Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Explain , themechanismof alkalinehydrolysis (reactionwithaqueous KOH)of tert-butyl bromide (2-Bromo-2- methyl - propane ) with energyprofile diagram. |
Answer» Solution : (i) Consider alkaline hydrolysis of tert-butyl bromide (2-Bromo-2- methylpropane) with aqueous NaOH or KOH <BR> 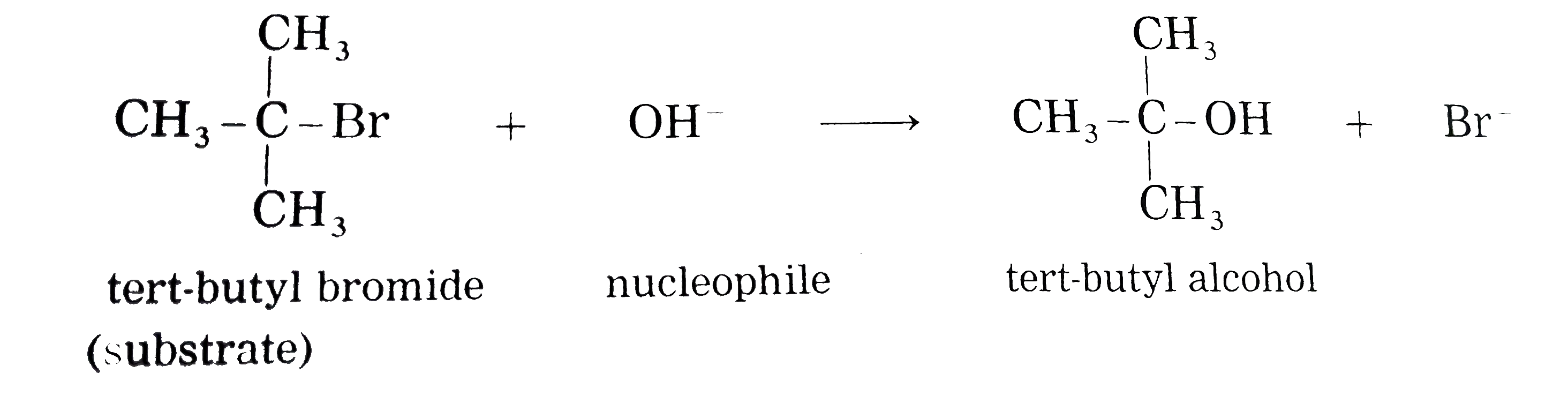 (ii) Kineticof thereaction: Due to steric hindranceof volumethree methly grouparoundcarbon , nucleophile`OH^(-)`cannotattack carbon atom directly. Hence, the reaction TAKES place in towsteps. Step I : Thisinvolves heterolytic fission of