Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Define the following: (a) Leaching (b) Methallurgy (c ) Anisotropy The boiling point of benzene is 353*23K. When 1.80 gram of non-volatile solute was dissolved in 90 gram of benzene, the boiling point is raised to 354.11 K. Calculate the moler mass of solute. [K_(b)for benzene =2.53K mol^(-1)] |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Leaching : It is a chemical method for the concentration of the ore. In this procfess the powdered ore is dissolved selectively in certain acids, BASES or other suitable reagents. The impurities remains undissolved as Sludge. The solution of ore is filtered and ore is recovered by precipitation or crystallisation. It is a process in which the ore is concentrated by chemical reaction with a suitable reagent which dissolves out the ore but not the impurities. For example, bauxite is leached with hot and concentrated solution of NaOH which `Al_(2)O_(3)` goes into solution forming solid sodium meta aluminate. `Al_(2)O_(3).2H_(2)O+2NaOHto underset("Soluble")(2NaAlO_(2))+3H_(2)O` The solution is then filtered to remove insoluble impurities like silca and otheroxides. The filtrate is diluted with WATER and seeded with small AMOUNT of freshly precipitated aluminium hydroxide as a result of which a white ppt. is formed. `NaAlO_(2)+2H_(2)Oto darrunderset("White ppt.")(Al(OH)_(3))+3H_(2)O` The ppt. is then separted, washed and ignited to get aluminium oxide in pure state. `2Al(OH)_(3)underset(Delta)tounderset("Pure alumina")(Al_(2)O_(3))+3H_(2)O` The process of leaching can also be applied in case of argentite and for certain ores containing gold. (b) Metallurgy : The entire scientific and technological process used for isolation of the metal from its ores is known as methllurgy. Types of metallurigical processes 1. Pyrometallurgy : In this process, extraction of metals takes place at very high temperature. Cu, Fe, Zn, Sn, etc., are extracted by this method. 2. Hydrometallurigical process : In this method, metals are extracted by this method. 3. Electro-metallurigical process : Electricity is used in this method for exteraction. ` Na, K, Li, Ca, etc.,` are exteracted from their MOLTEN salt solution through electrolytic method. The extraction and isolation of metals from ores involve the following major steps : Concentration of the ore, Converting ore into ore, Reduction Refining (Purification of the metal) (c ) Expression for maximum work : Consider an ideal gas confined in a cylinder with a frictionless piston. Suppose it expands reversibly from volume `V_(1)` to `V_(2)` at a constant temperature, the pressure of the gas is succssfully reduced from `p_(1)` to `P_(2).` 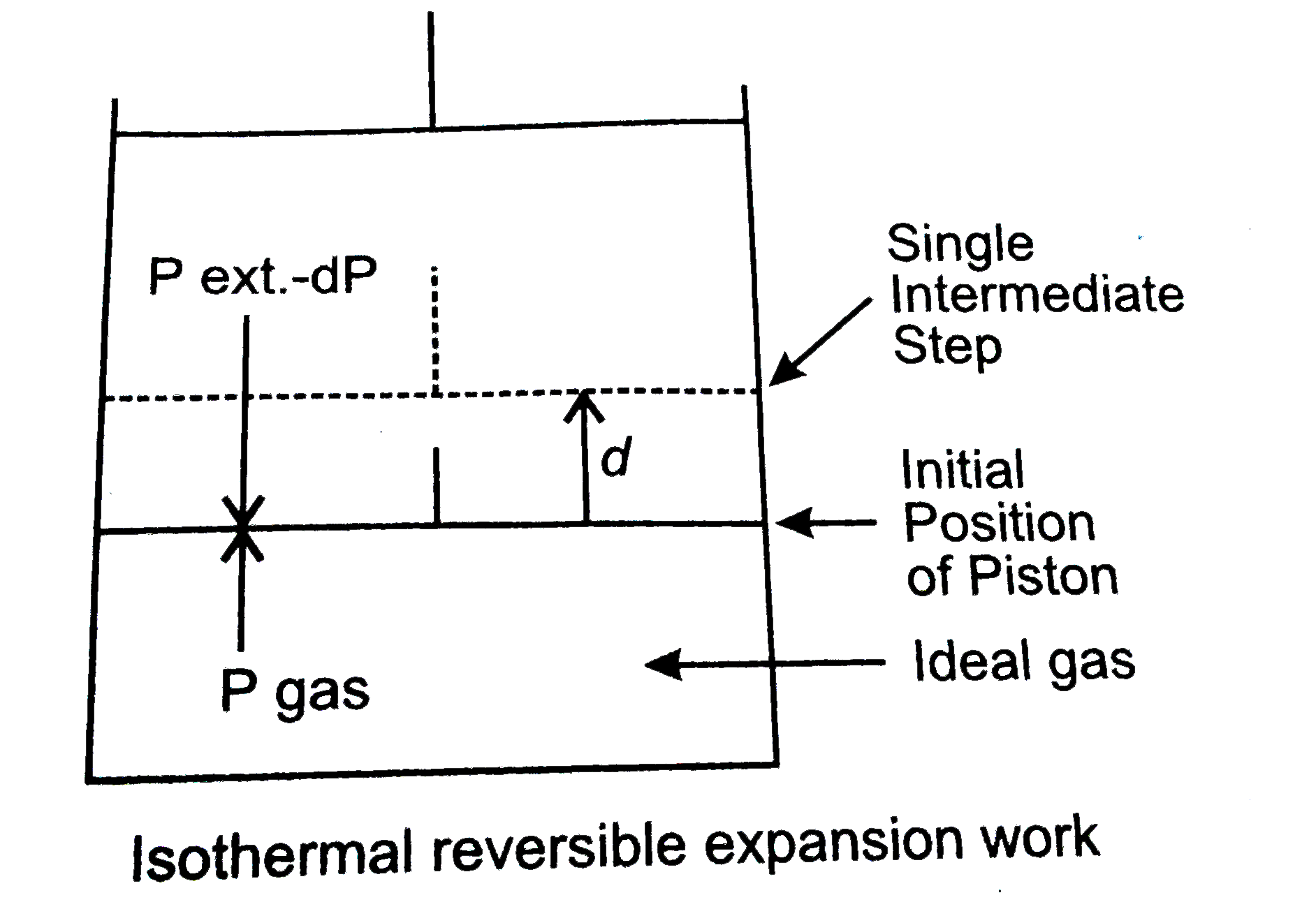 The work done by gas in one infinitesimal setp (dW), can be expressed as : `dW=PxxAdl` (A = cross-section area of piston)`PxxdV`where dV is the increase in volume. The total amount of work dony by the ideal gas from `V_(1)` to `V_(2)`is, therefore, `W=underset(V_(1))overset(V_(2))intP*dV` By the ideal gas equation, `P=(nRT)/(V)` `W=underset(V_(1))overset(V_(2))int(nRT)/(V)dV` `nRTunderset(V_(1))overset(V_(2))int(dV)/(V)` or `W_(max) =-2.303n RT log V_(2)//V_(1)` Weight of solute `=1.80` g Weight of solvent `=90`g `K_(b)` for benzene `=2.53K mol^(-1)` The elevation in the BOILING point `=354.11K-353.23K =0.88` K Substituting these values in expression we get `T_(b)=K_(b)M` `M=(1.80xx1000)/(x xx90)` `or 0.88=(2*53xx1*80xx1000)/(x xx90)` `x=(2*53xx1*80xx100)/(0.88xx90)` `x=57*5g mol^(-1)` Therefore, molar mass of the solute, `M_(2)=57*5g mol ^(-1).` |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?