Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
(i)Explain the concentration of copper pyrites and galena ores. (ii) Out of Lu(OH)_(3) and La(OH)_(3) which is more basic and why? |
Answer» Solution :(i) froth floatation: This method is commonly used to concentrate sulphide ores such as galena (PbS), zinc blende (ZnS) etc. In this method, the metallic ore particles which are preferentially wetted by oil can be separated from gangue. 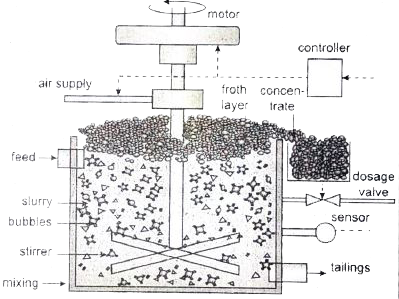 In this method, the crushed ore is suspended in water and mixed with frothing agent such as pine oil, eucalyptus oil etc. A small quantity of sodium ethyl xanthate which acts as a collector is also added. A froth is generated by blowing air through this mixture. The collector molecules attach to the ore particle and make them water repellent. As a result, ore particles, wetted by the oil, rise to the surface along with the froth. The froth is skimmed off and dried to recover the concentrated ore. The gangue particles that are preferentially wetted by water settle at the bottom. When a sulphide ore of a metal of interest contains other sulphides as impurities, depressing agents such as sodium cyanide, sodium carbonate etc are used to selectively prevent other metal sulphides from coming to the froth. For example, when impurities such as ZnS is present in galena (PbS), sodium cyanide (NaCN) is added to depresses the floatation property of ZnS by FORMING a layer of zinc complex `Na_(2)[ZN(CN)_(4)]` on the surface of zinc sulphide. (ii) 1. As we move from `Ce^(3+)` to `Lu^(3+)`, the basic character of `Lu^(3+)` ions decreases. 2. Due to the DECREASE in the size of `Lu^(3+)` ions, the ionic character of Lu-OH bond decreases, covalent character increases which results in the decrease in the basicity. 3. Hence, `LA(OH)_(3)` is more basic than `Lu(OH)_(3)`. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?