C- Br covalent bond in the substrate forming carbonium ion or carbocation and `Br^(-)` Thie process is a slow process. 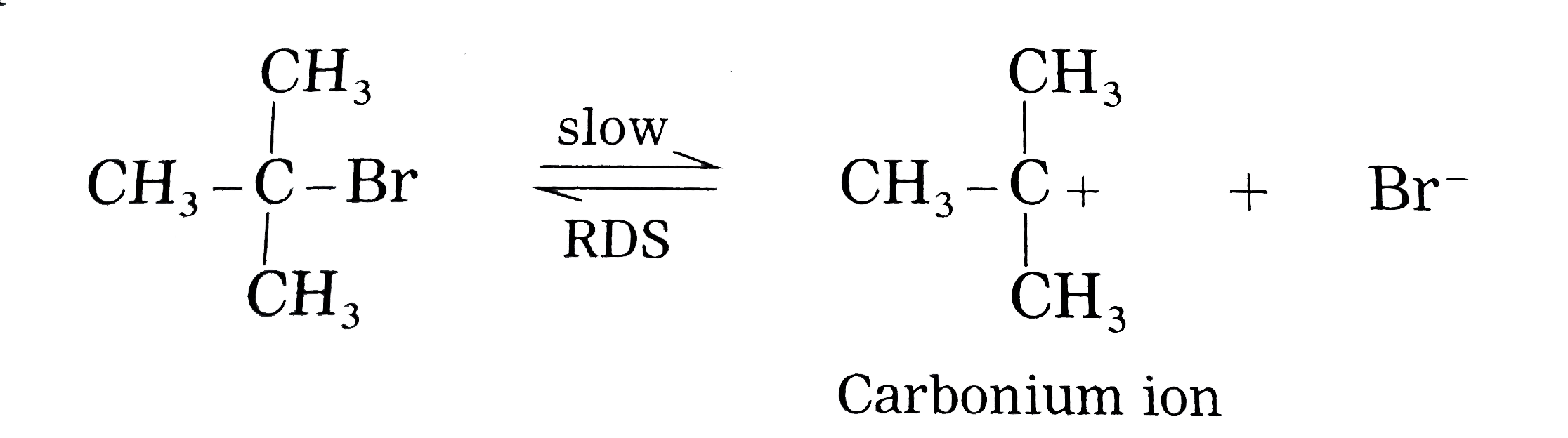 StepII : This step involves attack of nucleophile `OH^(-)` or carbocation forming C- OH bondand product tert - butylalchohol. Sinceit involvesionicchargeneutralisation it isa fast step. 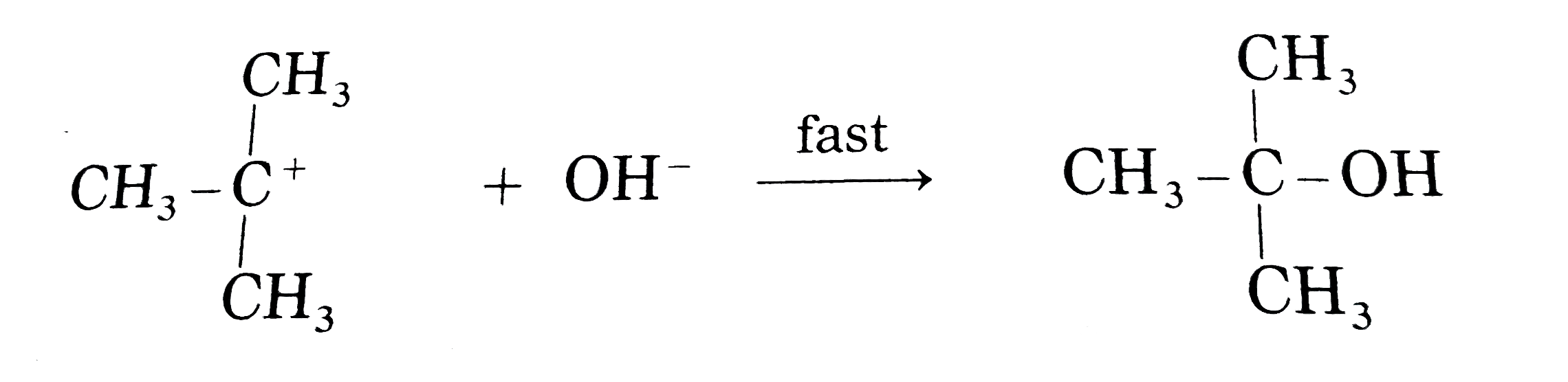 Rate Determining Step (R.D.S.) : Since the first step is a slow step, it is R.D.S., and therefore the rate of the reaction depends on the concentration of only one reactant, `(CH(3))_(3)C- Br`. Rate = R = `k [(CH_(3))_(3)C - Br]` where