Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Describe the principle involved in each of the following processes of metallurgy : (i) Froth floatation method (ii) Electrolytic refining of metals (iii) Zone refining of metals |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Forth floatation method : The method has been in use for removing gangue from sulphide ores. In this process, a SUSPENSION of thepowdered ore is made with water. To it , collectors and froth stabilisers are added. Collectors (e.g., pine oils, fatty acids, xanthates, etc.) enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles and froth stabilisers (e.g., Cresols,aniline) stabilise the froth. Themineral particles become wet by oils while the gangue particles bywater. A rotatingpaddle agitates themixture and draws air in it . As a RESULT, froth is formed which carries the mineral particles. The froth is light and is skimmed off. It is them dried for recovery of the ore particles. (ii) Electrolytic refining of metals: In this method, theimpure metal is made to act anode. A STRIP of thesame metal in pure form is used as Cathode. They are put in a suitable electrolyte both containing soluble salt of the same metal. The morebasic metal remains in the solution and the less basic ones go to the anode mud. Thereactions are Anode : ` M to M^(n+) +" ne"^(-)` Cathode : ` M^(n+) + "ne"^(-) to M` Copper and zinc are REFINED by this method. (iii) Zone refining of metals : This method is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in themelt than in thesolid state of the metal. A circular mobile heater is fixed at one end of therod of the IMPURE metal. The molten zonemoves along withthe heater which is moved forward. As theheater moves forward,the pure metal crystalises out of meltand theimpurities pass on into the adjacent molten zone. This process is repeated several times and the heater is moved in the same direction.At one end, impurities concentrated. 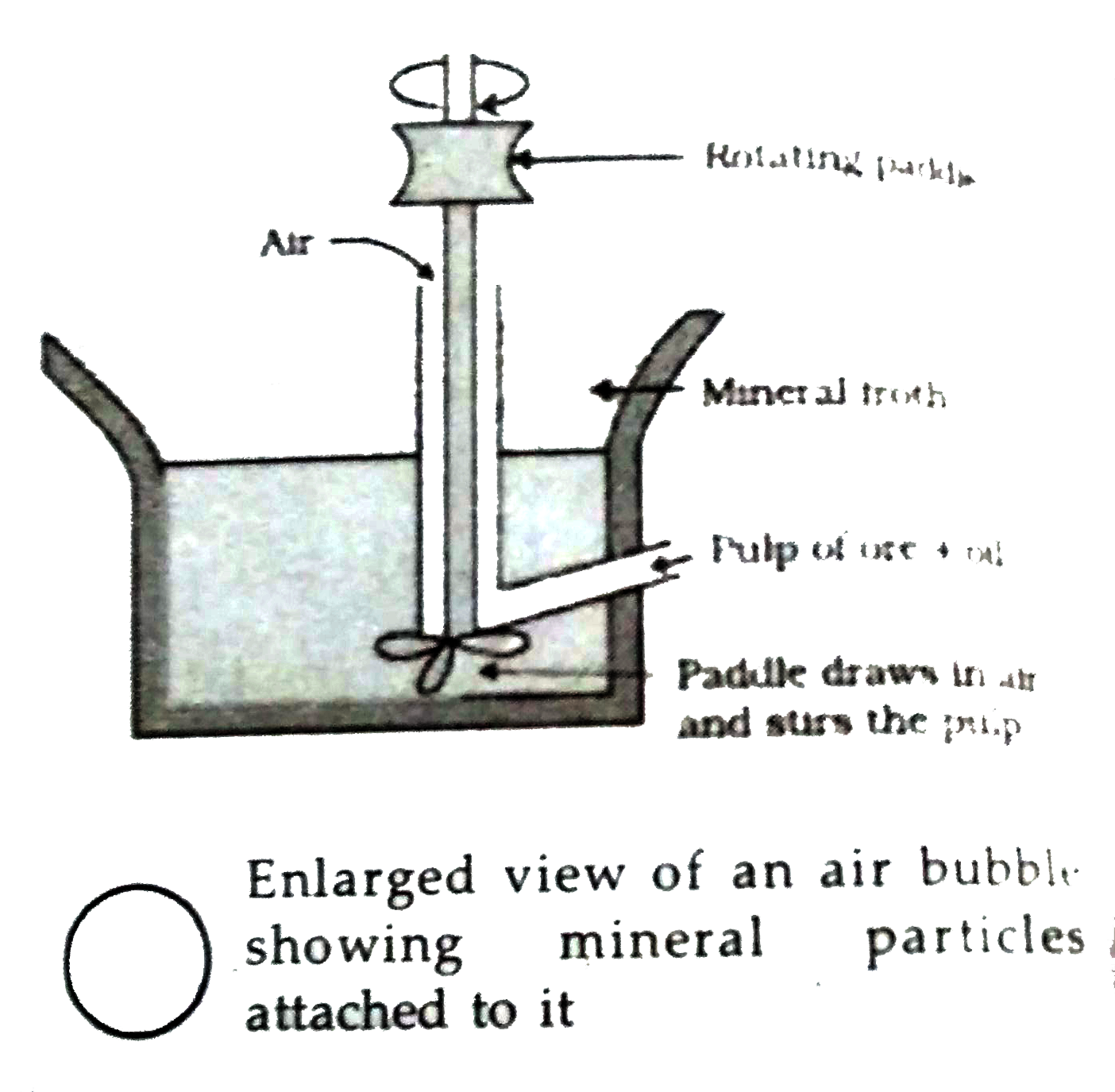 This method is very useful for producingsemiconductor and other metals of very high purity likegermanium, silicon, boron etc. 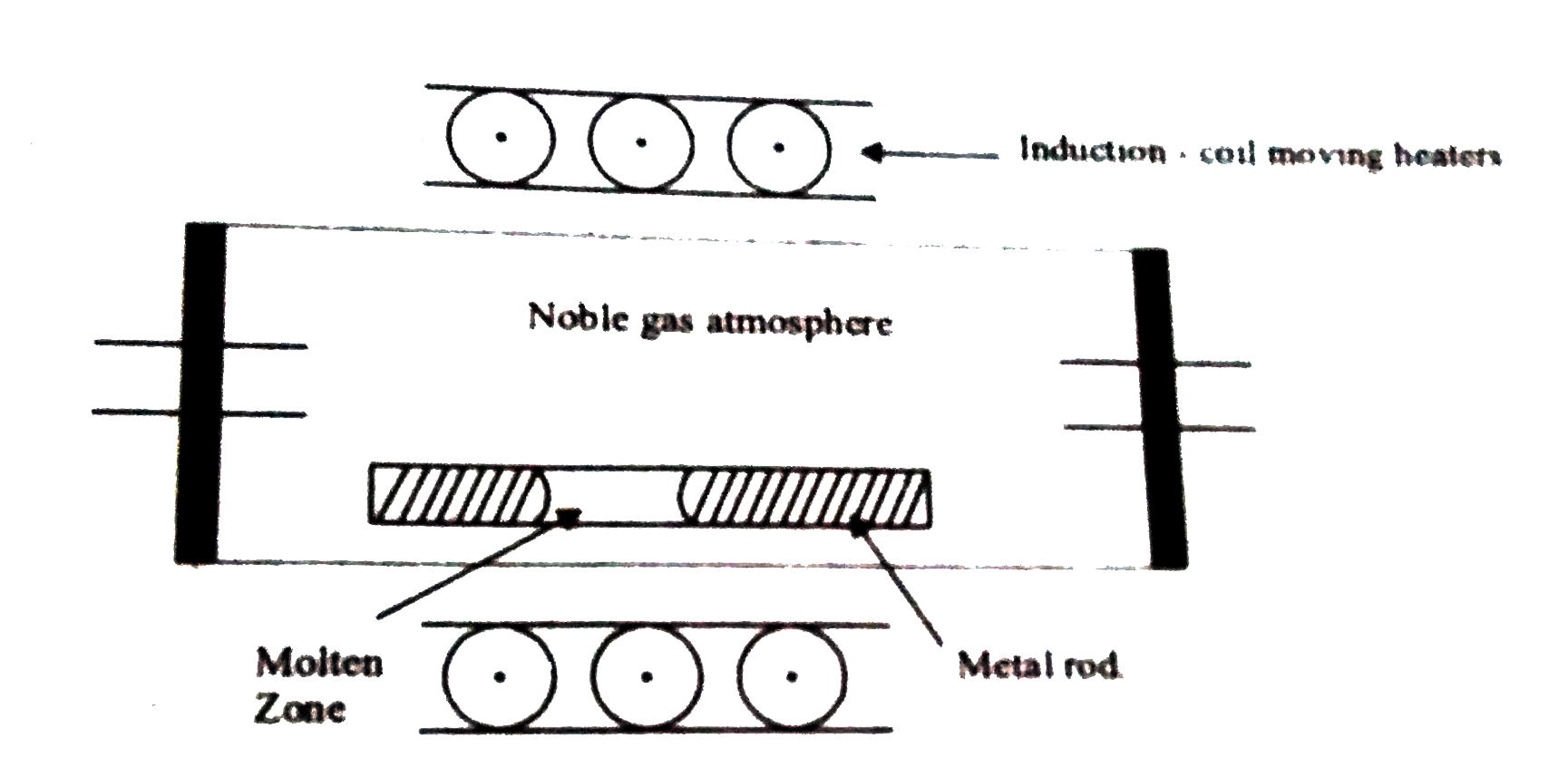
|
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?