Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Explain the extraction of iron from haematite. |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :Haematite ore `Fe_(2)O_(3)`, contains silica `(SiO_(2))`, alumina `(Al_(2)O_(3))` and phosphates as impurity or gangue. Coke is used for the reduction of ore.To remove acidic gangue `(SiO_(2))` a basic flux CaO is used which is obtained from time stone `CaCO_(3)`. (1) Roasting: Theconcentratedore is heatedstronglyin a limited currentof air,duringwhichmoistureis removedand the impurities areoxidised. `S + O_(2) overset(Delta) to SO_(2) uarr, 2As +3O_(2) to As_(0)O_(3) uarr` `P_(4) + 5O_(2) to2P_(2)O_(5) uarr`. FeO presentin the ore isoxidised to `Fe_(2)O_(3)`. `4FeO + O_(2) to 2Fe_(2)O_(3)` (2) Reduction (or smelting) : The roasted or calcined ore is then reduced by heating in a blast furnace. 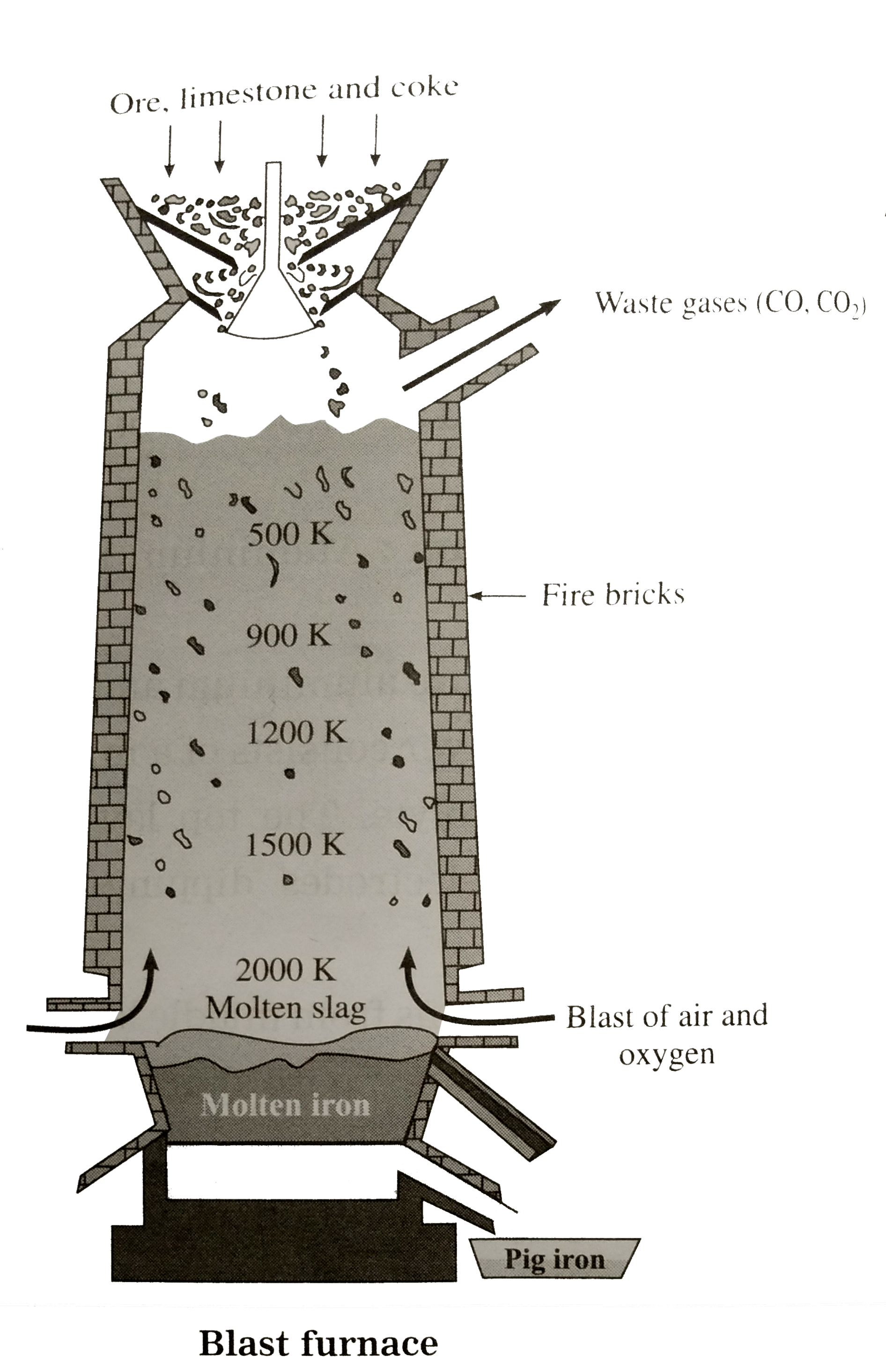 Blast furnace has three parts (i) the hearth, (ii) the bosh and (iii) the stack. The roasted ore in mixedwith cokeandlimestone in theapproximate ratio of 12 : 5: 3. A blast of hot air at about 1000 K is blown from downwards to upwards by layers arrangement. There are three zones of temperature in which three main chemical reactions take place. (i) Zone of combustion : The hot air blown from the bottom of the furnace oxidises coke to CO which is an exothermic reaction, due to which the temperature of the furnace RISES. `C+""^((1)/(2))O_(2) to CO DeltaH = - 220KJ` The hot GASES with CO rise up in the furnace and heat the chare coming down. CO acts as a fuel as well as a reducing agent. (ii) Zone of reduction : At about 900K, CO reduces `Fe_(2)O_(3)` to spongy (orporopus) iron. `Fe_(2)O_(3) + 3CO to2Fe + 3CO_(2)` Carbon alsoreduces partially `Fe_(2)O_(3)` to Fe. `Fe_(2)O_(3) +3C to2Fe + 3CO` Zone of slag formation : At 1200 K limestone, `CaCO_(3)`in the charge, decomposes and forms a basic flux CaO which further reacts at1500K withgangue`(SiO_(2),Al_(2)O_(3))`and forms a slag of `CaSiO_(3)` and `Ca_(3)AlO_(3)` whichis removedfrom thebottom. (iv) Zone of fusion : Theimpuritiesin ore like`MnO_(2)`and `Ca_(3)(PO_(4))`arereducedto Mnand Pwhile`SiO_(2)` is reduced to Si. Thespongy ironmovingdownin thefurancemeltsin thefusionzone and dissolvedtheimpurities like C, Si, Mn, phosphorus and sulphure. The molten iron collects at the bottom of furnace. The lighter slag floats on the molten iron and prevents its oxidation. The molten iron is removed and cooled in moulds. It is called pig iron or cast iron. It contains about 4% carbon. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?