Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Analyse the observation table which shows variation of image distance [v] with object distance [u] in the case of a convex lens. Answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations.{:("Sl.No","Object distance","Image distance"),(,"u [cm]","v [cm]"),(1,-90,+18),(2,-60,+20),(3,-30,+30),(4,-20,+60),(5,-18,+90),(6,-10,+100):}(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens ? Given reasons to support your answer.(b) Write the Sl.No of the observation which is not correct. How did you arrive at this conciusion ?(c ) Use an appropriate scale to draw the ray diagram for the observation at Sl. No 4 and find the approximate value of magnification. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) When `u=-30 cm , v=+30 cm`. This indicates that the OBJECT is at C1 [which is `2F_(1)`] R = 2f, 30 = 2f, f = 15 cm Focal length of the convex lens is + 15 cm. (b) If Object distance `u=-10 cm`, it means the object is placed between the optic centre and focus, a virtual erect image formed in this case on the same side as the object. Therefore v should be NEGATIVE according to Cartesian sign convention ie., `v=-100 cm` and not `v=+100` cm as mentioned in the table. Therefore SI. No 6 is incorrect. (c ) SI. No 4 `u=-20 cm , v=+60 cm F_(1)=-15 cm 2F_(1)=-30 cm` The object is between `F_(1)` and `2F_(1)`, an enlarged real and inverted image is formed BEYOND 2F, 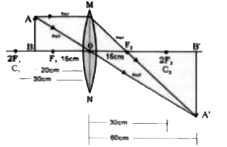 Magnification `=m = (v)/(u)=((+60))/((-20))=-3` |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- What is the reason for the twinkling of stars ?
- The change in magnetic field lines in a coil is the cause of induced electric current in it.Name the underlying phenomenon.
- Say True or False.The mass of the Earth is 6.4xx10^(6)kg.
- Whichof the follwing property of a proton can changewhileit moves freelyin a mageticfield ? (There may be more thanone correct answer).
- When an object is placed infront of a spherical mirror at a distance 30 cm, the magnification is -1. Illustrate the conclusions.
- Does the frequency of sound waes depend on the medium in which it travels?
- The relation between N (no. of molecules), P,V. & T is ...........
- What is magnification of a lens ?
- A person is said to be colour blind if he/ she has deficiency of rod shaped cells in retina of his eyes.
- "___________" prepares the 'Red List' that contains the names of endangered species from different countries.