Saved Bookmarks
Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 5751. |
Give an example of metal the vessel of which is suitable for storing a solution of ferrous sulphate. |
| Answer» Solution :A VESSEL of COPPER is a suitable choiceto store the solution of ferrous sulphate,because copper is less REACTIVE than IRON. | |
| 5752. |
Give an example of : (i) A metal that is liquid at room temperature. (ii) A non-metal that is liquid at room temperature. (iii) An inert gas (At. No lt 20) |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Mercury (II) BROMINE (iii) Helium or Neon or Argon. |
|
| 5753. |
Give an example of hydrated salt which is blue and soluble in water |
| Answer» SOLUTION :COPPER sulphate pentahydrate, `CuSO_(4)*5H_(2)O` | |
| 5754. |
Give an example of hydrated salt which is efflorescent |
| Answer» SOLUTION :SODIUM carbonate decahydrate, `Na_(2)CO_(3)*10H_(2)O` | |
| 5755. |
Give an example of double displacement reaction other than the one given in activity 1.10. |
|
Answer» Solution :When sodium CARBONATE reacts with calcium chloride, it forms a precipitate of calcium carbonate and sodium chloride. In this reaction, exchange of carbonate and chloride ions form two new compounds. `underset("Sodium carbonate")(Na_(2)CO_(3)(aq))+ underset("Calcium carbonate")(CaCl_(2) (aq)) to underset("Calcium carbonate")(CaCO_(3)(aq))+underset("Sodium chloride")(2NaCl(aq))` This is double displacement reaction. |
|
| 5756. |
Give an example of double displacement reaction (only reaction with complete balanced equation). |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`NACL(AQ)+AgNO_(3)(aq)toAgCl(s)darr+NaNO_(3)(aq)` | |
| 5758. |
Give an example of a sulphide ore which is reduced to metal by heating along i.e., by roasting. |
|
Answer» Solution :CINNABAR (HgS) on roasting is first changed to MERCURIC oxide which on further HEATING is reduced to mercury. `2HgS(s)+3O_2(g) to^(Heat) 2HgO(s)+2SO_2(g)` `2HgO(s) to^(Heat) 2Hg(l)+O_2(g)` |
|
| 5759. |
Give an example of a reaction in which an element combines with acompound to form a product. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Oxygen COMBINES with SULPHUR dioxide to FORM sulphur trioxide : ` SO_(2)+O_(2)toSO_(2)` | |
| 5760. |
Give an example of a metal which is the best conductor of heat. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :SILVER or COPPER | |
| 5761. |
Give an example of a metal which : (i) is a liquid at room temperature : (ii) can be easily cut with a knife , (iii) it is the best conductor of heat : (iv) is a poor conductor of heat. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Mercury (ii) SODIUM (iii) Silver (IV) LEAD. |
|
| 5762. |
Give an example of a metal which... (i) is a liquid at room temperature. (ii) can be easily cut with a knife. (iii) is the best conductor of heat. (iv) is a poor conductor of heat. |
| Answer» Solution :(i) Mercury is a liquid at ROOM temperature. (ii) Sodium, potassium can be easily cut with a knife. (III) SILVER and copper are GOOD conductor of heat. (iv) Lead is a POOR conductor of heat. | |
| 5763. |
Give an example of a metal which (i) is a liquid at room temperature. (ii) can be easily cut with a knife. (iii) is the best conductor of heat. (iv) is a poor conductor of heat. |
| Answer» Solution :(i) mercury, (II) SODIUM, (iii) silver, (iv) LEAD. | |
| 5764. |
Give an example of a metal which (i) is a liquid at room temperature (ii) can be easily cut with a knife (iii) is the best conductor of heat(iv) is a poor conductor of heat |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Mercury (ii) Sodium (iii) Silver (IV) LEAD | |
| 5765. |
Give an example of a metal which(i) is a liquid at room temperature. (ii) can be easily cut with a knife.(iii) is the best conductor of heat. (iv) is a poor conductor of heat. |
| Answer» Solution :(i) MERCURY(II) Sodium(III) Silver (iv) LEAD. | |
| 5766. |
