Saved Bookmarks
| 1. |
Explain the metallurgy of iron. |
|
Answer» Solution : Iron is chiefly extracted from haematite ore `(Fe_(2)O_(3))` (i) Concentration by Gravity Separation: The powdered ore is washed with a steam of water.As a result, the lighter sand particles and other impurities are washed away and the heavier ore particles settle down (II) Roasting and Calcination: The concentrated ore is strongly heated in a limited supply of air in a reverberatory furnace.As a result, moisture is driven out and SULPHUR, arsenic and phosphorus impurities are oxidized off (iii) Smelting (in a Blast Furnace): The charge consisting of roasted ore, coke and limestone in the ratio 8: 4: is smelted in a blast furnace by introducing it through the cup arrangement at the top.There are three important areas in the furnace a.The Lower Regions (combustion Zone) : The temerature is at `15006(@)C` . In this regoins coke burns with oxygen to FORM `CO_(2)` when the charge comes in contact with a hot blast of air . `C+ O_(2)underset(Delta)overset(1500^(@)C) to Co_(2) + ("heat")` It is exothermic reaction since heata is liberated . 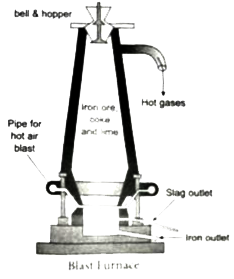 b.The Middle Regions ( Fusion Zone ) : The temperature prevails at `100^(@)C` in this regions `Co_(2)` is reduced to Co . `CO_(2)+ C underset(Delta) overset(1000^(@))to2CO-"Heat"` Limestone decomposes to calcium oxide and `CO_(2)` `CaCO_(3) underset(Delta)to CO_(2) - "Heat"` These two reactions are endothermic due to absorption of heat . Calcium oxide combines with silica to form calcium silicate slag. `CaO + SiO_(2)rightarrowCasiS_(3)` c.The Upper Regions ( Reduction Zone ) : The temperature prevails at `400^(@)C`. Inthis regions carbon monoxide reduces ferric oxide to form a fairly pure spongy iron . `Fe_(2)O_(3) + 3CO overset(400^(2)C)to 2Fe+ 3CO_(2)` . THe molten iron is collected at the bottom of the furnance after removing the slag . The iron this formed is called pig iron . It is remelted and cast into different moulds . This iorn is called cast iron . |
|
Discussion
No Comment Found
Related InterviewSolutions
- What is the name given to a pure substance with only one kind of atoms?
- What is the difference between pure gold and 22 carat gold? Which type of gold is used for making ornaments ?
- The term pH was coined by ______
- Write the formula of the product formed when the element A (atomic number 19) combines with the element B (atomic number 17). Draw its electronic dot structure. What is the nature of the bond formed?
- Which of the following metal is not found in a free state ?
- Why are alcohols poor conductors of electricity ?
- Which one of the following element is used as the standard for measuring the relativeatomic mass of an element in now a days?
- The thickness of _______ increases in the electrorefming of copper
- What do you think would happen when a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder is heated ?
- What is the formula of the next homologue of propene (C_3H_6)?