Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Draw the graph of the equation 2x-y+3=0. Using the graph, find the value of y when (a) x=2, (b) x=-3. |
|
Answer» Solution :We have `2x-y+3=0 rArr y= 2x+3.""` …(i) Putting x=0in (i) , we get `y= (2 xx 0 + 3) = 3.` Putting x=1in (i), we get`y= ( 2xx 1 + 3) = 5.` Putting x=-1in (i), we get `y= [2 xx (-1) + 3] =1.` Putting x= -2in (i), we get `y=[2 xx (-2) + 3] =-1.` Thus, we have the following table: `{:(x,0,1,-1,-2),(y,3,5,1,-1):}` On a graph paper, draw lines X'OX and YOY' representingthe x-axis and the y- axis RESPECTIVELY. On this graph paper, plot the points A(0,3), B(1,5),C(-1,1) and D(-2,-1). Join AB, AC andCD to get a straight line BACD. Produce it in both ways to get the required graph. 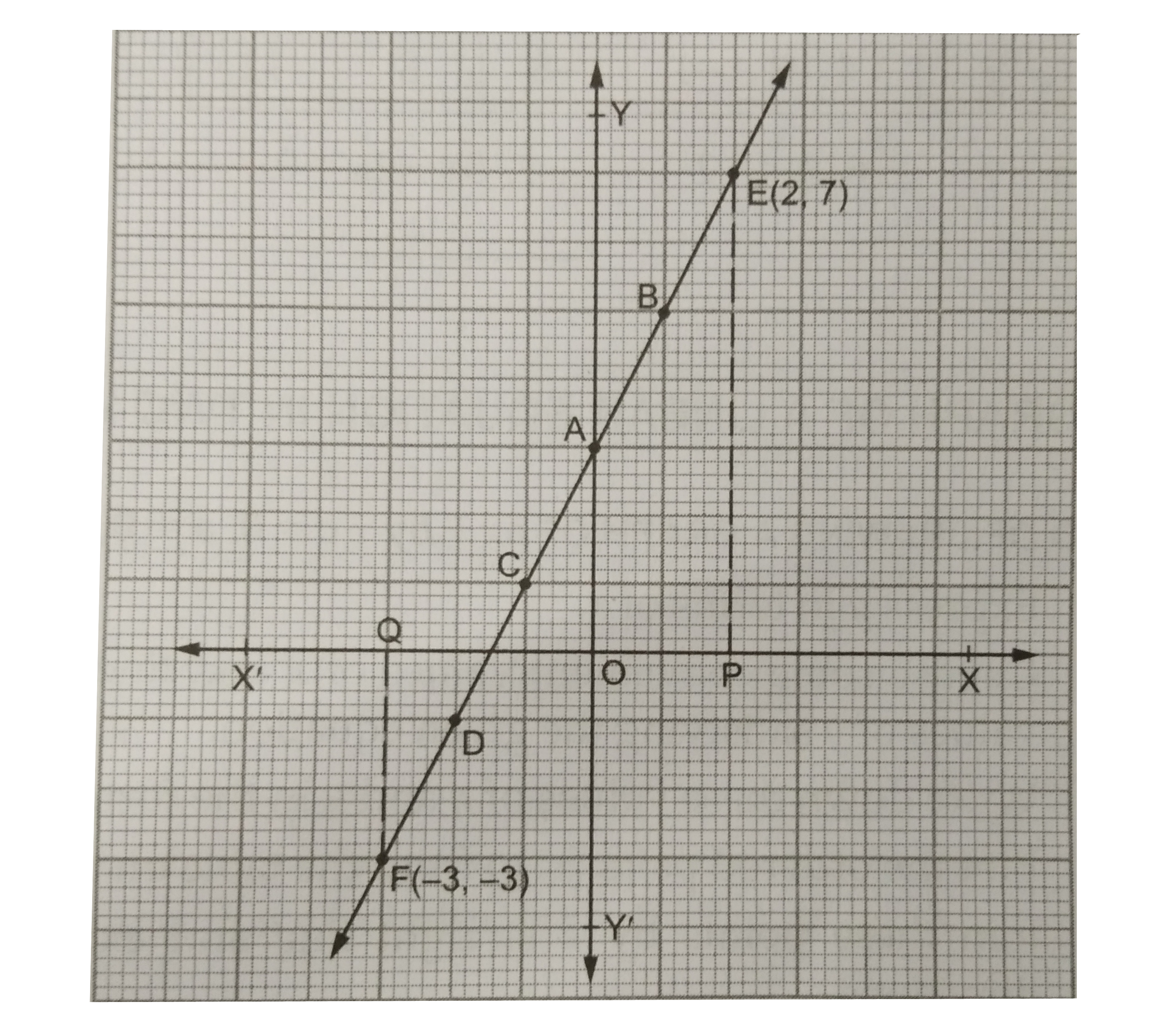 (a)On the axis, we take a point P for which x=2, i.e., OP=2. FromP, draw `PE bot X'OX`, meeting the graph line BACD produced at E. Then, E(2,7) shows that `(x=2 rArry=7),` i.e., when x=2, then y=7. (b) On the x-axis, we take a point Q for which `x=-3`, i.e., OQ = 3 units. From Q, draw `QF bot X'OX`, meeting the graph line BACD produced at F. Then, `F(-3,-3)` shows that `(x=-3 rArr y=-3)`, i.e., when x=-3, then y= -3. |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- Prove that 8sqrt(5) is irrational.
- A point C is said to lie between the points A and B if
- ABC is a triangle in which altitudes BE and CF to sides AC and AB are equal (see the given figure). Show that ( i ) triangle ABE ~= triangle ACF (ii) AB = AC i.e ABC is an isoceles triangle
- (a) (i) By takingany twoirrational numbers,prove that their sumis arational number. (ii) By takingany twoirrational numbers, prove that their difference is a rational number. (b) Insert in between1/7 and 2/7 (i)a rational number : (ii) an irrational number.
- Find the mean of all prime numbers between 20 and 50.
- The perimeter of an isosceles triangle is 100 cm. If the base is 36 cm, find the length of the equal sides.
- If A=60^(@), verify that : (i) sin^(2)A+cos^(2)A=1"(ii) "sec^(2)A-tan^(2)A=1
- Construct a DeltaABC whose perimeter is 10.5 cm and the base angles are 60^(@) and 45^(@).
- Draw an angle of 80^(@) with the help of protractor . Then, construct angles of (i) 40^(@) (ii) 160^(@) and (iii) 120^(@) .
- Water is pouring into a conical vessel of diameter 5.2m. And slant height 6.8 m(as shown in the adjoining ) , at the rate of 1.8 m^(3)per minute .How long will it take to fill the vessel?