Give an example of a double displacement reaction other than the one given in Activity 8. |
|
Answer» Solution :`underset("nitrate")underset("Lead")(Pb(NO_(3))_(2)(aq))+underset("iodide")underset("Potassium")(2KI(aq))tounderset("iodide")underset("Lead")(PbI_(2)(s))+underset("nitrate")underset("Potassium")(2KNO_(3)(aq))` When we aqueous solutions of lead nitrate, `Pb(NO_(3))_(2)` and potassium iodide, KI, we obtain a precipiate of lead iodide and a solution of potassium nitrate. In this reaction, the CATIONS, `Pb^(2+)` and `K^(+)` EXCHANGE their anions, `NO_(3)^(-)` and `I^(-)` to GIVE the new substances `PbI_(2)` and `KNO_(3)`. |
|
| 5767. |
Give two example of a double displacement reaction |
| Answer» Solution :`UNDERSET(("Silver NITRATE"))(AgNO_(3)(aq))+underset(("Sodium CHLORIDE"))(NaCl(aq))rarrunderset(("Silver Chloride"))(AGCL(darr))+underset(("Sodium Nitrate"))(NaNO_(3)(aq))` | |
| 5768. |
Give an example of a double displacement reaction other than the one given in Activity 1.10. |
| Answer» SOLUTION : `2KBr(aq)+BaCl_(2)(aq) to 2KCl(aq)+BaBr_(2)(aq)` | |
| 5769. |
Give an example of a double displacement reaction other than the one between barium chloride and sodium sulphate solutions. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`UNDERSET("Silver NITRATE")(AgNO_(3)(aq))+underset("Sodium chloride")(NACL(aq))rarrunderset("Silver chloride")(AgCl(s))+underset("Sodium nitrate")(NaNO_(3)(aq))` | |
| 5770. |
Give an example of a double - displacement reaction. |
|
Answer» Solution :The REACTION between an acid and a BASE GIVING salt and water as products. `HCl(aq.)+NaOH(aq.)toNaCl(aq.)+H_(2)O(l)`. |
|
| 5771. |
Give an example for thermal decomposition and photochemical decomposition reactions. Write the relevant balanced chemical equation. |
|
Answer» Solution :Thermal decomposition - On HEATING potassium chlorate using MANGANESE dioxide as catalyst, it decomposes into potassium chloride and oxygen. `underset((s))(2KClO_(3))underset(MnO_(2))overset("light")(to)underset((s))(2KCl)+underset((s))(3O_(2))uarr` Photochemical decomposition - When WHITE coloured silver chloride is exposed to sunlight, it turns grey and decomposes to FORM metallic silver and CHLORINE gas. `2AgCl(s)overset("sunlight")(to)2Ag(s)+Cl_(2)(g)` |
|
| 5772. |
Give an example each of (i) open chain (ii) branched chain and (iii) ring compounds. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Open chain compound (n-pentane): `CH_(3)-CH_(2)-CH_(2)-CH_(2)-CH_(3)` (II) Branched chain compound (isobutane): `CH_(3)-UNDERSET(CH_(3))underset(|)(CH)-CH_(3)` (iii) Ring (CYCLOPENTANE): 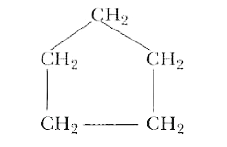
|
|
| 5773. |
Give an example each (i) gas in liquid (ii) solid in liquid (iii) solid in solid (iv) gas in gas |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Carbon-di-oxide dissolved in water (Soda water) (ii) SODIUM chloride dissolved in water. (III) Copper dissolved in GOLD (Alloy) (iv) Mixture of HELIUM - Oxygen gases |
|
| 5774. |
Give an account of the process adopted by Mendeleev for the classification of elements. How did he arrive at "periodic law"? |
| Answer» Solution :To make the study of elements easy, Mendeleev tried to classify the elements on the basis of their CHEMICAL properties. He wrote the properties of each element on a separate card and tried to arrange them in DIFFERENT ways. He arranged all the 63 elements that were known in the order of their increasing atomic MASSES in horizontal rows (called periods) such that elements with similar properties were placed one below the other in the same vertical column (called groups). There were 7 periods and 8 groups in total. The CLASSIFICATION was based on similarities in physical and chemical properties and the compounds formed by elements with hydrogen and oxygen i.e., formulae of hydrides and oxides). He noticed that elements of similar properties would repeat at PERIODIC (regular) intervals (8th, 18th, or 32nd position). On this basis, he stated the periodic law as follows: "The properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses." Hence, he named the table as the Periodic Table of elements. | |
