Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Explain the following : (a) Carbon tetrachloride is used as fire extinguisher. (b) Use of chloroform as anaesthetic is decreasing. (C)Chloroform is kept with a little ethyl alcohol in a dark brown coloured bottle. (d) Iodoform gives precipitate with AgNO_(3) on heatingwhile chloroform does not. (E) Alkyl iodides become darken on standing in presence of light. (f) A small amount of Nal or KI catalyses the hydrolysis of R-CI or the reaction, R-CI +R' ONa to R-O-R' + NaCI (g) while preparing alkyl halides from alkanes ,dry gaseous hydrohalgen acids are used instead of their aqueous solutions. (h) Hydrogen atom of chloroform is definitely acidic in nature. (i) Vinyl halide is less reactive while allyl halide is more reactive than alkyl halides. or Vinyl chloride does not gives S_(N) reaction but allyl chloride gives. (j) Why is free radical halogenation of alkanes is seldom used for laboratory preparation of alkyl halides ? Underwhat condition good yields of monosubstituted chloride can be obtained ? (K) What effect shouldthe following resonance of vinyl chloride have on its dipole moment? H_(2)C-overset(delta^(+))(CH)-overset(delta^(-))(CI) hArr H_(2)overset(delta^(-))(C)-CH=overset(delta^(+))(CI) (I) 2-Chloro-3-methylbutane on treatment with alcoholic potash gives2- methylbut-2-ene as themajorproduct. (m) Compare the rates of (i) S_(N^(1)) " and (iii) S_(N^(2)) reactions ofallyl chloride and n-propyl chloride. (N)When CH_(3) CH = CHCH_(2)CI reacts with alcoholic potassium cyanide, a mixture of isomeric product is obtained. (O) the formation of the products giving the structures of the