Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 37951. |
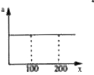
Velocity (v) versus displacement (x) plot of a body moving along a straight line is as shown in the graph. The corresponding plot of acceleration (a) as a function of displacement (x) is |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 37952. |
The sky wave propagation is suitable for radioactive frequency. |
|
Answer» SPACE WAVES |
|
| 37953. |
A double convex lens, made from a material of refractive index mu_1,is immersed in a liquid of refractive index mu_2, where mu_2 gt mu_1 . What change,if any, would occur in the nature of the lens? |
|
Answer» Solution :Focal LENGTH of lens (REFRACTIVE INDEX `mu_1` ) in a liquid of refractive index `mu_2`is Formula:` f_1=(mu_1 - 1)/(mu_1/mu_2) xx f_a` Given ` mu_2 GT mu_1 , i.e., mu_1/mu_2 lt 1` so ` f_1 = (mu_1 - 1)/(1 - mu_1/mu_2) f_a` So the focal length of lens in liquid will be of opposite sign of the focal length of lens in air, i.e., nature of lens will change. Hence, lens would now behave like a DIVERGING (concave) lens. |
|
| 37954. |
A real object is kept in front of a lens. The object is a linear extended object with its length perpendicular to the optic axis of the lens. With reference to different cases of image formation by lenses, math the column-l with column - II |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37955. |
You are arguing over a cell phone while trailing an unmarked police car by 25 m, both your car and the police car are travelingat 120 km/hr. Your argument diverts your attention from the police car for 2.0 s ( long enough for you to look at the phone and yell, " I won't do that ! " ). At the beginning of that 2.0 s, the police officer begins braking suddenly at 5.0 m//s^(2). (a) What is the separation between the two cars when your attention finally returns ? Suppose that you take another 0.40 s to realize your danger and uegin braking . (b) If you too brake at 5.0 m//s^(2), what is your speed when you hit the police car ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37956. |
Current in an a.c. circuit is wattless if ………….of the circuit is zero. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :RESISTANCE. | |
| 37957. |
Nuclear fission and fusion processes are examples of "_____________". |
|
Answer» NEWTON's laws |
|
| 37958. |
A coil in the shape of an equilateral triangle of sidel is suspended between the pole piecesof a permanentmagnet such that B fixed in planeof the coil if due tocurrentI in the trianglea troque gammaacts on it then side of the triangle is |
|
Answer» `(1)/SQRT(3)(R )/(B1)` |
|
| 37959. |
Determine the radius of the first orbit of the hydrogen atom. What would be the velocity and frequency of the electron in the first orbit ? Given : h=6.62xx10^(-34) J s, m =9.1xx10^(-31) kg, e=1.6xx10^(-19) C, k = 9xx10^(9)m^(2)C. |
|
Answer» Solution :Given `h=6.62xx10^(-34) J-s,` `m=9.1xx10^(-31) kg` `e=1.6xx10^(-19)C,` `k=9xx10^(9)NM^(2)C^(-2), n=1` i) `r_(1)=(n^(2)h^(2))/(4pi^(2)" mke"^(2))` `=((1)^(2)xx(6.62xx10^(-34))^(2))/(4xx(3.14)^(2)xx9.1xx10^(-31)xx9xx10^(9)(1.6xx10^(-19))^(2))` `therefore r_(1)=0.529 overset(0)A cong 0.53 overset(0)A` ii) `V=sqrt((KZ)/(MR))xxe` `=sqrt((9xx10^(9)XX1)/(9.1xx10^(-31)xx0.53)xx1.6xx10^(-19)` `therefore V=2.19xx10^(6) ms^(-1)` iii) `v=(KZe^(2))/(nhr)` `=(9xx10^(9)xx1xx(1.6xx10^(-19))^(2))/(1xx6.62xx10^(-34)xx0.529xx10^(-10))` `therefore v=6.6xx10^(15)Hz.` |
|
| 37960. |
A galvanometer has a resistance of 100 Omega. A current of 2 xx 10^(-3) A can pass through the galvanometer. How can it be converted into (a) Ammeter of range 20 A and (b) oltmeter of range 20 V? |
| Answer» Solution :`(100)/(999) OMEGA (B) 9900 Omega` | |
| 37961. |
The ratio of the nuclear radii of the gold isotope ._79^197Au and silver isotope ._47^107Ag is |
