Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
(i) Explain about the hydrolysis of salt of strong base and weak acid. Derive the value of K_(h) for that reaction. (ii) Identify the Lewis acid and the Lewis base in the following reactions. (1) CaO + CO_(2) rarr CaCO_(3) (2) |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) 1. Coordination number : The number of nearest neighbours that surrounding a particle in a crystal is called the coordination number of that particle. 2. In aqueous solution, `CH_(3)COONa` is completely dissociated as follows. `CH_(3) COONa_((aq)) rarr CH_(3)COO_((aq))^(-) + Na_((aq))^(+)` 3. `CH_(3)COO^(-)` is a conjugate base of the weak acid `CH_(3)COOH` and it has a tendency to react with `H^(+)` from water to produce unionised acid. But there is no such tendency for `Na^(+)` to react with `OH^(-)` 4. `CH_(3) COO_((aq))^(-) + H_(2)O_((l)) harr CH_(3) COOH_((aq)) + OH_((aq))^(-)` and therefore `[OH^(-)] gt [H^(+)]`, in such cases, the solution is basic due to the HYDROLYSIS and pH is greater than 7. 5. Relationship between equilibrium CONSTANT, hydrolysis constant and the dissociation constant of acid is derived as follows : `K_(h) = ([CH_(3)COOH][OH^(-)])/([CH_(3)COO^(-)][H_(2)O])` `K_(h) = ([CH_(3)COOH][OH^(-)])/([CH_(3)COO^(-)])""...(1)` `CH_(3)COOH_((aq)) harr CH_(3) COO_((aq))^(-) + H_((aq))^(+)` `K_(h) = ([CH_(3)COO^(-)][H^(+)])/([CH_(3)COOH])""...(2)` Equation `(1) xx (2)` `K_(h) .K_(a) = [H^(+)] [OH^(-)]` `[H^(+)] [OH^(-)] = K_(w)` `therefore""K_(h) . K_(a) = K_(w)` `K_(h)` valuein terms of degree of hydrolysis (h) and the concentration of salt (c) for the equilibrium can be obtained as in the case of Ostwald.s dilution law `K_(h) = h^(2) C and [OH^(-)] = sqrt(K_(h).c)`. (ii) 1. `CaO + CO_(2) rarr CaCO_(3)` (a) CaO - Lewis base , All metals oxides are Lewis bases (b) `CO_(2)`-Lewis acid , `CO_(2)` contains a polar DOUBLE bond. 2. 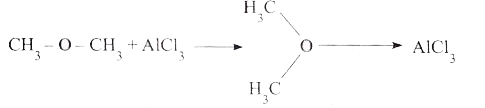 (a) `CH_(3) - O - CH_(3)`-Lewis base , Electron rich SPECIES (b) `AlCl_(3)`-Lewis acid , `AlCl_(3)` is electron deficient molecule. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?