Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Explain Werner's theory of coordination compounds with suitable examples. |
|
Answer» Solution :Werner's theory : Werner's theory : POSTULATES : 1) EVERY complex compound has a central metal atom (or) ion. 2) The central metal shows two TYPES of valencies NAMELY primary valency and secondary valency. A) Primary valency : The primary valency is numerically equal to the oxidation state of the metal. Species or groups bound by primary valencies undergo complete ionization.These valencies are identical with ionic bonds and are non-directional. These valencies are represented by discontinuous lines (.....) Eg : `CoCl_(3)` contains `Co^(3+) and 3Cl^(-)` ions. There are three Primary Valencies or three ionic bonds. B) Secondary Valency: Each metal has a characteristic number of Secondary Valencies. They are DIRECTED in space around the central metal. The number of Secondary Valencies is called Coordination numbe (C.N .) of the metal. These valencies are directional in Nature. For example in `CoCl_(3). 6NH_(3)` Three `Cl^(-)` ions are held by primary Valencies and `6NH_(3)` molecules are held by Secondary Valencies. In `CuSO_(4).4NH_(3)" complex "SO_(4)^(2-)` ion is held by two Primary Valencies and `4NH_(3)` molecules are held by Secondary Valencies. 3) Some negative ligands, depending upon the complex, may satisfy both primary and secondary valencies. Such ligands, in a complex, which satisfy both primary as well as secondary valencies do not ionize. 4) The primary valency of a metal is known as its outer sphere of attraction or ionizable valency while the Secondary valencies are known as the inner sphere of attraction or coordination sphere. Groups bound by secondary valencies do not undergo ionization in the complex.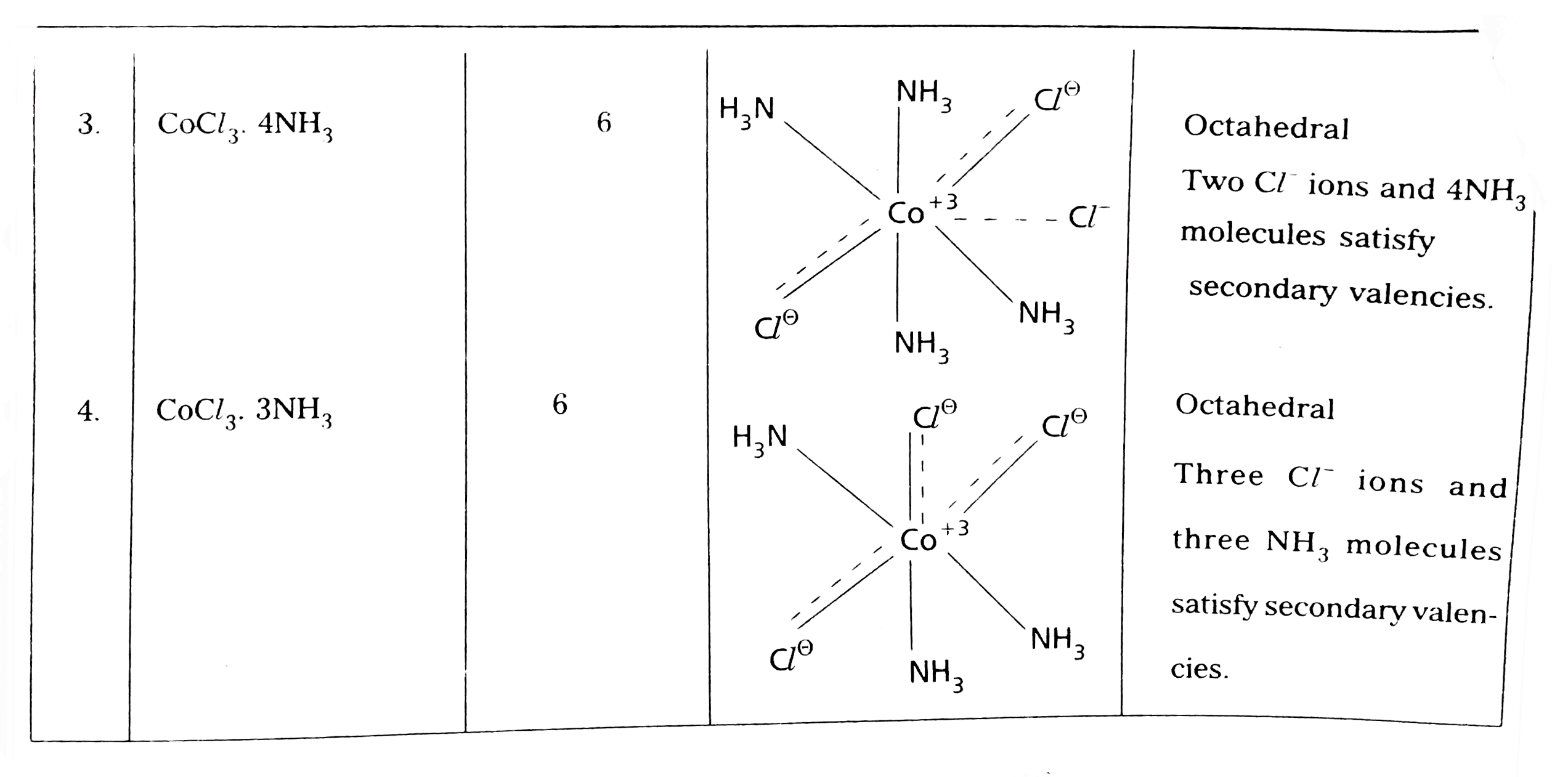 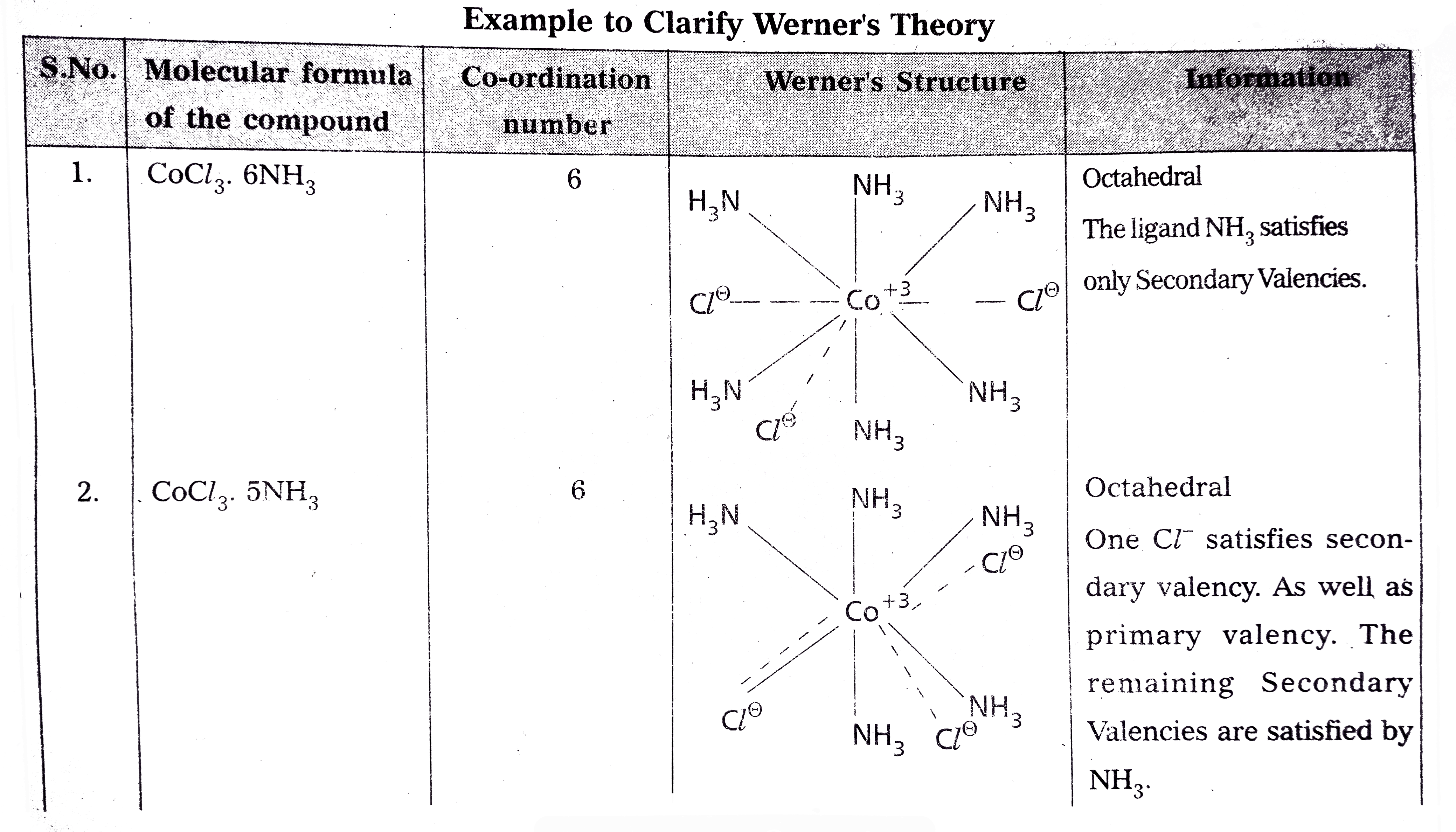 
|
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?