|
Answer» 1.23 `THEREFORE R_1/R_2=(A_1/A_2)^(1//3)=(197/107)^(1//3)`=1.225 |
|
| 37962. |
Find the saturation current in a diode with a tungsten cathode at cathode temperature of 2700 K, if the length of the cathode is 3 cm and its diameter is 0.1 mm. The constant B=6xx10^(5)A//(m^(2)K^(2)) |
|
Answer» `logi_("SAT")=logpi+logd+logl+logB+2logT-0.434logA_(0)//kT` |
|
| 37963. |
The total magnetic induction at point 0 due to curved portion and straight portion in the following figure, will be |
|
Answer» `(mu_0 I )/(2 pi r)[pi- PHI+ tanphi ]` |
|
| 37964. |
An electric field is applied to a semiconductor. Let the number of charge carriers be n and the average drift speed be v. If the temperature is increased, |
|
Answer» both n and v will INCREASE |
|
| 37965. |
Infinite number of masseseach of 2 kg are placed along x-axis at distance 1m, 2m, 4m, 8m …….. from the origin O, what is the magnitude of gravitational potential at 'O'? (G = gravitational constant) : |
|
Answer» `-G` `=-GM[(1)/(1)+(1)/(2)+(1)/(4)+(1)/(8)+………….]` `=-GM[(1)/(1-(1)/(2))]=-GMxx2=-Gxx2xx2=-4G` Thus CORRECT CHOICE is (d). |
|
| 37966. |
The current in a conductor varies with time 't' as I = 3 + 4t^2. Where I in amp and t in sec. The electric charge flows through the section of the conductor between t = 1s and t = 3s |
|
Answer» `(14)/(3) C ` |
|
| 37967. |
What are solids ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :SOLIDS are the MATERIALS having definite SHAPE and VOLUME. | |
| 37968. |
Consider two satellites A and B of equal mass m, moving in the same circular orbit about the earth, but in opposite sense as shown in figure. The orbital radius is R. The satellite undergo a collision which is perfectly inelastic. For this situation, mark out the correct statements. [Take mass of earth as M] |
|
Answer» The total energy of the satellite plus earth's system before collision is `-(GMm)//r`. `E=-(GM m)/(2r)-(GM m)/(2r)=-(GM m)/(r )` Let the orbital velocity be `v_(1)`. Then from momentum conservation, `mv-mv=2mv_(1)` `rArr v_(1)=0` As velocity of combined mass just after collision is zero, the combined mass will fall towards the earth. At this instant, the total energy of the system only consists of the gravitational potential energy given by `U=(GMxx2m)/(2r )=(GM m)/(r )`. |
|
| 37969. |
The angular velocity of body changes from 1 revolution per 16 seconds to 1 revolution per second without applying an external torque. The ratio of radii of gyration in two cases is : |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `omega_(1)=2pixx(1)/(16)andomega_(2)=2pixx1` ALSO `I_(1)omega_(1)=I_(2)omega_(2)orMK_(1)^(2)omega_(1)=MK_(2)^(2)omega_(2)` `(K_(1))/(K_(2))=sqrt((omega_(2))/(omega_(1)))=sqrt((16)/(1))=(4)/(1)` |
|
| 37970. |
A thin metallic spherical shell a carries Q on it. A point charge Q_(1) is placed at the centre of the shell and another charge q is placed outside as shown in figure ahead. All the charges arepositve. Discuss the various forces acting on Q_(1). |
|
Answer» Solution :Here the net force on `Q_(1)` will be zero because the net electric field inside a condcutro due to charges on it and outside is zero. The force applied .by q on `Q_(1)`will have the VALUE `(Q_(1)q)/(4 pi epsilon_(0)R^(2))` TOWARDS left. Equal and opositve force will be applied by the charge Q on the shell to MAKE net force on `Q_(3)` = 0 . shell will o this by rearranging its charge as shown below. 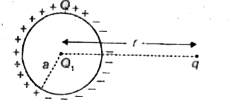
|
|
| 37971. |
Light of wavelength 488 nm is produced by an argon laser which is used in the photo-electric effect. When light from this spectral line is incident on the emitter, the stopping (cut-off) potential of photoelectrons is 0.38 V. Find the work function of the materialfrom which the emitter is made. |
