Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Explain isomerism in Haloalkanes. |
|
Answer» Solution :Haloalkanes show three types of isomerism : (i) Chain isomerism (ii) Position isomerism (iii) Optical isomerism (i) Chain isomerism : When two or more haloalkanes with same molecular FORMULA differ in the size of chain of carbon atoms, they are SAID to chain isomers of each other. `UNDERSET("1-chlorobutane")(CH_(3)-CH_(2)-CH_(2)-CH_(2)-Cl) "" underset("1-chloro-2-methylpropane")(CH_(3)-overset(CH_(3)" ")overset("|")("CH")-CH_(2)-Cl)` (ii) Position isomerism : When two or more haloalkanes with same molecular formula differ in the position of halogen atoms ATTACHED to different carbon atams of the chain, they are said to be position isomers of each other. `underset("1-Chloropropane")(CH_(3)-CH_(2)-CH_(2)-Cl)""underset("2 - Chloropropane")(CH_(3)-overset("Cl ")overset("|")("CH")-CH_(3))` (iii) Optical isomerism : The haloalkanes with same molecular formula and structural formula when differs in the spatial arrangement of atoms or group of atoms rotates the plane polarised light are called optical isomers. 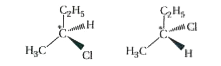
|
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?