Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Explain why are aryl halides extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions? |
|
Answer» Solution :Aryl halides are extremely less REACTIVE towards nucleo-philic substitution reaction due to the following reasons : (1) Reasonance effect : In haloarenes, the electron pairs on halogen atom are in conjugation with `pi`-electrons of the benzene ring. The DELOCALIZATION of these electrons `C-Cl` bond acquires partial double bond character. 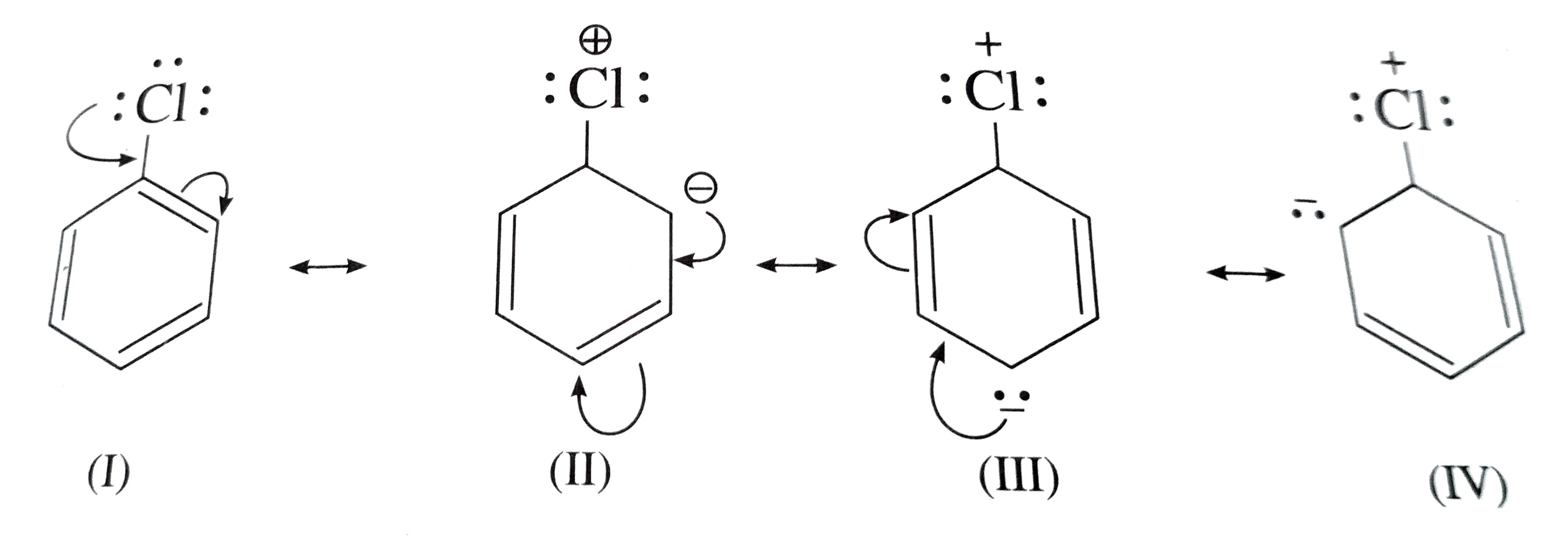 Due to partial double bond character of `C-Cl` bond in aryl halides, the bond cleavage in haloarene is difficult and are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution. (2) Different hybridization state of carbon atom in C-X bond : In aryl halides, the carbon of C-X bond is `sp^(2)` hybridized with more s-character and shorter bond length of 169 PM which requires more energy to break C-X bond. It is difficult to break a shorter bond than a longer bond, therefore, aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction. (3) Instabillity of phenyl cation : In aryl halides, the phenyl cation formed due to self ionisation will not be stabilized by resonance. Thus cations are not formed and hence aryl halides do not UNDERGO nucleophilic substitution reaction easily. (4) As any halides are electron rich molecules due to the presence of `pi-` bond, they repel electron rich nucleophilic. attack. Hence, aryl halides are less reactive toward nucleophilic substitution reactions. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?