Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Describe the construction and workingof lead accumulator(lead storage cell). |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(A) Principle : (1) The lead accumulator is a secondaryelectrochemicalcell and it is also called lead accumulatoror lead storage battery. (2) It is a reversible cell. (B) Construction : In a lead accumulator, the negativeterminal(anode) is made up ofleadsheets packed withspongylead,while thepositive terminal (cathode) is made up oflead grids packedwith `PbO_(2)` . Sulphuricacid of about `38%` strength`(% w//w)`or specificgravity1.28 or 4.963molar is the electrolytein which the leadsheetsand lead gridsare dipped.The positiveterminal and negativeterminalare alternativelyarrangedin the electrolyteand are separatelyinterconnected . 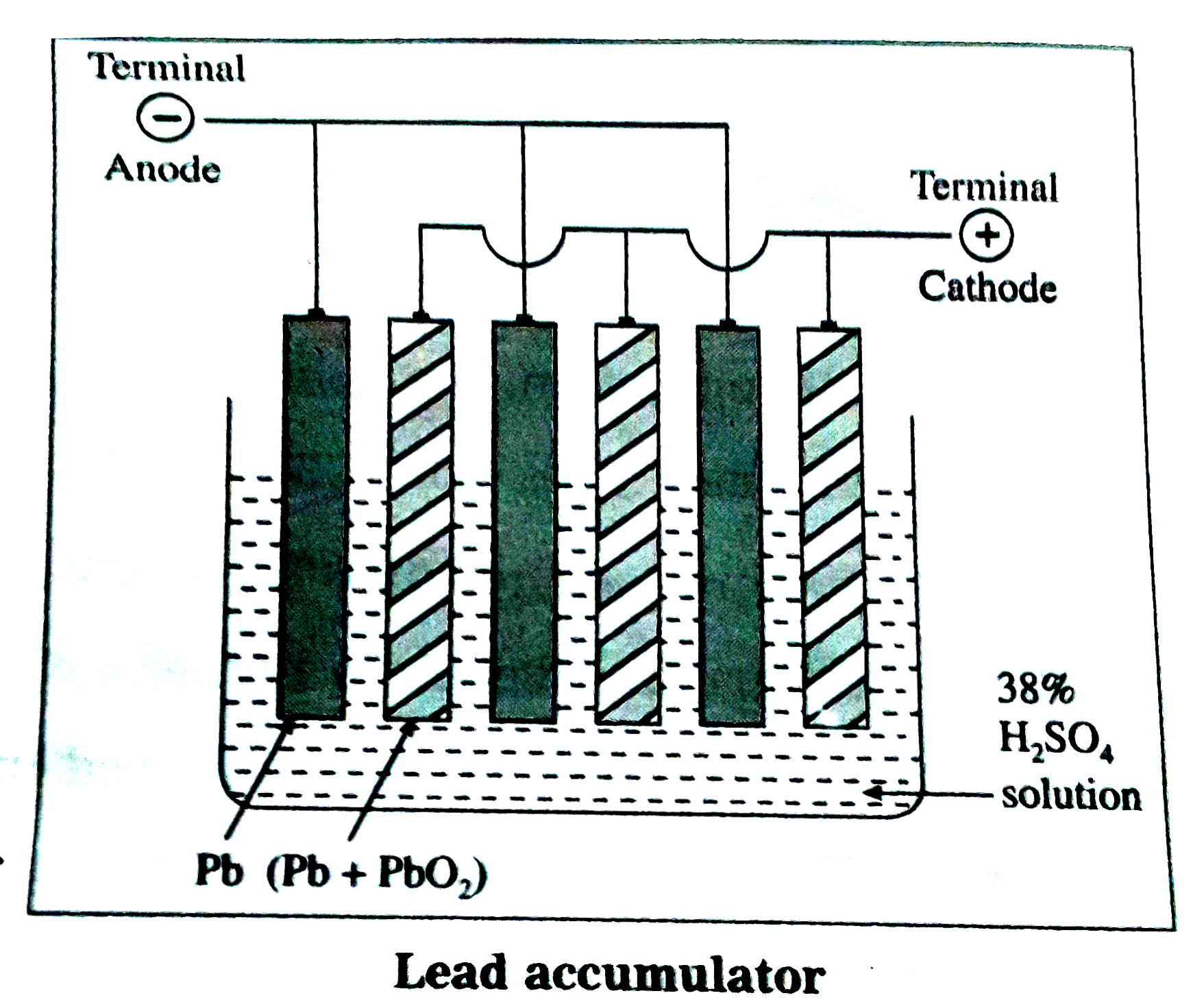 (C ) Representation of leadaccumulator : `underset(("Anode"))(-Pb_((s)))|PbSO_(4(s))|underset(38%)(H_(2)SO_(4(aq)))| PbSO_(4(s))|underset(("Cathode"))(PbO_(2(s)))|Pb^(+)` (D) Workingof a lead accumulator : (1) Discharging: When the electriccurrent is withdrawnfrom lead accumulator,the followingreactionstake place : Oxidationat the -ve electrodeor anode : `({:(Pb_((s))rarrPb_((aq))^(2+)+2e^(-),("oxidation")),(Pb_((aq))^(2+) +SO_(4(aq))^(2-)rarr PbSO_(4(s)),("precipitation")):})/(Pb_((s))+SO_(4(aq))^(2-)rarrPbSO_(4(s))+2e^(-)("overall oxidationat anode"))` Reduction at the +ve electrode or cathode : `({:(PbO_(2(s))+4H_((aq))^(+)+2e^(-)rarrPb_((aq))^(2+)+2H_(2)O_((l)),("reduction")),(Pb_((aq))^(2+)+SO_(4(aq))^(2-) rarr PbSO_(4(s)),("precipitation")):})/(PbO_(2(s))+4H_((aq))^(+)+SO_(4_(aq))^(2-)+2e^(-) rarrPbSO_(4(s))+2H_(2)O_((l))("overall oxidationat anode"))` (2) Net cell reaction : (i) Thus, the overall cell reactionduringdischargingis `Pb_((s)) + PbO_(2(s)) + 4H_((aq))^(+) 2SO_(4(aq))^(2-) rarr 2PbSO_(4(s)) + 2H_(2)O_((l))`OR `Pb_((s)) + PbO_(2(s))+ 2H_(2)SO_(4(aq))rarr2PbSO_(4(s)) + 2H_(2)O_((l))` During theoperation, the concentrationof `H_(2)SO_(4)` decreasesand specificgravitydecreasesfrom 1.28to 1.17. (ii) Rechargingof the cell : The dischargedbatteryis connectedto external electricsource anda higherexternalpotentialis appliedacrossits ELECTRODES and currentis passedin reversedirection. As a resultthe cell reactiongets reversedgenerating`H_(2)SO_(4)`. Reductionat the -ve electrodeor cathode : `PbSO_(4(s)) + 2e^(-) rarr Pb_((s)) + SO_(4(aq))^(2-)` Oxidationat the+ve electrodeor anode : - `PbSO_(4(s)) + 2H_(2)O_((l)) rarr PbO_(2(s)) + 4H_((aq))^(+) + SO_(4(aq))^(2-) + 2e^(-)` The netreactionduring chargingis `2PbSO_(4(s)) + 2H_(2)O_((l)) rarr Pb_((s)) + PbO_(2(s)) + 4H_((aq))^(+) + 2SO_(4(aq))^(-) ` OR `2PbSO_(4(s)) + 2H_(2)O rarrPb_((s))+PbO_(2(s)) + 2H_(2)SO_(4(aq))` (E) Applications : (1) It is USED a sourceof d.c. electricsupply. (2) It is usedin automobilein ignition circuitsand lightingthe head lightsby connecting6 batteriesgiving 12 V potential . (3) It isalsoused in invertors. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?