|
Answer» Solution :`lambda=488nm =488xx10^(-9)m, upsilon_(0)=0.38V` `H upsilon=phi_(0)+(1)/(2)mv_("max")^(2), h (c )/(lambda)=phi_(0)+eV_(0)` `phi_(0)=h (c )/(lambda)-eV_(0)=(6.6xx10^(-34)xx3xx10^(8))/(488xx10^(-9))-1.6xx10^(-19)xx0.38=3.46xx10^(-19)J=2.16eV` |
|
| 37972. |
यदि कोई वस्तु समतल दर्पण सामने 5 cm की दूरी पर रखी है तो वस्तु से प्रतिबिम्ब की दूरी होगी ? |
|
Answer» 5 cm |
|
| 37973. |
A Gaussian surface does not enclose a charge. Does it mean that E=0 on its surface? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :No. There can be electric FIELD on the Gaussian SURFACE even if the charge enclosed by it is zero. However, the net flux through the surface will be zero. For instance, the Gaussian surface may have a POINT charge outside it. | |
| 37974. |
Match List-I (Electromagnetic wave type) with List-II (Its association/application) and select the correct option from the choices given below the lists: |
|
Answer» `{:(A,B,C,D),("(i)","(II)","(III)","(IV)"):}` |
|
| 37975. |
When a charged particle moves in a magnetic field, does its KE always remain constant? |
|
Answer» Solution :A charged PARTICLE moving in a MAGNETIC field of CONSTANT INTENSITY does not gain kinetic energy. This is because the force is `VEC F = q (vec V xx vec B)` and work done, `W = vec f.vec s` or in 1 second, `vec F. vec V = a(vec V xx vec B ) vec V =0`because of property of scalar triple product. |
|
| 37976. |
An e.m.f. of 5 volts is produced by a self inductance, when the current changes at a steady rate from 3A to 2A in 1 mile-second. The value of self inductance is: |
|
Answer» Zero |
|
| 37977. |
Sea water at frequency v=4xx10^(8) Hz has permittivity in ~~ 80 in_(0), permeability mu = mu_(0) and resistivity rho = 0.25 Omega, Imagine a parallel plate capacitor immersed in sea water and driven by an alternating voltage source V(t)=V_(0)sin 2pi vt.What fraction of the conduction current density is the displacement current current density ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Let distance between two plates of capacitor be .d. and voltage applied is `V(t)=V_(0)sin 2pi vt` Hence electric FIELD, `E=(V_(0))/(d)sin 2pi v t ""`….(1) By Ohm.s law, `I_(c )=sigma E=(E )/(rho)` `therefore I_(c ) = (V_(0))/(rho d) sin 2pi v t` Let`(V_(0))/(rho d) = J_(0)^(c )""`....(2) `therefore J_(c ) = J_(0)^(c )sin 2pi vt ""`.....(3) Now displacement current density, `J_(d)=in(delta E)/(dt)=(in delta)/(dt)[(V_(0))/(d)sin 2pi vt]""`[`because`From equation (1)] `=(in 2piv V_(0))/(d)cos 2pi vt` Let`(2pi v V_(0))/(d)=J_(0)^(d)""`....(4) `therefore J_(d) = J_(0)^(d)cos pi vt ""`...(5) By taking ratio of (4) and (2), `(J_(0)^(d))/(J_(0)^(2))=(2pi v in V_(0))/(d)xx(rho d)/(V_(0))` `= 2 pi v in rho` `= 2piv xx80 in_(0) xx 0.25 [because in = 80 in_(0), rho = 0.25 Omega m]` `= 4pi in_(0) v xx 10` `=(10 v)/(9xx 10^(9)) "" [because4pi in_(0)=(1)/(9xx10^(9))]` `= (10xx4xx10^(8))/(9xx10^(9))[because v=4xx10^(8)Hz]` `=(4)/(9)` |
|
| 37978. |
Two capacitors of equal capacitance (C_(1) = C_(2))are shown in the figure. Initially, while the switch S is open, one of the capacitors is uncharged and the other carries charge Q_0The energy stored in the charged capacitor is U_0Sometime after the switch is closed, the capacitors C_(1) and C_(2)carry charges Q_(1) and Q_(2)respectively, the voltages across the capacitors are V_(1) and V_(2) ,and the energies stored in the capacitors are U_(1) and U_(2) .Which of the following statements is INCORRECT ? |
|
Answer» `Q_(0) =1/2 (Q_(1)+Q_(2))` |
|
| 37979. |
Fractional of total power carried by side bands is given by |
|
Answer» <P>`(P_(s))/(P_(T))= m^(2)` |
|
| 37980. |
One long conductor carries current I along y-axis with charge density lambda. An electric field exists along z-axis. In what direction, a charged particle at point P, distance x apart from the wire (along x-axis), be projected with velocity v so that it moves undeflected? |