intermediates. (q) Arrange C_(6)H_(5)CH_(2)CH_(2)CI, ""C_(6)H_(5)CHCICH_(3)"and"C_(6)H_(5)CH=CHCI in the order of their decreasing activitieswithalcoholic silver nitrate. (r) Arrange CH_(3)CH_(2)Br,C_(6)H_(5) " and "C_(6)H_(5)CH_(2) Br in order of their decreasing activities with KCN. (s) Chlorobenzene is less reactive as compared to ethyl chloride. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) the dense vapours form a protectivelayer on the burning objects and prevent the oxygen or air to come in contact with the burning objects. (b) Due to side effects , as it causes liver damage, etc, it is rarely used as anaesthetic these days. (c) when exposed to sunlight and air . chloroform slowly decomposes into phosgene and hydrogen chloride. Phosgene is extremely poisonous gas. As to prevent thedecomposition it is stored in dark brown coloured BOTTLE and 1% ETHYL alcohol is added. This retards the decomposition and converts phosgene into harmless ethyl carbonate. `CHCI_(3) +[O] to COCI_(2) + HCI,` `COCI_(2) + 2C_(2) H_(2)OH to (C_(2)H_(5)) CO_(3) +2HCI]` (d) C-I bond being less stable than C-CI bond and thus undergoes fission on heating giving `I^(-)` ions which combine with `Ag^(+)` ions to form a yellow ppt. (e) Alkyl iodides are less stable and lose free iodine . this iodine makes the remaining iodide darken. (f) NaI or KI reactswith R-CI to form R-I. the alkyl iodide is comparatively more reactive than alkyl chloride it undergoes hydrolysis readily or reacts with R' ONa to form ether. `R-I +HOH to R-OH +HI` `R-I +R' ONa to R -O -R'+NaI` (g) DRY hydrohalogen acids are stronger acids and better electrophiles than `H_(3)O` formed in the aqueous