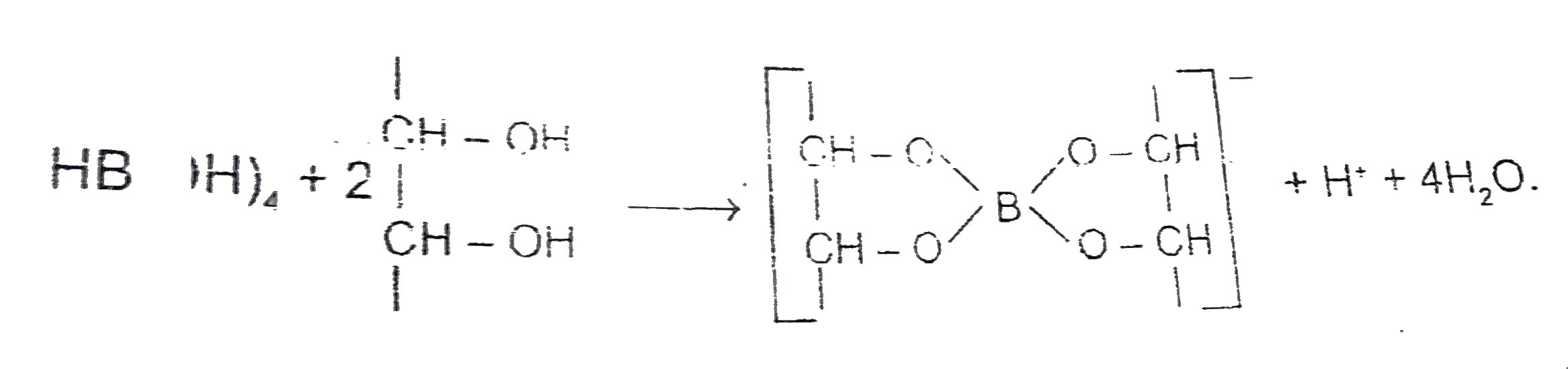 `B_(2)H_(6)(B)+3O_(2)toB_(2)O_(3)+3H_(2)O` `CoO + B_(2)O_(3)to Co(BO_(2))_(2)`(cobalt metaborate -blue colour bead). |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?