k isa rate constant of thereaction `SN^(-1)`reaction : The rate of this reaction depends only on theconcentration of one substance (tert-butyl bromide) and is independent of concentration of alkali added. This is first (1st) order Nucleophilie Substitution reaction denoted as `SN^(1)` reaction. STEREOCHEMISTRY and mechanisim of thereaction: The reaction takes placein two steps and both the steps involveformation of transition state (T.S.). 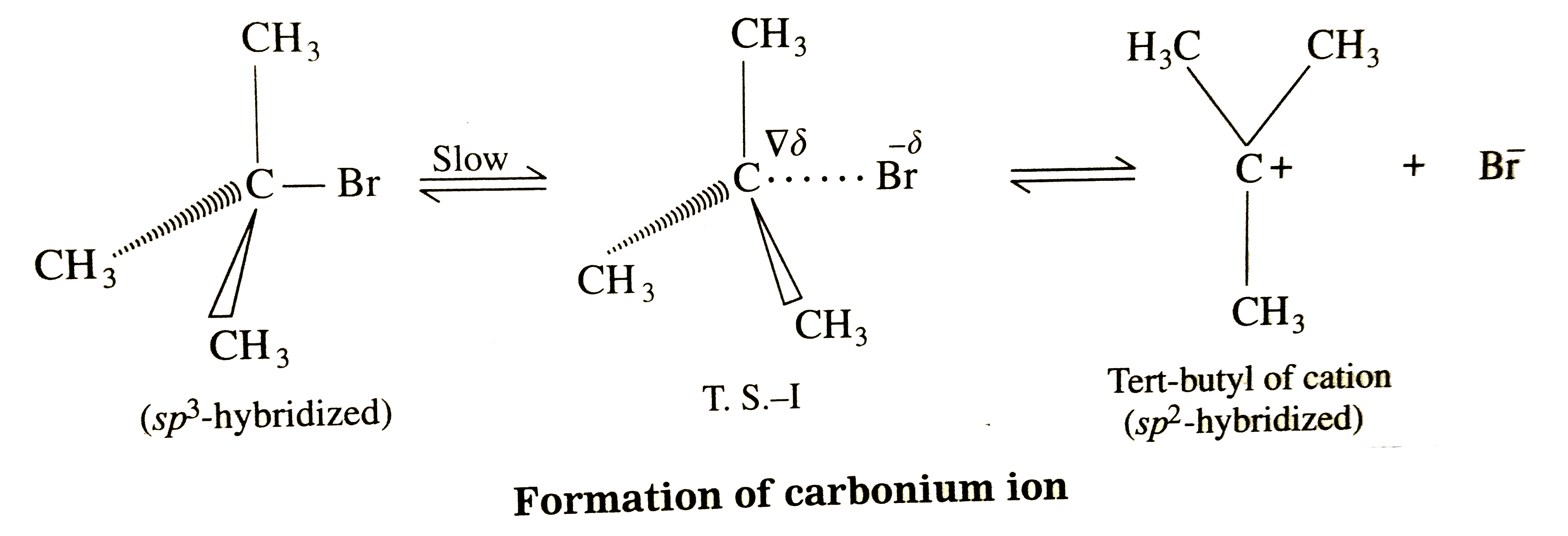 In this transition state, C -Br bondis partiallyboken, So thatcarbonatom carries partial positive`(+delta)`and Brcarries