Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Define: : Explain, with energy profile díagram, the mechanísm of alkaline hydrolysis of methyl bromide or Bromomethane |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) Stereochemistry and Kinetics of the reaction (R.D.S.): This hydrolysis reaction takes place only in one step which is a rate DETERMINING step i.e. R.D.S. The rate of hydrolysis reaction depends on the concentration of `CH_(3)Br` and `OH^(-)` which are present in the R.D.S. of the reaction. Rate = R = `k [CH_(3)Br] xx [OH^(-)]` Where K is rateconstateof THEREACTION . `SN^(2)` reaction : Since the rate of the reaction depends on the concentrations of two substances it is bímolecular second order (2nd)Nucleophilic Substitution reaction denoted by `SN^(-2)`. (3) Mechanism of the reaction : It is a one step continuousprocess. The reaction takes place in the followingsteps: 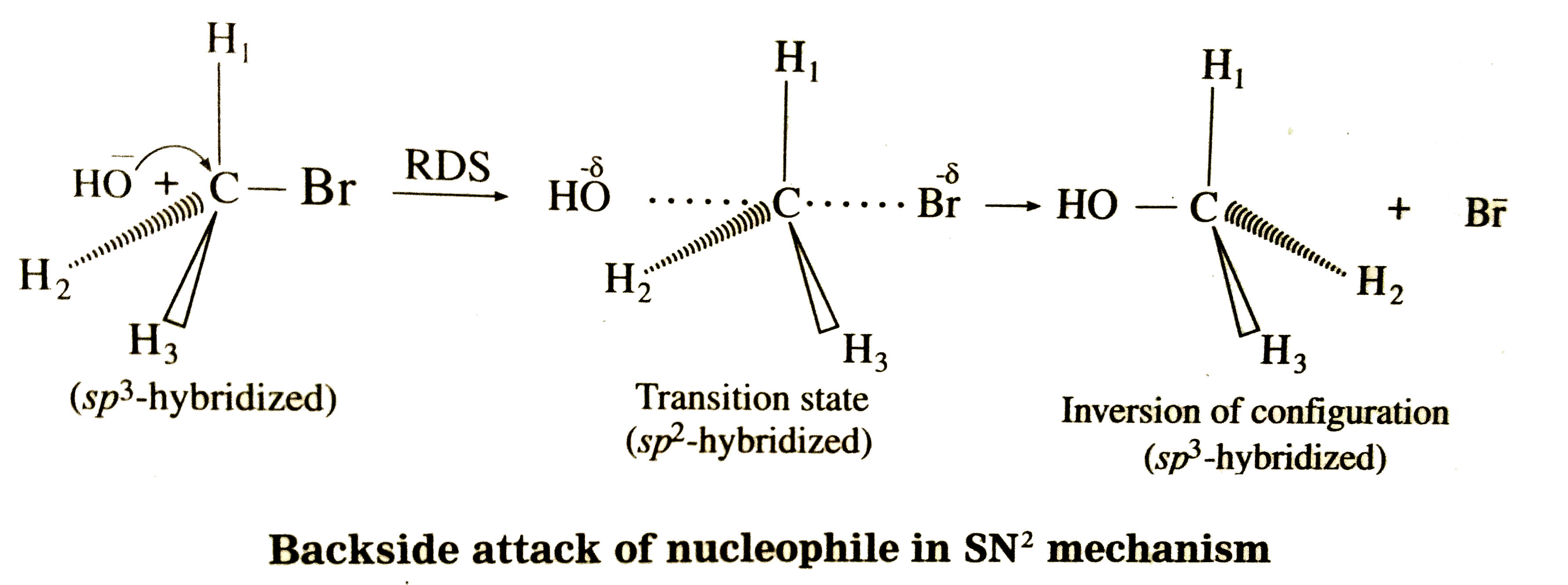 Backside attack of the nucleophile : Nucleophile `OH^(-)` attackscarbon atom of `CH_(3)Br`form back side i.e.,formoppositesideto Brto experienceminimum repulsion andrequiresminimun enegryfor theattack. Transition state : When a nucleophile, `OH^(-)` approaches carbon atoms of `CH_(3)Br`thepotentialenergy of the systemincreaseuntil a transition state (T.S.) of maximum potential energy is formed in which C- Br bond is partially broken and C- OH bond is partially formed. The negative