Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in Current Affairs.
This section includes 7 InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your Current Affairs knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1. |
What is the name given to a pure substance with only one kind of atoms? |
|
Answer» ELEMENT |
|
| 2. |
What is the difference between pure gold and 22 carat gold? Which type of gold is used for making ornaments ? |
| Answer» Solution : Pure gold is a 24 carat gold, which is very soft, hence ornaments cannot be made from it, while 22 carat gold is an ALLOY (mixture) of 22 parts of pure gold and 2 parts of either copper or silver and it is HARD. As a result, 22 carat gold is used for MAKING designed ornaments. | |
| 4. |
Write the formula of the product formed when the element A (atomic number 19) combines with the element B (atomic number 17). Draw its electronic dot structure. What is the nature of the bond formed? |
Answer» SOLUTION :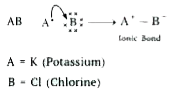
|
|
| 6. |
Why are alcohols poor conductors of electricity ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Because they do not PRODUCE IONS in solution. | |
| 7. |
Which one of the following element is used as the standard for measuring the relativeatomic mass of an element in now a days? |
| Answer» Solution :`C-12` | |
| 9. |
What do you think would happen when a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder is heated ? |
| Answer» Solution :Ferrours SULPHIDE, a COMPOUND of IRON and sulphur, will be FORMED. | |
| 10. |
What is the formula of the next homologue of propene (C_3H_6)? |
| Answer» Solution : Since the HOMOLOGUES differ by `-CH_2` unit in their formulae, the next HOMOLOGUE of propene is `C_3H_6 + CH2toC_4H_8` . It is the molecular formula of BUTENE. | |
| 11. |
Which two of the following compounds could belong to the same homologous series ? C_(2)H_(6)O_(2),C_(2)H_(6),CH_(4)O |
| Answer» Solution :`C_(2)H_(6)O` and `CH_(4)O` having difference in molecular formula EQUAL to - `CH_(2)` belong to the same homologous series of alcohols `(C_(3)H_(5)OHandCH_(3)OH)`. | |
| 12. |
Which of the following is (are) the correct isomer(s) of pentane ? |
|
Answer» `CH_(3) - CH = underset(CH_(3))underset(|)C-CH_(3)` |
|
| 13. |
Which of the following affect solubility? |
|
Answer» TEMPERATURE |
|
| 15. |
Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon |
|
Answer» Solution :Dilute hydrochloric ACID REACTS with magnesium RIBBON FORMING magnesium chloride and evolving hydrogen gas Magnesium + Hydrochloric acid `rarr` Magnesium chloride + hydrogen `Mag(s) + 2HCl (aq) rarr MgCl_(2)(aq) + H_(2)(g)` |
|
| 16. |
Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings |
|
Answer» Solution :Dilute hydrochloric acid REACTS with iron filings to GIVE iron CHLORIDE and hydrogen gas. Iron + Hydrochloric acid `rarr` Iron chloride + Hydrogen `Fe(s) + 2HCL (aq) rarr FeCl_(2)(aq) +H_(2)(g)` |
|
| 17. |
Write the property of electrical conductivity of carbon compounds. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :CARBON COMPOUNDS are non-conductor of ELECTRICITY. | |
| 18. |
Which of the following is a redox reaction ? |
|
Answer» `CaCO_(3) to CAO + CO_(2)` |
|
| 19. |
What will be the structural formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane? |
Answer» Solution :The molecular formula of cyclopentane is `C_(5)H_(10)`. Five CARBON ATOMS of cyclopentane are connected by SINGLE bonds in a cyclic FORM. Following are the structural formula and elecgtron dot STRUCTURE of cyclopentane. 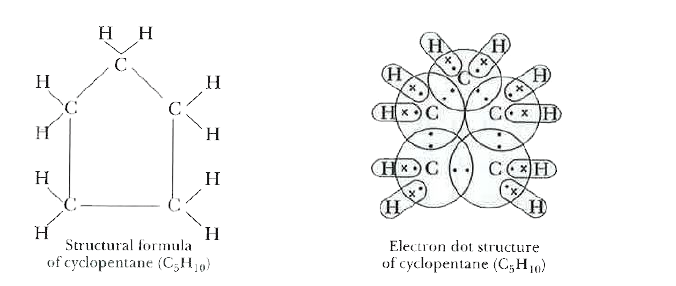
|
|
| 20. |
Translate the statement into chemical equations and then balance them: Hydrogen gas combine with nitrogen to form ammonia. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`underset("NITROGEN")(N_(2)(g)) +underset("HYDROGEN")(3H_(2)(g)) to underset("Ammonia")(2NH_(3)(g))` | |
| 21. |
Which one will not migrate towards cathode in an electrolytic cell ? |
|
Answer» Lead ion |
|
| 22. |
Write the formula and name of the lower homologue of ethanoic acid. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :HCOOH = Methanoic ACID | |
| 23. |
When marble chips are treated with HCI , which of the following gas is liberated? |
|
Answer» `CO_2` |
|
| 24. |
Which of the following equations is (are) not correctly balanced ? |
|
Answer» `Mg+2HCI to MgCI_(2)+H_(2)` |
|
| 25. |
Translate thestatements into chemical equations and then balance them: Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`underset("Barium CHLORIDE")(BaCl_(2)(aq))+ underset("Almunium sulphate")(Al_(2)(SO_(4))_(3)) to underset("Aluminium chloride")(2AlCl_(3)(aq))+ underset("Barium sulphate")(3BaSO_(4))` | |
| 26. |