partial negative charge`(-delta)` whichfurther breaks formingcarbocationand `Br^(-)`. Tert-butyl cation has a planar structure and the `CH_(3),-C-CH_(3)` bondangleis `120^(@)` . It isthe intermediateof the rection . ITIS unstable . In thisstep,hybridisation of carbon atom charngesform `sp^(3)`(tetrahedral geometry ) to `sp^(2)`(planner geometry). 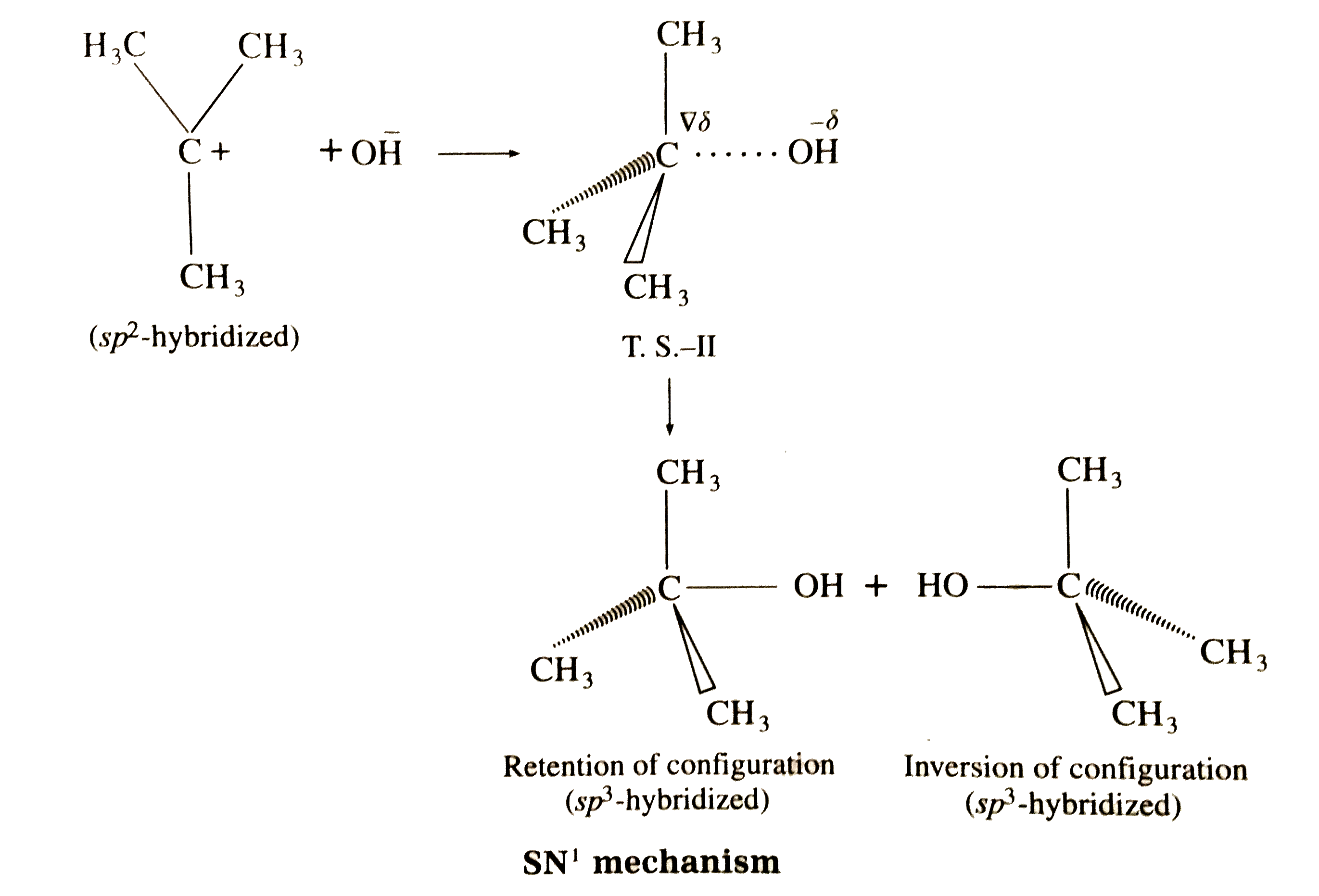 In thistransitationstate , C-OH bond ispartiallyformed so thatcarbonatomcarries partial positivecharge `(+delta)` and OH carriespartialnegativecharge `(-delta)`which furtherforms tert-butyl alchohol. Formationof a racemicmixture :Since `OH^(-)`hasequalprobability of the attack on carbocation from frontside and from backside, the products obtained are equal. In case of optical activealkyl halide, a racemic mixture is obtained. Energyprofil digram: In thediagram both thetransition state, T.S.-I and T.S.-II are shown. 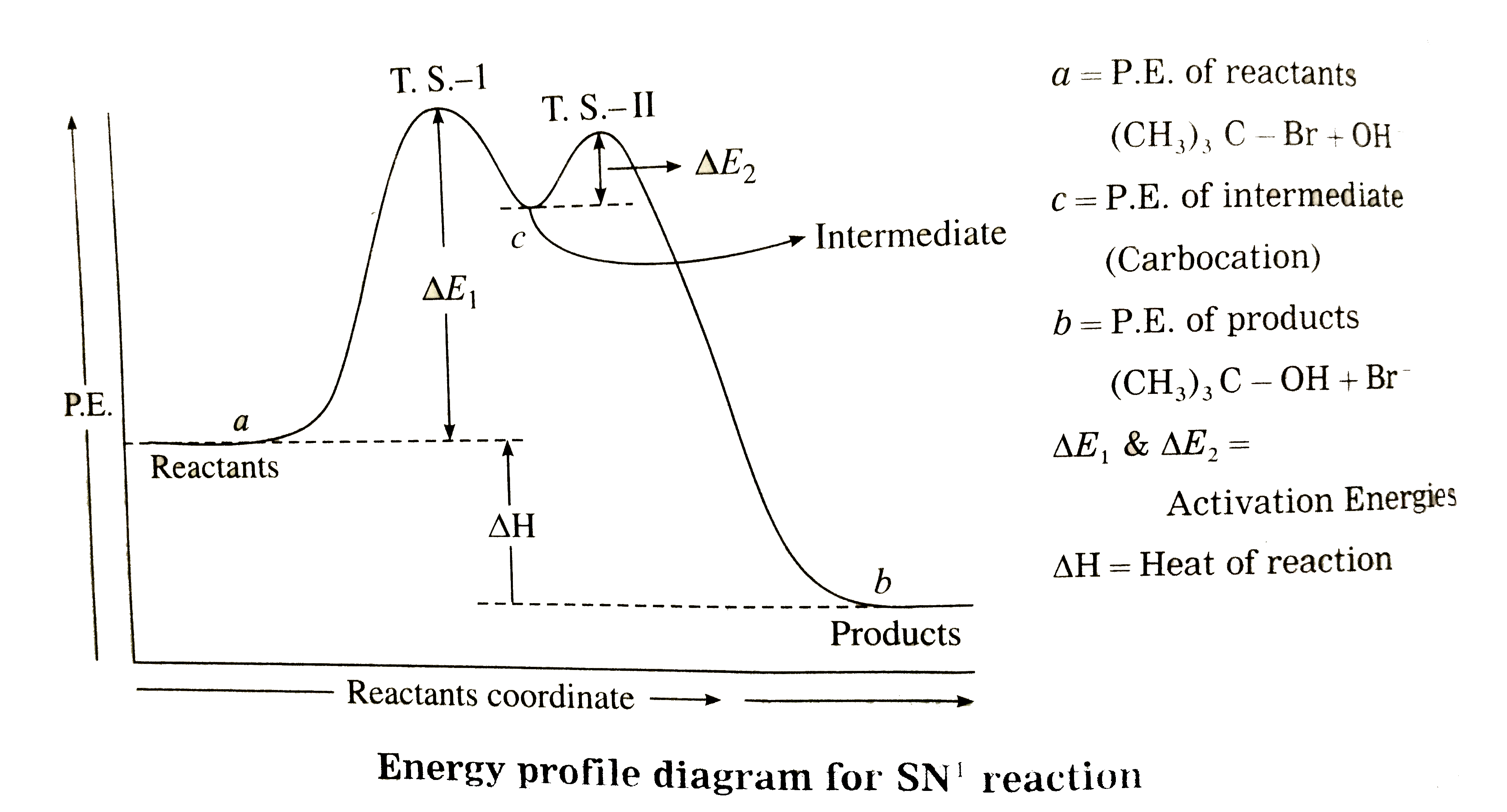 Energyof activationis `SN^(-1)` : The first step requires higher acti-vationenergy AE,. Second step requires lower activation energy `DeltaE_(2)` Heat of reaction `(DeltaH)`: Itis theenergydifferencebetweenproductsand reactants. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?