charge is equally shared by both incoming nucleophile OH and outgoing, leaving GROUP `-Br^(-)` In `CH_(3)Br` , carbon atom is `sp^(3)` - hybridized and `CH_(3)Br` moleculeis tetrahedral. In the transition state the hybridisation of carbon atom changes to `sp^(2)` hybridisation and the T.S. complex molecule becomes planar i.e.,`H_(1),H_(2) and H_(3)`atoms lie in one plane while Br and OH lie collinear and on opposite SIDES perpendicular to the plane containing `H_(1)H_(2) and H_(3)`. Inversion of configuration : The transition state decomposes fast by the complete breaking of the C-Br bond and the new C-OH bond is formed on the other side. The breaking of C-Br bond and the ace simultaneously. The energy required to breakthe C-Brbondis partlyobtained formthe energyreleasedwhen C_OH bond is formed . Theformation of product `CH_(3)OH` is accompained by complete or 100% inversion of configuration forming again `sp^(3)`-hybridized carbon atom giving tetrahedral `CH_(3)OH` molecule. Butin this structurethe positions of `H_(2)`and `H_(3)`atomsin the reactant`(CH_(3)Br)`and inproductareonopposite side. This inversionof configurationis calledWalden inversion. Energy profile DIAGRAM : This is obtained by plotting potential energy of the species in the reaction verses reaction coordinate during the course of the reaction. 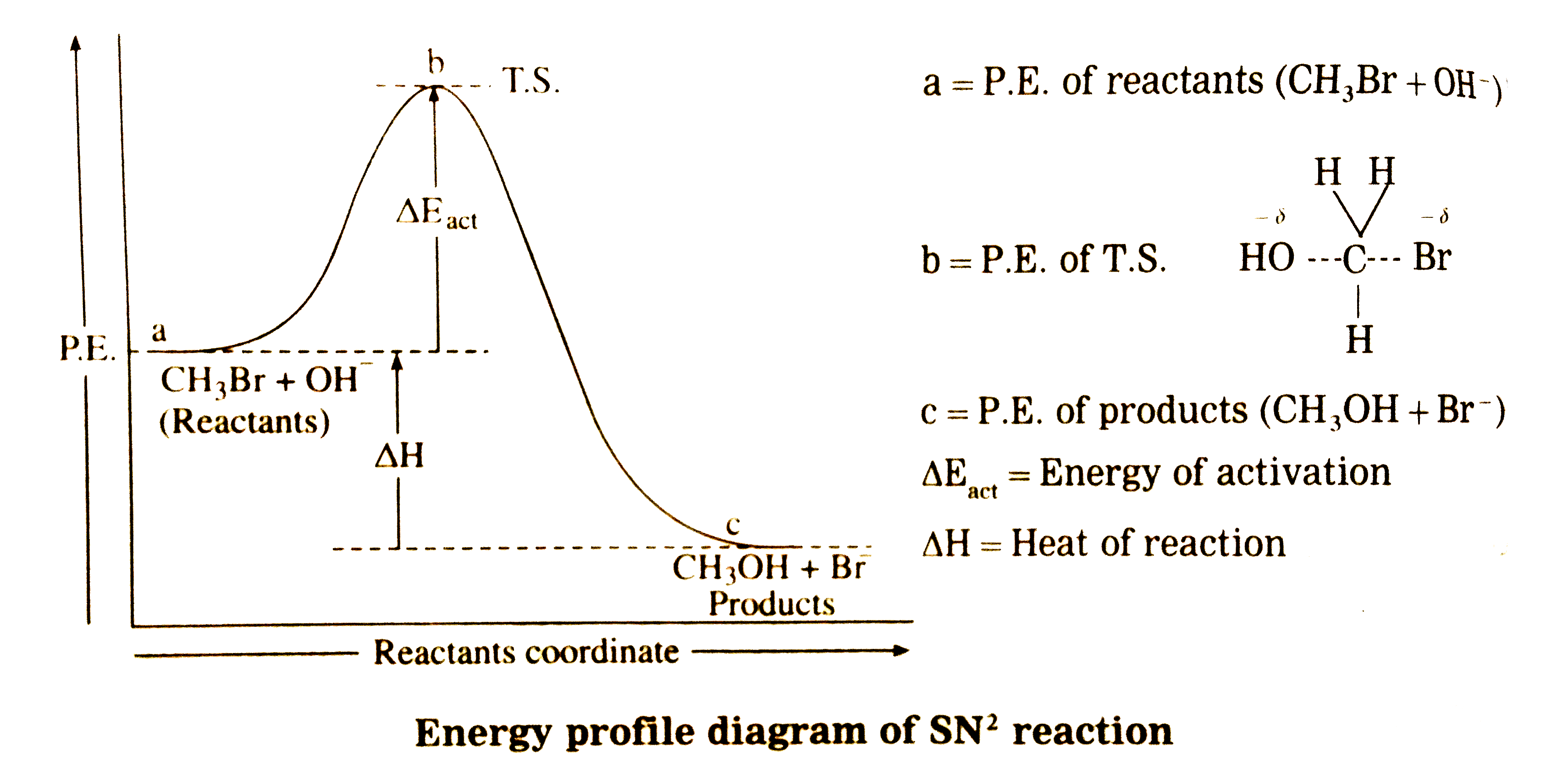
|
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?