Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Derive an expression for Ostwaid's dilution law. |
|
Answer» Solution :Ostwaid dilution law: It relates the dissocation constant of the WEAK ACID `(K_a)` with its degree of dissociation (a) and the concentration ( c). Considering a weak acid, the dissociation of ACETIC acid can be represented as `CH_3COOH LEFTRIGHTARROW CH_3COO^(-)+H^+` The dissociation constant of acetic acid is `K_a=([H^+][CH_3COO^-])/([CH_3COOH])` 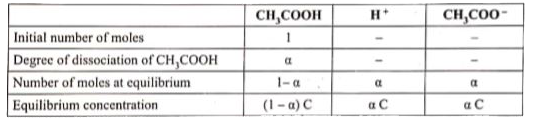 Substituting the equilibrium concentration in equation `K_a=((aC)(aC))/((1-a)C)impliesK_a=(a^2C^2)/((1-a)C)` `K_a=(a^2C)/((1-a))`.....(1) We know that weak acid dissociates only to a very small compared to one a is so small `therefore` equation (1) becomes `K_a=a^2C` `a^2=K_a/C implies a=sqrt(K_a/C)`....(2) Similarly for a weak base, `K_b=a^2C` `a=sqrt(K_b/C)` The concentration of `H^+` can be calculated using the `K_a` value as below `[H^+]=ac` `a=([H^+])/C` Substituting a value in equation (2) `([H^+])/C=sqrt(K_a/C)to[H^+]=sqrt(K_a/C).C` `[H^+]=sqrt((K_a.C^2)/C)implies[H^+]=sqrt(K_a.C)` For a weak base `[OH^-]=sqrt(K_b.C)` |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?