| 5775. |
Give an account of the process adopted by Mendeleev for the classification of elements. How did he arrive at "Periodic Law" ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) When Mendeleev started his work, 63 elements were KNOWN. He studied the compounds of these elements with oxygen and HYDROGEN. He selected hydrogen and oxygen as they are very reactive and formed compounds with most elements. The formulae of the hydrides and oxides formed by an element were TREATED as one of the basic properties of an element for its classification. (ii) Elements with similar properties were arranged in a group. (III) Mendeleev observed that elements were automatically arranged in the order of increasing ATOMIC masses. |
|
| 5776. |
Give an account of the process adopted by Mendeleev for the classification of elements. How did he arrive at “Periodic Law”? |
| Answer» Solution : (i) When Mendeleev started his work, 63 elements were known. He STUDIED the compounds ofthese elements with oxygen and hydrogen. He selected hydrogen and oxygen as they are very reactive and formed compounds with most elements. The formulae of the hydrides and oxides formed by an element were TREATED as one of the basic properties of an element for itsclassification. (ii) Elements with similar properties were arranged in a group. (iii) Mendeleev observed that elements were automatically arranged in the order of INCREASING atomic masses. | |
| 5777. |
Give a test to differentiate chemically between butter and vegetable oil . |
| Answer» Solution :When brown-coloured bromine water is added to both the samples, oil, an unsaturated compound, decolourizes bromine water due to an addition reaction, whereas the BUTTER SHOWS a negative RESULT as it is a SATURATED compound. | |
| 5778. |
Give a test that can be used to differentiate between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. |
|
Answer» Solution :Butter CONTAINS saturated fats while cooking oil contains unsaturated fats. Unsaturated compound decolourise the pink COLOUR of ALKALINE `KMnO_(4)` solution. When butter is treated with a few DROPS of alkaline `KMnO_(4)` solution, the pink colour of `KMnO_(4)` does not disappear, while, when cooking oil is treated with a few drops of alkaline `KMnO_(4)` solution, its pink colour disappears. |
|
| 5779. |
Give a test that can be used to differentiate between butter and cooking oil. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :If a carbon COMPOUND decolourises bromine water, it will be an unsaturatedcompound. Thus, we can distinguish between a COOKING OIL and butter by the bromine water TEST. (i) Cooking oil decolourises bromine water. This shows that it is an unsaturated compound. (ii) Butter does not decolourise bromine water. This shows that it is a saturated compound. |
|
| 5780. |
Give a test that can be used to differentiate chemically between butter and cooking oil. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :BUTTER CONTAINS saturated FATS.Therefore ,it cannot be hydrogenated on the other hand,oil has unsaturated fats.That is why it can be hydrogented to saturated fats (Solids). | |
| 5781. |
Give a chemical test to distinguing between butter and cooking oil. |
| Answer» Solution :Butter and COOKING oil can be distinguished by using alkaline `KMnO_(4)` Being unsaturated only cooking oil decolourises the pink bolour of alkaline `KMnO_(4)` where as butter does not because it is saturated. Bromine water test is ALSO used where brown COLOUR is DISCHARGED by the cooking oil. | |
| 5782. |
Generate the homologous series for compounds containing up to four carbons for the other functional groups given in Q.30. |
|