|
Answer» VERTICALLY upward 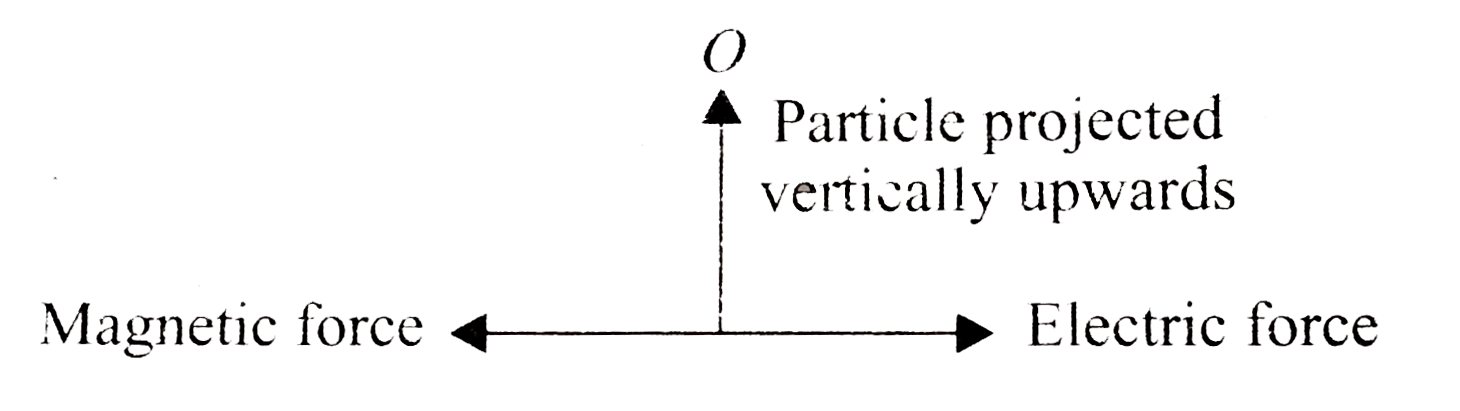 . .
|
|
| 37981. |
In the circuit shown alongside, the ammeter and the voltmeter redings are 3A and 6A, respectively. Then, the value of the resistance R is |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 37982. |
What is unit of intensity of magnetisation ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`I = M/V = Am^-1` | |
| 37983. |
A conducting spherical shell of radius R has a charge Q. A small sphere of radius r_(0) (r_(0) lt R) currying a charge g is introduced inside the large shell. What is the potential i. at a point r (r gt r_(0)) due to inner sphere ii. it at a point r=R iii. at a point r=r_(0) |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`i. V_(0)=(1)/(4pi epsi_(0)) q/R` II. `V=(1)/(4pi epsi_(0)R) [Q+e]` iii. `V=1/(4pi EPSI) [q/r_0+Q/R]` |
|
| 37984. |
The coulomb's force between the 2 point charges 104C and 5µC placed at a distance of 150cm is |
|
Answer» 0.2N |
|
| 37985. |
The maximum K.E. of a photoelectrons is 3eV. What is stopping potential ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :STOPPING POTENTIAL `V_0 = K_max/E = (3eV)/e` = 3V |
|
| 37986. |
Three particles A, B, C are thrown from the top of a tower with the same speed. A is thrown straight up, B is thrown straight down and C is thrown horizontally. They hit the ground with speeds va,v_b and v_c and respectively. |
|
Answer» `v_a =v_b=v_c` `:. v_c= sqrt(u^2 +v^2)` Hence `v_a` =`v_b` <`v_c` |
|
| 37987. |
The temperature coefficient of resistance of conductors is |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 37988. |
How much height of water in cm would be filled in a container of height 14 cm, so that it appearshalf filled to the observer when viewed from the top of the container (mu_omega = 4/3) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37989. |
A proton is traveling along the X - direction with velocity 5 xx 10^6 " " ms^(-1) . The magnitude of force experienced by the proton in a magnetic field. vec B = (0.2 hat i + 0.4 hat k) telsa is |
|
Answer» a. `3.2 xx 10^(-13)` N |
|
| 37990. |
In the given circuit in the steady state (C_1= 2 mF and C_2 =6mF) |
|
Answer» `V_1=V_2 = 6Vand Q_1= Q_2 = 18 MC` |
|
| 37991. |
The thrust developed by a rocket-motor is given by F = mv + A(P_1 -P_2) where m is the mass of the gas ejected per unit time, v is velocity of the gas, A is area of cross-section of the nozzle, P_1 and P_2 are the pressures of the exhaust gas and surrounding atmosphere. The formula is dimensionally |
|
Answer» CORRECT |
|
| 37992. |
The surface of a charged conductor is an equipo tential surface Comment on this statement. |
| Answer» Solution :In a charged CONDUCTOR, at any point inside or at the SURFACE, the POTENTIAL is same. So the surface is EQUIPOTENTIAL. | |
| 37993. |
Explain the input and output characteristics curves for a common emitter transistor. |
Answer» Solution :COMMON emitter characteistics. The circuit diagram for common emitter p-n-p transistor is shown in fig.(a). The input is applied ACROSS the emitter and base and output is TAKEN across collector and emitter. Here emitter is common to both input and output circuits. The most important characteristics of common base connections are input characteristic and output characteristics.  `(i)` Input Characteristics A graph showing the relationship between base-emitter voltage and base-current and constant collector-emitter is called input characteristics of the transistor. To obtain input characteristic , the emitter is forward biased by base emitter voltage `V_(be)` and the collector is reverse biased by collector emitter voltage `V_(ce)`. The collector voltage `V_(ec)` is KEPT constant at a suitable value. The base voltage `V_(be)` is varied in small steps and the base current `I_(b)` is noted corresponding to each value of the base-emitter voltage. A curve is then plotted between `V_(bc)` and `I_(b)` for a given value of `V_(ce)`. This is one characteristic. Similar characteristic curves can be drawn for different fixed VALUES of `V_(ce)("say"-2V,-4V"etc)` as shown in fig. (b) .  `(ii)` Output characteristics . A graph showing the relationship between the collector base voltage and collector current at constant output characteristic of the transistor. To obtain output characterisitics the base current is kept constant at a suitable value the collector emitter voltage `V_(ce)` is varied in small steps and the collector current `I_(c)` is noted corresponding to each value of the base current `I_(b)` . A curve is then plotted between `V_(ce)` and `I_(c)` for a given value `I_(b)`. This is one characteristic. Similar characteristic curves can be drawn for different fixed  values of `I_(b)` (say `10muA`, `15muA`, `20muA` etc. as shown in fig.(c) |
|
| 37994. |
Refractive index of water is 4/3 and that of glass is 3/2 . What is the refractive index of glass with respect to water ? |
|
Answer» `9/8` Refractive index of glass in WATER = `n_(32)` Refractive index of water in air = `n_(21)` `n_(31)=n_(32)xxn_(21)=(n_(31))/(n_(21))=(3//2)/(4//3)=9/8` |
|
| 37995. |
How is size of a nucleus experimentally determined? Write the relation between the radius and mass number of the nucleus. Show that the density of nucleus is independent of its mass number. |
|
Answer» Solution :Size of a NUCLEUS is experimentally ESTIMATED from Rutherford’s alpha-particle scattering experiment. Radius R of a nucleus of mass NUMBER A is GIVEN by the relation: `R =R_(0)[A]^(1/3)`, where `R_(0)`=a constant=1.2 fm. |
|
| 37996. |
Three charges -1, +q and +q are situated in x-y plane at points (0, -a)(0,0) and (0, a) respectively. The potential at a point distant r(r gt a) in a direction making an angle theta from y - axis will be |
|
Answer» `(kq)/(r )` |
|
| 37997. |
The diameter of the objective of a telescope is 3 cm and its focal length is 60cm. If the diameter of the pupil of the eye is 2 mm, find the normal magnification of the telescope. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :For normal MAGNIFICATION, M = DIAMETER of the objective/Diameter of the pupil = 3/0.2 = 15 |
|
| 37998. |
The diameter of the objective of a telescope is 3 cm and its focal length is 60cm. If the diameter of the pupil of the eye is 2 mm, find the normal magnification of the telescope and the focal length of the eyepiece. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`f_0= 60CM, M = 15, f_e= ? ` `M = f_0/f_e, f_e = f_0/M = 60/15 = 4`CM |
|
| 37999. |
Two parallel long wires separated by a distance 'd' carry equal current 'i' What is the magnetic induction at a point mid way between the wires if (a) currents are in the same direction ? (b) currents are in opposite direciton ? |
| Answer» Solution :(a) ZERO (B)` (mu_0 i)/(2PI d//2) + (mu_0i)/(2pid//2) = (2 mu_0 i)/(pid)`. | |
| 38000. |
A disc revolves with a speed of 33(1)/(3) rev/min, and has a radius of 15 cm. Two coins are placed at 4 cm and 14 cm away from the centre of the record. If the coefficient of friction between the coins and the record ? |
|
Answer» Solution :For the COIN to revolve with be disc, the force of friction should be enough to provide the necessary centripetal force, i.e, `(mv^(2))/(r )le mu mg`. Now`v = r omega`, where `omega =(2pi)/(T)` is the angular frequency of the disc. For a given `mu` and `omega`, the condition is `r le (mu G)/(omega^(2))`. The condition is SATISFIED by the nearer coin (4 CM from the centre). |
|