Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Explain the structure of DNA and RNA . |
|
Answer» Solution :Structure of DNA : To understand the structure of DNA , we should known the charagaff's rule , which states that : 1. Base composition on DNA for a particular organism is constant throughout all the somatic cells 2. Base composition ALWAYS varies from one organism to another and is expressed by the dissymmetry ratio , `(A+T)/(G+C)` 3. Organisms closely related to ech other often have similar base composition and hence have closed values for their dissymmetry ratio. 4. In a given organism the amount of adenine is always equal to the amount of thymine (A=T) and amount of guanine is equal to amount of cytosine (G=C). 5. In a given organism the total amount of purine bases are always equal to total numberof pyrimidine bases (i.e.,) (A+G=T+C). M. wilkins found that within the crystal there is a repeat distance of 3.4 NM and there are ten subunits per turn. watson - Crick model for DNA : From the above observations watson and crick constructed a model for DNA. This model consists of two right handed polynucleotide chains that are complimentary and coiled about the same axis to form DOUBLE - helix .Some specific base pairs can be spatially accommodated and these are A-T and G-C pairs. The bases are closely associated with each other by hydrogen bonding. The helix has diameter of about 2.0 nm and contains 10 nucleotide pairs in each turn of helix as shown above: 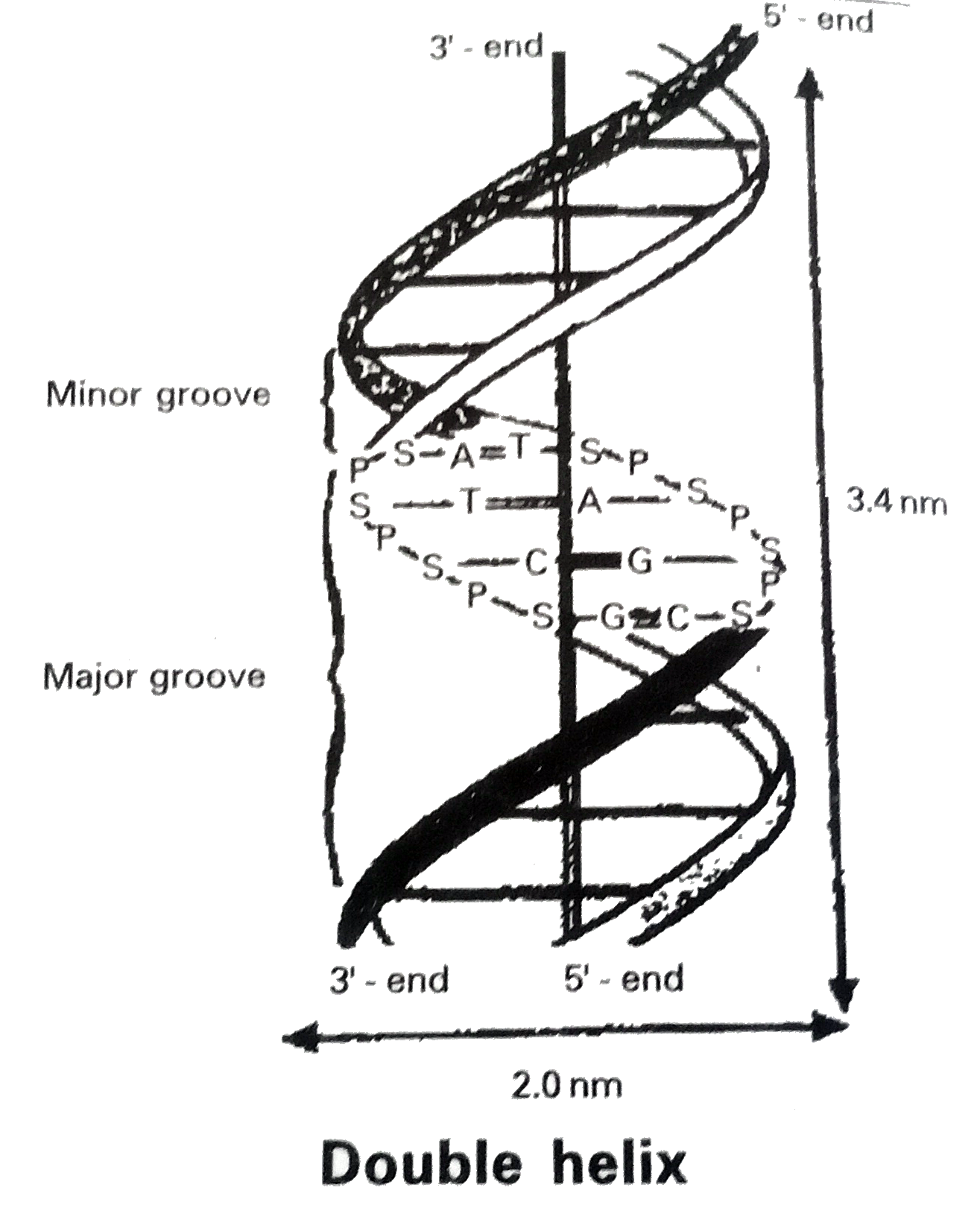 Structure of RNA : The native RNA is single stranded rather than a double stranded helical structure CHARACTERISTICS of DNA. However , given the complementary base sequence with opposite polarity , the single of RNA may fold back on itself like a hairpin and thus acquire double stranded pattern. In the region of hairpin loops, "A" pairs with U and G pairs with C.The base pairing inRNA hairpins is frequency imperfect. The proportion of helical regions in various type of RNA varies over a wide range . 
|
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?