Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Considering the parameters such as bond dissociation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and hydration enthalpy, compare the oxidising power of F_(2) and Cl_(2). Oxidizing power is a combined effect of bond dissociation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and hydration enthalpy. |
Answer» Solution :Comparing `F_(2)` and `Cl_(2)` with the given parameters. 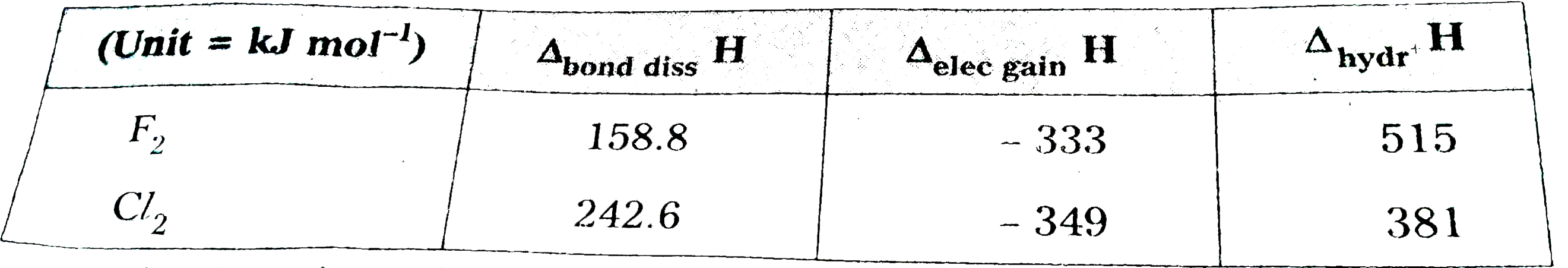 Form the data given above, it is clear that the BOND dissociation enthalpy and electron gain enthalpy are higher for CHLORINE but pydration energy is much higher for fluorine. It compensates the effect of other two and thus, makes flourine more oxidizing than chlorine. `(1)/(2)X_(2)(g)overset(1//2Delta_("diss")H^(0))toX(g)overset(Delta_("eg")H^(0))toX^(-)(g)overset(Delta_("hyd")H^(0))toX^(-)("aq")` The relative oxidizing power of the HALOGENS can be further illustrated by their reactions with water. `2"F"_(2)(g)+2" H"_(2)O(l)to4H^(+)("aq")+4F^(-)("aq")+O_(2)(g)""...(i)` `Cl_(2)(g)+H_(2)O(l)toHCl("aq")+HOCl("aq")""...(ii)` |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?