solutions. Furthermore, `H_(2)O` is a nucleophile and can easily react with R-X toformalcohol. (h) Chlorine is more electronegative than carbon. Due to three chlorine atoms the carbon acquires partial positive charge on account of -I effect . The carbon atom thus attracts the electron pair of C-H bond towardsitself MAKING the hydrogen atom removal as proton easier 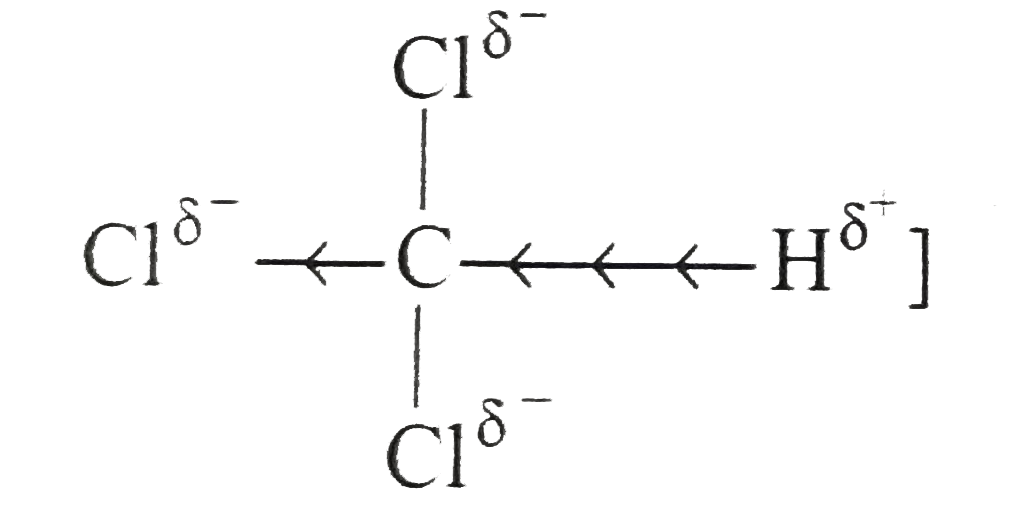 (i) in vinyl chloride C-CI bond is stable due to resonance (as in chloro benzene)  Hence CI atom cannot be repleaced .Further `sp^(2)` -hybridized carbon is more acidic than `sp^(3)-`carbon . In allyl chloride `S_(N)` reaction is easier allkyl carbonium ion formed after removal of `CI^(-)` is stabilized by resonance. `H_(2) C=CH -CH_(2)CI to CI^(-) +H_(2)C=CH-overset(**)(CH_(2))` `harr H_(2)overset(***)(C)-CH=CH_(2)` (j) Serveral isomeric monosubstituted halides are formed because alkanes have different types of hydrogenatoms Their separation is difficult. thus free radical halogenation method is not used unless the parent hydrocarbon possesses equivalenthydrogen atoms. Good yields are obtained in hydrocarbons such as `CH_(3)-CH_(3) (CH_(3))_(4)C,` cyclopropane etc, (k) The dipole moment increase because the distance between positiveand negative partial charges increases . (L) elimination occurs in accordance to Saytzeff's rule i.e., elimination of hydrogen from the carbon which is attached with least number of hydrogen atoms. 