Answer» Solution :HOMOLOGOUS series for HALOGEN group : `[C_(n)K_(2n+1)X]` `CH_(3)Cl,C_(2)H_(5)Cl,C_(3)H_(7)Cl,C_(4)H_(9)Cl` Homologous series for aldehyde group : `[C_(n)H_(2n)O]` `HCHO,CH_(3)CHO,CH_(3)CH_(2)CHO,CH_(3)CH_(2)CH_(2)CHO` Homologous series for ketone group : `[C_(n)H_(2n)O]` `CH_(3)COCH_(3),CH_(3)COC_(2)H_(5),CH_(3)COC_(3)H_(7),CH_(3)COC_(4)H_(9)` Homologous series for carboxylic acid group : `[C_(n)H_(2n)O_(2)]` `HCOOH,CH_(3)COOH,CH_(3)CH_(2)COOH,CH_(3)CH_(2)CH_(2)COOH` |
|
| 5783. |
Generally, when metals are treated with mineral acids, hydrogen gas is liberated but when metals (except Mn and Mg) are treated with HNO_3, hydrogen is not liberated why? |
| Answer» Solution :It is because `HNO_3` is a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises the `H_2` PRODUCED to `H_2O` and it self get REDUCED to any of the oxides of the nitrogen LIKE `NO_2,NO` etc. | |
| 5784. |
Generally transition elements form coloured compounds. But Sc^(+3) forms colourless compounds. Justify. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Electronic configuration of Sc (ii) energy difference among the ORBITALS of ‘d-‘ SUBSHELL. (iii) BASIC principle behind exhibition of colour (iv) COMPARISON of electronic configuration of alkali, alkaline earth and transition metals (v)electronic configuration of Sc+3 (vi) comparison of electronic configuration of scan- dium ion with other transition metal IONS |
|
| 5785. |
Generally, non-metals are not lustrous. Which of the following non-metal is lustrous ? |
|
Answer» SULPHUR |
|
| 5786. |
Generally metals react with acids to give salt and hydrogen gas. Which of the following acidsdoes not give hydrogen gas on reacting with metals (except Mn and Mg)? |
|
Answer» `H_2SO_4` |
|
| 5787. |
Write the general formula of alkynes. |
|
Answer» `CnH_(2n+2)` |
|
| 5788. |
General formula for alkane is…………….. |
|
Answer» `C_(n)-H_(2n)` |
|
| 5789. |
Select whether the statement is true or false .Gay-Lussac’s law of chemical combination is valid for all substances. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 5791. |
Gas laws are universally applicable for all gases whereas such universal laws could not be established for solids and liquids. Comment on this statement. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Gases differ from SOLIDS and liquids in the extent of intermolecular forces of attraction. Since gases are characterised by negligible forces of attraction, the molecules behave independent of the neighbouring molecules. Due to large intermolecular spaces, the coefficient of volume expassion is same for all gases. Moreover, in case of gases, the molecules are considered as point masses and hence, the volume OCCUPIED by the molecules is negligible in comparison to the total volume. Therefore, thephysical behaviour of all gases being similar, certain laws could be established which are universally applicable. In cases of liquids and solids, the molecules are CONSIDEREDAS rigidsheres and the coefficient of volume expansion is not uniform for all substances, such universal laws can be established. | |
| 5792. |
Gas liberated when zinc is treated with concentrated nitric acid is ______ . |
|
Answer» nitrous oxide |
|
| 5793. |
Galvanisation of iron means coating iron with |
|
Answer» Zinc |
|
| 5795. |
Furan is a carbocyclic compound. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FURAN is a HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUND. | |
| 5796. |
Fullerene is an allotropic form of … |
|
Answer» phosphours |
|
| 5797. |
Fuels such as coal and petroleum contain some amount of ......... and ......... in them. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :NITROGEN, SULPHUR | |
| 5798. |
Froth floatation process is used for the concentration of which ore? |
|
Answer» SULPHIDE |
|
| 5799. |
Froth floatation process is preferable for ………….. Ores |
| Answer» SOLUTION :LIGHTER (or) SULPHIDE | |