What is that instrument which can detect the presence of electric current in a circuit. |
|
Answer» Galvanometer |
|
| 27. |
Which of the following is an allotrope of carbon ? |
|
Answer» Diamond |
|
| 28. |
Write the balanced equation for the chemical reactions : Hydrogen + Chlorine Hydrogen chloride |
| Answer» Solution :`H_(2)(G)+ Cl_(2)(g) to 2HCL(g)` | |
| 29. |
What is the chemical formula of baking soda? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :CHEMICAL formula of BAKING SODA is `NaHCO_3` . Preparation `NAOH + CO_2 to NaHCO_2` |
|
| 30. |
There are three elements E, F, G with atomicnumbers 19, 8 and 17 respectively. Classify the elements as metals and nonmetals. |
| Answer» Solution : E = METAL, F = nonmetal, G = nonmetal | |
| 31. |
Zinc reacts with sodium hydroxide to form………. |
|
Answer» Zinc HYDROXIDE +`H_(2)O` |
|
| 32. |
What change does zinc undergo when it is reactedwith dilute H_(2)SO_(4) ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :A zinc atom LOSES two electrons and GETS oxidized into ` ZN^(2+)` ion. ` Zn to Zn^(2+) +2e` |
|
| 33. |
Which metals produce fire on water ? |
| Answer» Solution :Sodium and POTASSIUM PRODUCE FIRE on WATER. | |
| 34. |
Which one of the following has the largest ionisation energy?ArClKAl |
|
Answer» AR |
|
| 35. |
Which one of the following elements exhibit maximum number of valence electrons ? |
|
Answer» Na |
|
| 36. |
What is the maximum number of electrons present in the main energy level in which the 'g' subshell appears for the first time? Find the atomic number of the element to be discovered in which the differentiating electron is the only electron in the first 'g' subshell |
| Answer» Solution :Corresponding 'f' value of 'g' subshell is '4'. Principal quantt1m number in which 'g' subshell can exist is '5'. The maximum number of electron!r that can be accommodated in fifth orbit is 2 x 52 = 50 electrons. Orbitals to be filled before filling of 'Sg' subshell are: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3P, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4D, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6D, 7p, 8s, 5g. Atomic number of the ELEMENT should be 121. | |
| 37. |
Which of the following metals exist in free state in nature ? Cu , Al , Mg , Au , Fe , Ag |
| Answer» SOLUTION :AU and AG | |
| 40. |
Three elements A, B and C have 3, 4 and 2 electrons respectively in their outermost shell. Give the group number to which they belong in the Modern Periodic Table. Also, give their valencies. |
Answer» SOLUTION :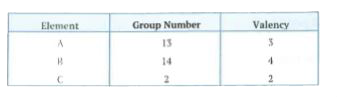
|
|
| 41. |
Three elements having a single electron in theiroutermost shell. |
| Answer» Solution :(i) LITHIUM (LI) (2,1) (ii) SODIUM (Na) (2, 8 1)(iii) Potassium (K) (2 , 8,8 ,1). | |
| 42. |
Transition elements : cl-block :: Inner transitionelements : ___________ |
| Answer» Solution :f-block - The d-block elements have 2 incompleteoutermost SHELLS whereas the f-block elementshave 3 OUTERMOST shells which are INCOMPLETE . | |
| 43. |
The state in which molecular attractions are very strong is |
|
Answer» solid |
|
| 44. |
WhenSO_(2) gas is allowed to react with acidified potassiumdichromate solution , the yellow colour of the solution changes to green. This is due to the formation of |
|
Answer» `Cr_(2)O_(3)` |
|
| 45. |
Which one of the following is an example of a heterogeneous mixture ? |
|
Answer» ALUM and water |
|
| 46. |
What is Electronegativity? |
| Answer» SOLUTION : ELECTRONEGATIVITY of an ELEMENT is the measure of the tendency of its atom to ATTRACT the shared pair of electrons towards itself in a covalent bond. | |
| 47. |
What is the maximum number of electrons present in the main energy level in which thegsubshell appears for the first time? Find the atomic number of the element to be discovered in which the dif- ferentiating electron is the only electron in the first 'g'subshell. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i)LVALUE for 'g' subshell (ii) total number of degenerate orbitals in'g'subshell (III) number of ELECTRONS in'g'subshell (iv) main energy level in Which'g' subshell first APPEARS (v) orbitals that have lower energy than the flrstg orbital |
|
| 48. |
Which one is an oxide of group 2 metal? |
|
Answer» MGO |
|
| 49. |
What is formed on burning magnesium ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION : Magnesium oxide (MGO) is formed on BURNING magnesium. | |
| 50. |
Write the essential condition for following reaction to take place : 2AgBr to 2Ag+Br_(2) Write one application of this reaction. |
|
Answer» Solution :`2AgBroverset("Sunlight")(to)2Ag+Br` PRESENCE of sunlight is NECESSARY for the reaction to take place. This reaction is USED in black and white PHOTOGRAPHY. |
|