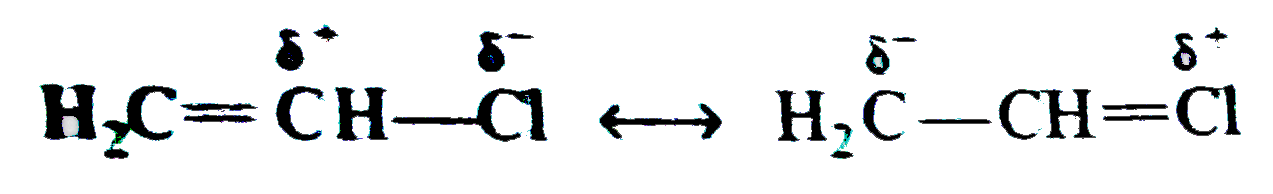 (m) (i) Allyl chloride is much more reactive than n-propy. chloride and the + charge of its intermediate `R^(+)` is stabilized by resonance `(H_(2)C =CH -overset(**)(CH_(2)) harr H_(2)overset(**)(C)=CH-CH_(2))` (ii) Allyl chloride is again more reactive but not to the extent of `S_(N^(1))` reaction and stabilized the transition state. (n)It can undergo `S_(N^(1)) " and " S_(N^(2))` reactions. By `S_(N^(2))` reaction only one product (A) is formed. `underset("1-Chlorobut")(CH_(3)CH =CHCH_(2)CI) +CN^(-) overset(("Slow"))underset(S_(N^(2)))to CH_(3)CH=CH-underset(CN)underset(vdots)(CH_(2)) ......CI` `overset(("Fast"))(to)CH_(3)CH=underset((A))(C)HCH_(2)CN` By `S_(N^(1))` reaction the intermediate is carbocation (resonance stabilized ) and can give a mixture of two isomeric products (A) and (B). `CH_(3)CH =CHCH_(2) CI overset(("Slow"))underset(S_(N^(1)))(to)` 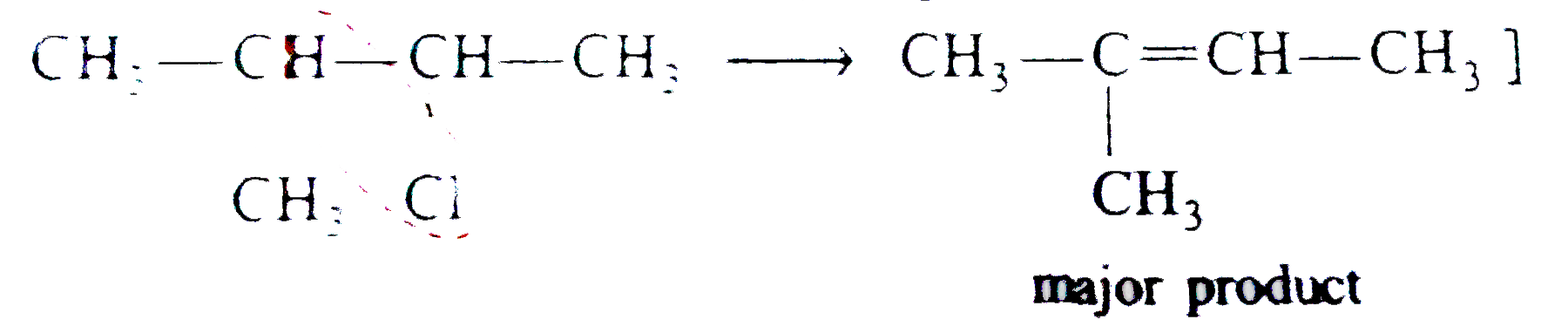 (O) 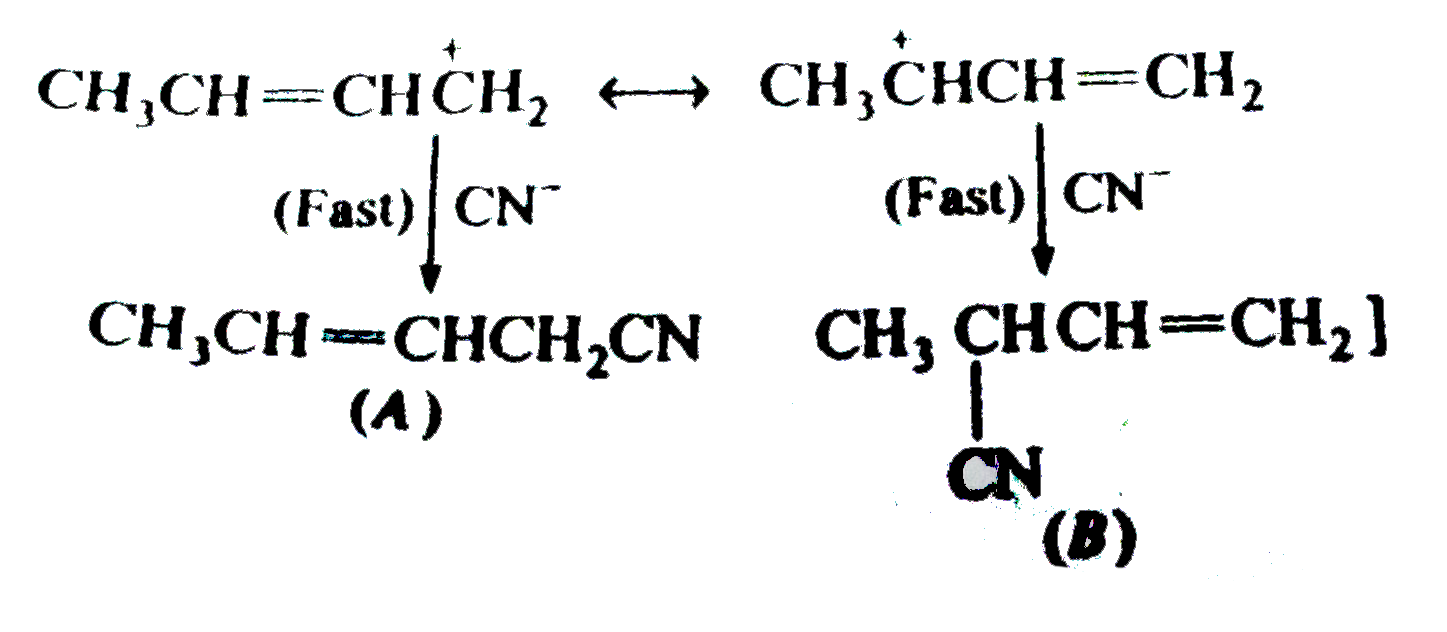 In this reaction the majorproduct (4-chlorobut-1-ene) is formed by `S_(N^(2))` mechanism. Now thesecond product is formed by the initial formation of carbocation and attacked by the double bond on the +ve carbonatom to form a second (cyclic) carbocation which eventually gives the product. 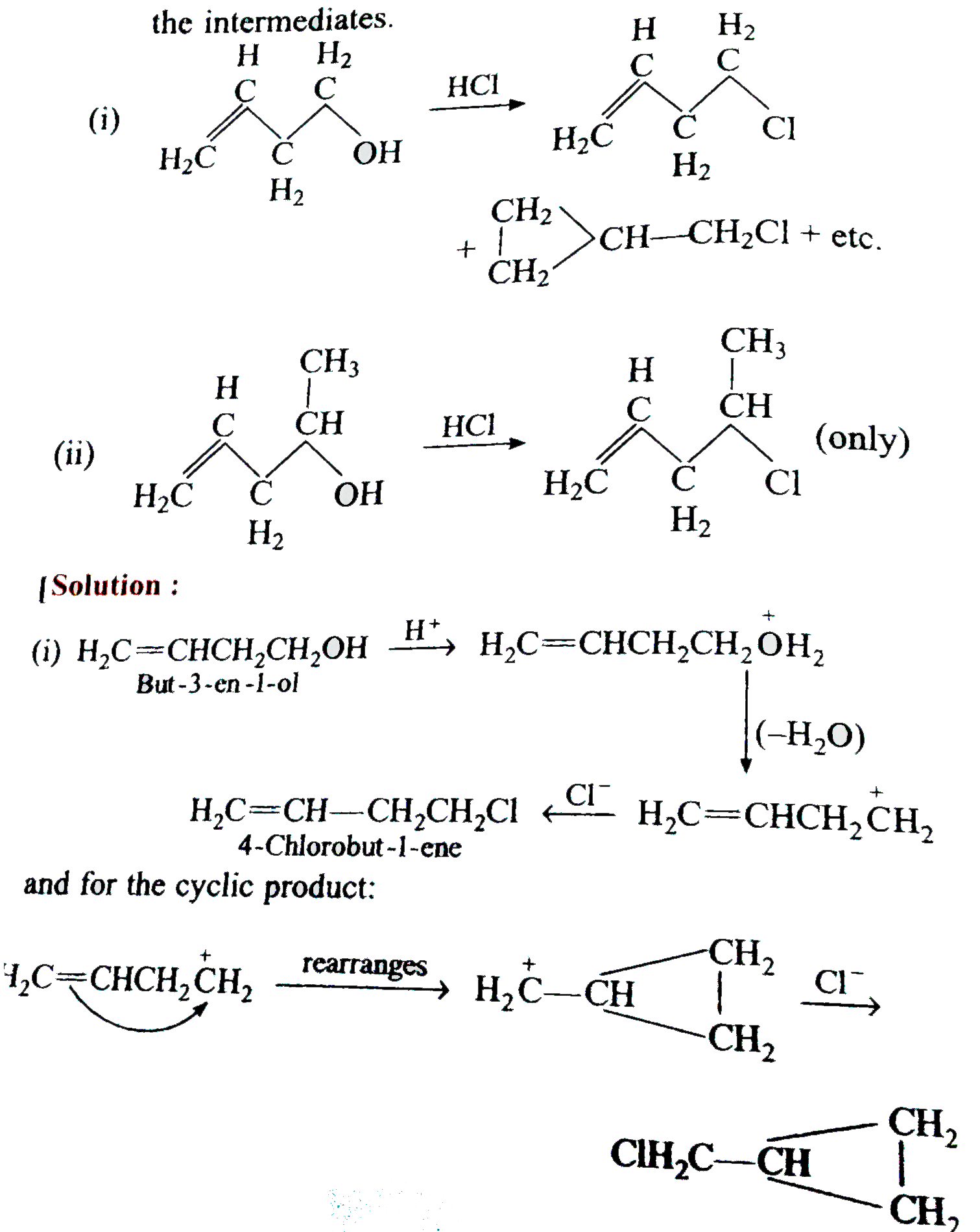 In this reaction the +I effect of `CH_(3) -` group avoids cyclisation . (p) (i)  because in EQUATION (ii) C-CI bond is stable due to resonance hence nucleophilic attack is not preferred. (q) `C_(6)H_(5)CHCICH_(3) gt C_(6)H_(5)CH_(2)CH_(2)CI gt C_(6)H_(5)CH=CHCI` (r) `C_(6)H_(5)CH_(2)Br gt CH_(3)CH_(2)Br gt C_(6)H_(5)Br` (s) The low reactivity of chlorobenzene is due to partial double bondcharacter of C-CI bond i.e., it is shorter and stronger bond in comparison to C-CI bond in ethyl chloride. 
|
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?