Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
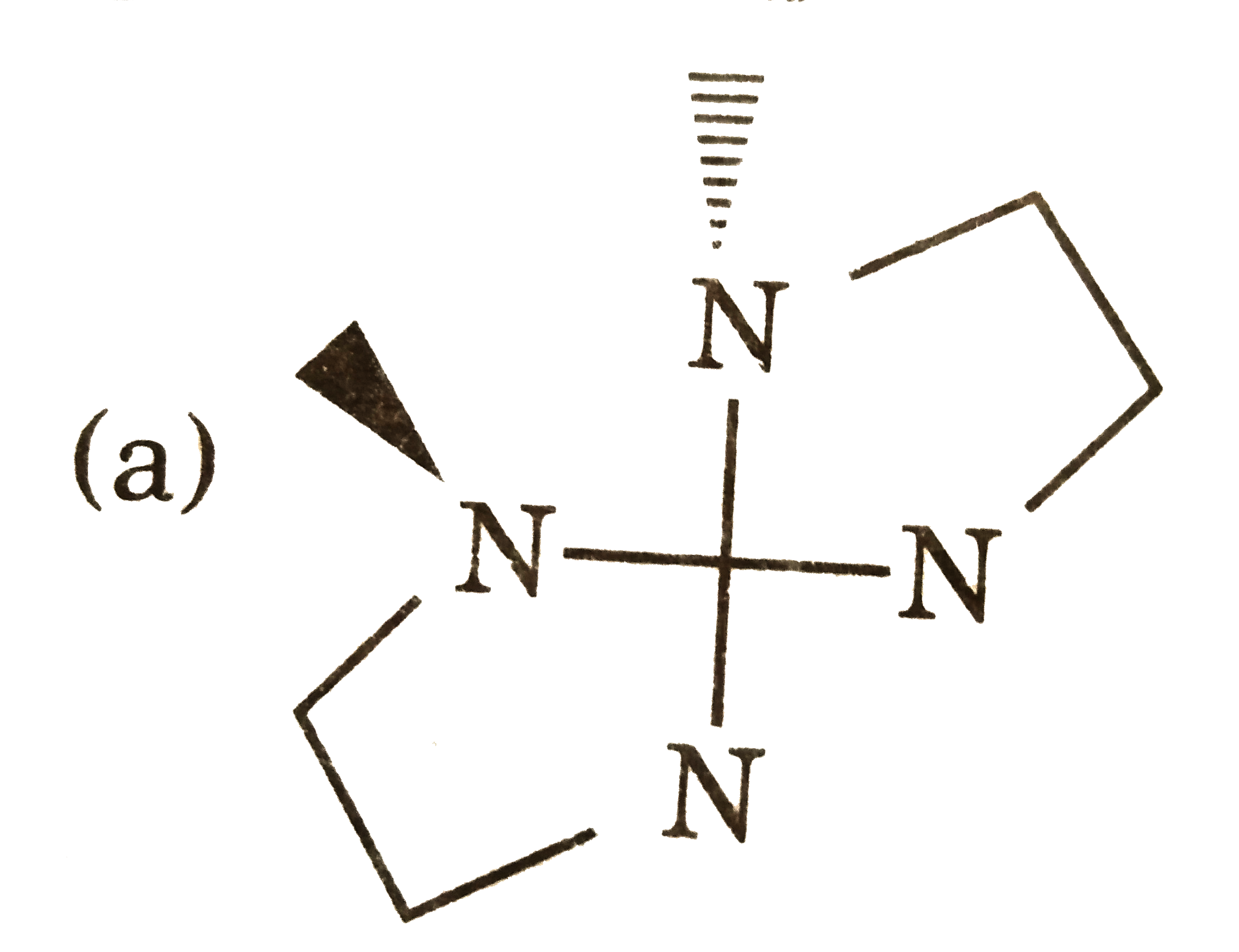
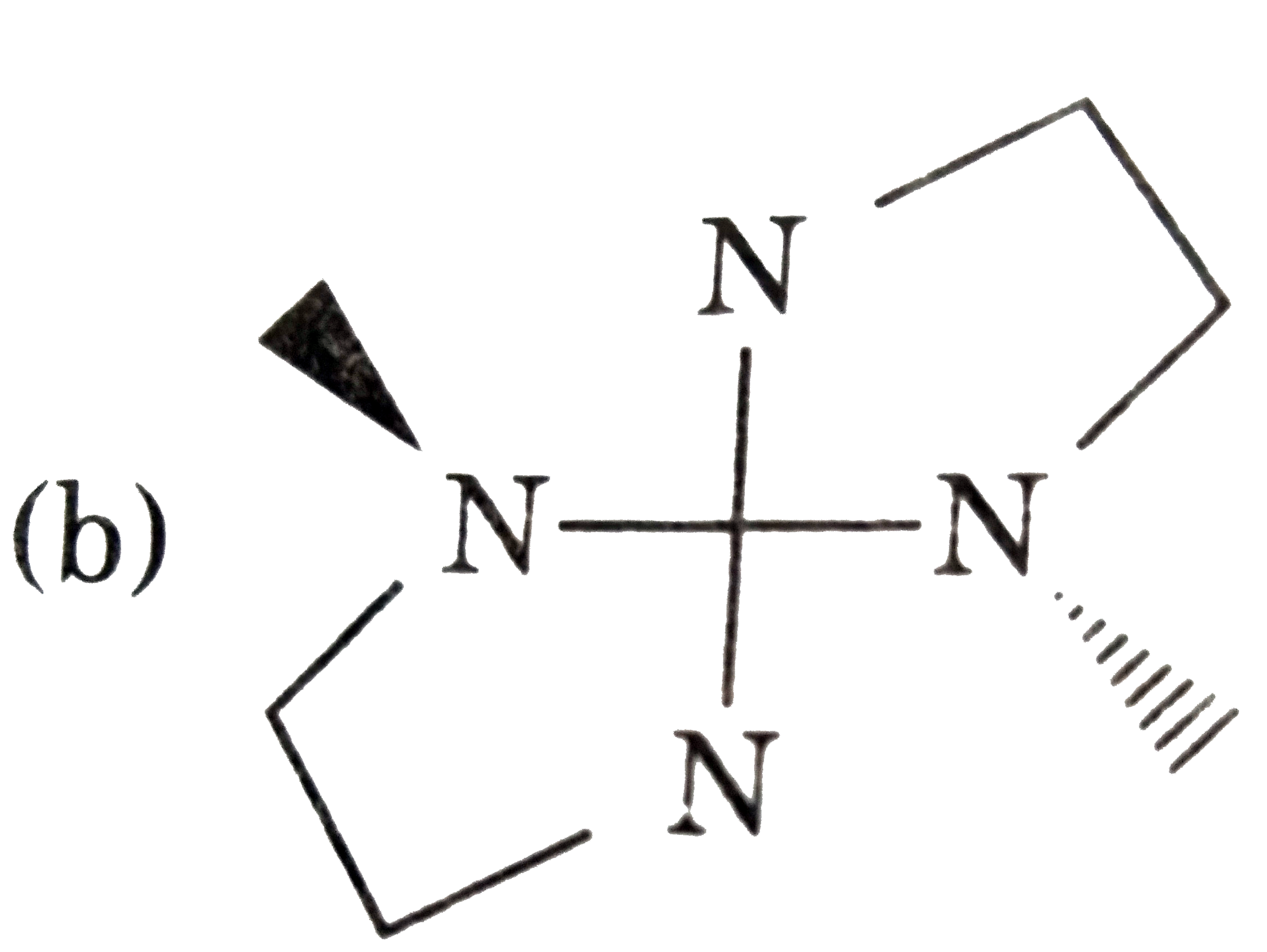
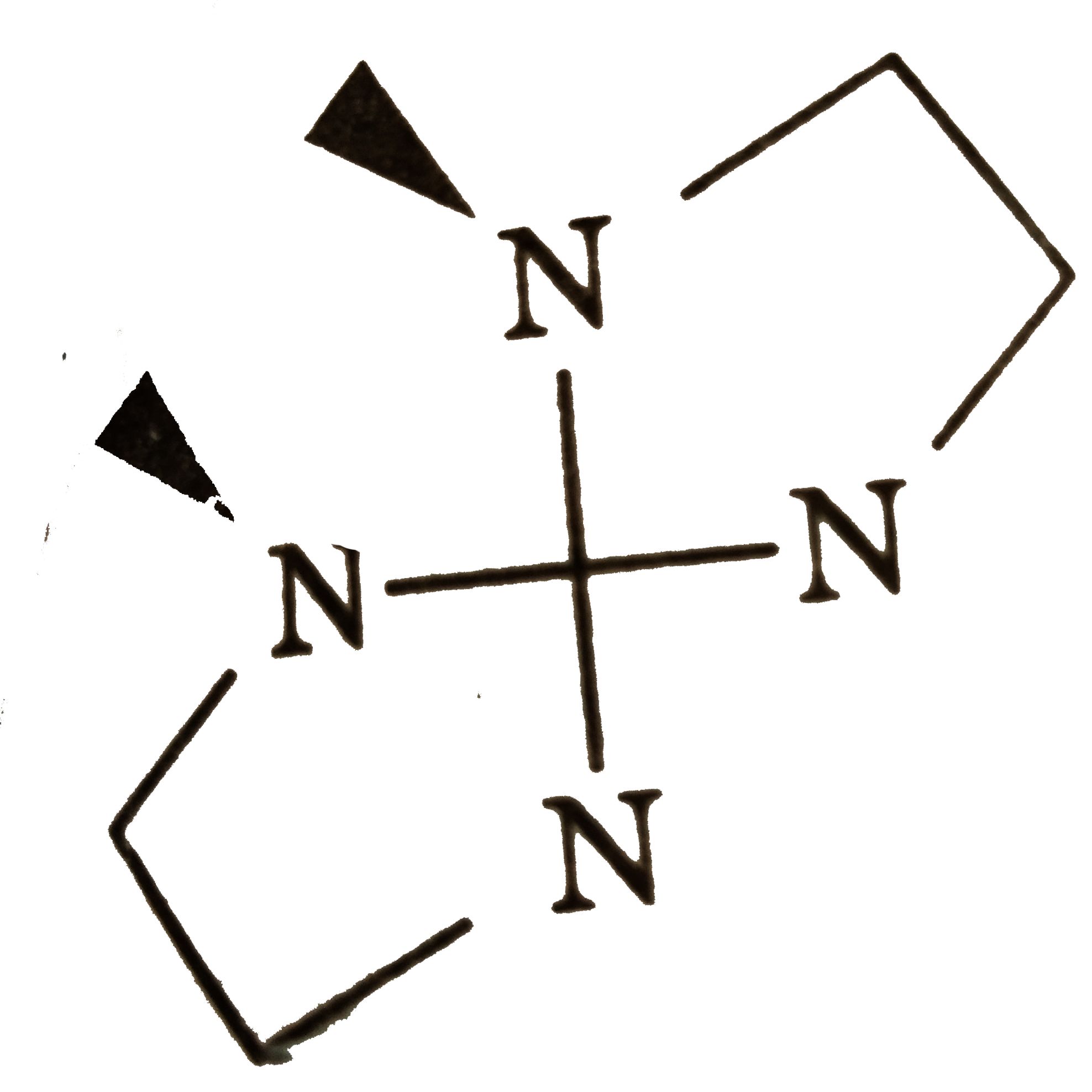
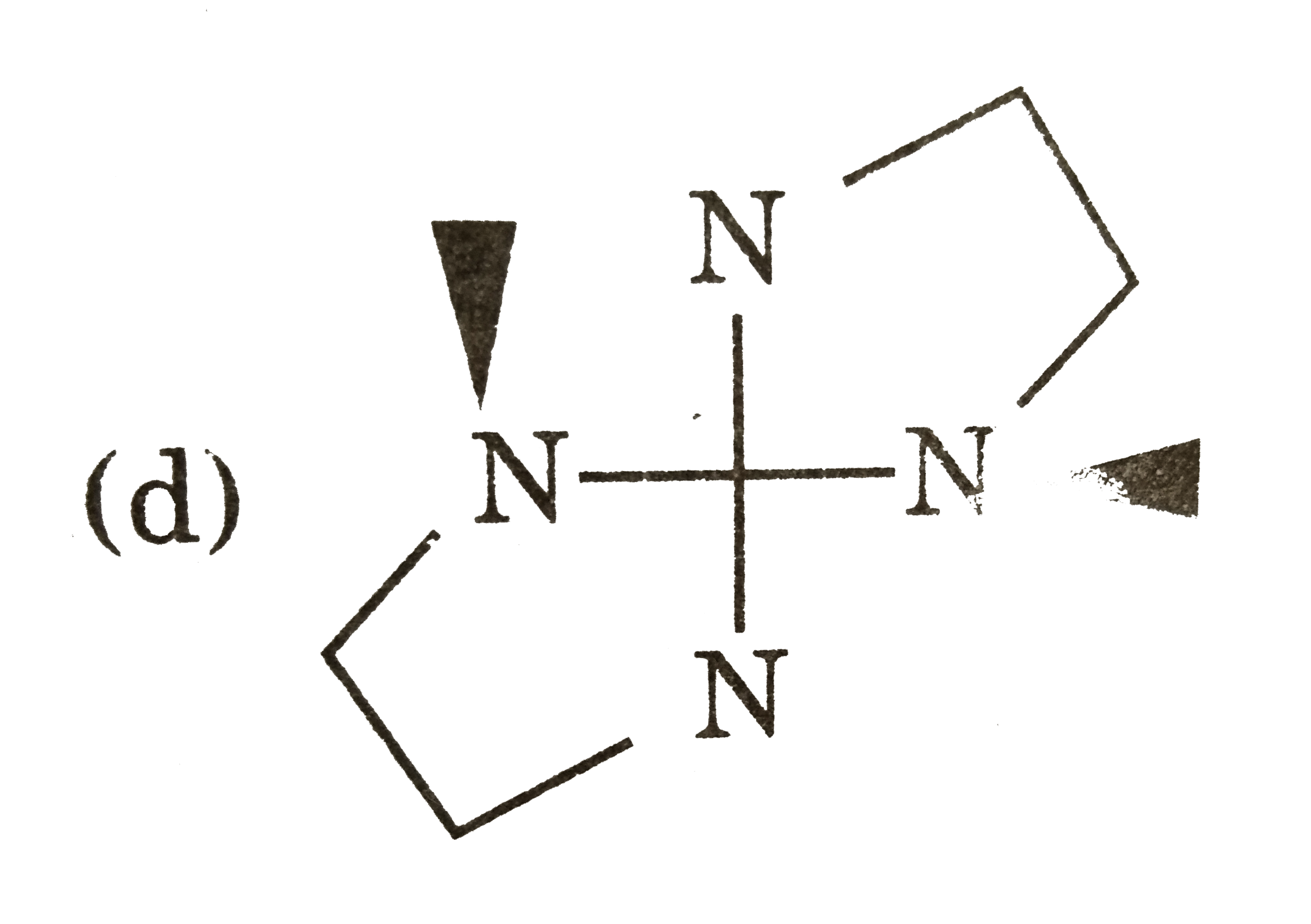
In certain cases, achiral ligands can become chiral on coordination to a metal, leading to a complex that is chiral. Usually the non-chiral ligand contains a donor that rapidly inverts as a free ligand, but that becomes locked in one configuration on co-ordination. An example is MeNHCH_(2)CH_(2)NHMe, where two N atoms become chiral centres on co-ordination to a metal atom. Consider two bidentate ligands for square planar complexes only : A A to Me-NH-CH_(2)-CH_(2)-NHMe CD to Me-NH-CH_(2)-CH_(2)-NH_(2) In the complex solution [M(CD)_(2)], identify the complex isomer which does not have any mirror planes but is nor chiral. |
|
Answer»
(C ) has PLANE of symmetry, (a) and (d) are optically active. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ?
- To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution.
- The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ?
- Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life
- What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ?
- Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide
- Which of following pair is Diastereomers:
- What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to
- Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ?
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ?