Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Describe the behaviour of a wire undergradually increasing load. |
|
Answer» Solution :Behviour of a wire under increasing load : Let a wire is susdpended at one end and loads are attached to the other end. When loads are GRADUALLY the following changes are noticed. 1. Proportionality limit (A) : When load is increased the elongation of the wire gradually increases. The MAXIMUM load upto which the elogation is directly pro- portional to the load is called propor- tionality limit (A). The graph frawn bet- ween load and extension is a straight line . So point A is called proportionality limit. In this region Hooke.s Law is obeyed. 2. Elastic limit (B) : If the load is increased above the proportionality limit the elongation is not proportional to the load. Hooke.s law is not obeyed. But it exgibits elasticity which means that it regains the original length if load is removed. The maximum load on the wire upto which it exhibits elasticity is called elastic limit (B in the gaph). 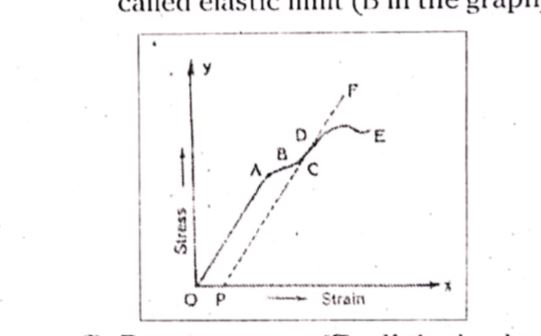 3. Permanent set (C) : If the load on the wire is increased beyond elastic limit say upto .C. , the elongation is not pro- portional to load. On removai of the load the wire does not regain its original length. in figure permanent set is given by OP. So OP is called permanent set. 4. Point of ultimate tensile strength (D) : If the load is further increased, upto .D. then strain increases rapidly even though there is no INCREASE in stress. At this stage the restoring forces seems to be subdued to then deforming forces. Elongation without increase in load is called creeping . This behaviour of metal is called yielding. 5. Fracture point (E) : If the load is incre- ased beyond yield point the elongation is very RAPID, even for small changes in load the wire becomes thinner and breaks. This is shown as E. The breaking force per unit area is called breaking stress. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- What is the reason for the twinkling of stars ?
- The change in magnetic field lines in a coil is the cause of induced electric current in it.Name the underlying phenomenon.
- Say True or False.The mass of the Earth is 6.4xx10^(6)kg.
- Whichof the follwing property of a proton can changewhileit moves freelyin a mageticfield ? (There may be more thanone correct answer).
- When an object is placed infront of a spherical mirror at a distance 30 cm, the magnification is -1. Illustrate the conclusions.
- Does the frequency of sound waes depend on the medium in which it travels?
- The relation between N (no. of molecules), P,V. & T is ...........
- What is magnification of a lens ?
- A person is said to be colour blind if he/ she has deficiency of rod shaped cells in retina of his eyes.
- "___________" prepares the 'Red List' that contains the names of endangered species from different countries.