Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in Current Affairs.
This section includes 7 InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your Current Affairs knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1. |
Consider the following assembly language program for a hypothetical processor. A, B, and C are 8 bit registers. The meanings of various instructions are shown as comments.MOV B, # 0; B ← 0MOV C, # 8; C ← 8Z :CMP C, # 0; compare C with 0JZX; jump to X if zero flag is setSUB C, # 1; C ← C – 1RRC A, # 1; right rotate A through carry by one bit. Thus:; if the initial values of A and the carry flag are a7…a0 and; c0 respectively, their values after the execution of this; instruction will be c0a7…a1 and a0 respectively.JC Y; jump to Y if carry flag is setJMP Z; jump to ZY :ADD B, # 1; B ← B + 1JMP Z; jump to ZX :(A) the number of 0 bits in A0(B) the number of 1 bits in A0(C) A0(D) 8 |
| Answer» | |
| 2. |
Consider the following three claims1. (n + k)m = Θ(nm), where k and m are constants2. 2n + 1 = O(2n)3. 22n + 1 = O(2n) Which of these claims are correct ?(A) 1 and 2(B) 1 and 3(C) 2 and 3(D) 1, 2, and 3 |
| Answer» | |
| 3. |
Let G = (V, E) be an undirected graph with a subgraph G1 = (V1, El). Weights are assigned to edges of G as follows : A single-source shortest path algorithm is executed on the weighted graph (V, E, w) with an arbitrary vertex ν1 of V1 as the source. Which of the following can always be inferred from the path costs computed?(A) The number of edges in the shortest paths from ν1 to all vertices of G(B) G1 is connected(C) V1 forms a clique in G(D) G1 is a tree |
| Answer» | |
| 4. |
The following are the starting and ending times of activities A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H respectively in chronological order: “asbscsaedsceesfsbedegseefehsgehe”Here,xs denotes the starting time and xe denotes the ending time of activity X. W need to schedule the activities in a set of rooms available to us. An activity can be scheduled in a room only if the room is reserved for the activity for its entire duration. What is the minimum number of rooms required ?(A) 3(B) 4(C) 5(D) 6 |
| Answer» | |
| 5. |
The cube root of a natural number n is defined as the largest natural number m such that m3 ≤ n. The complexity of computing the cube root of n (n is represented in binary notation) is:(A) O(n) but not O(n0.5)(B) O(n0.5) but not O((log n)k) for any constant k > 0(C) O((log n)k) for some constant k > 0, but not O ((log log n)m) for any constant m > 0(D) O((log log n)m) for some constant k > 0.5, but not O((log log n)0.5) |
| Answer» | |
| 6. |
Let G (V, E) be a directed graph with n vertices. A path from vi to vj in G is sequence of vertices (vi, vi+1, ……., vj) such that (vk, vk+1) ∈ E for all k in i through j – 1. A simple path is a path in which no vertex appears more than once.Let A be an n x n array initialized as follow Consider the following algorithm.for i = 1 to n for j = 1 to n for k = 1 to n A [j , k] = max (A[j, k] (A[j, i] + A [i, k]); Which of the following statements is necessarily true for all j and k after terminal of the above algorithm ?(A) A[j, k] ≤ n(B) If A[j, k] ≥ n – 1, then G has a Hamiltonian cycle(C) If there exists a path from j to k, A[j, k] contains the longest path lens from j to k(D) If there exists a path from j to k, every simple path from j to k contain most A[j, k] edges |
| Answer» None | |
| 7. |
What is the weight of a minimum spanning tree of the following graph ?(A) 29(B) 31(C) 38(D) 41 |
| Answer» | |
| 8. |
In a permutation a1…..an of n distinct integers, an inversion is a pair (ai, aj) such that i aj. If all permutations are equally likely, what is the expected number of inversions in a randomly chosen permutation of 1…..n ?(A) n(n – 1)/2(B) n(n – 1)/4(C) n(n + 1)/4(D) 2n[log2 n] |
| Answer» None | |
| 9. |
Consider the following 2-3-4 tree (i.e., B-tree with a minimum degree of two) in which each data item is a letter. The usual alphabetical ordering of letters is used in constructing the tree.What is the result of inserting G in the above tree ?A) B) C) D) None of the above(A) A(B) B(C) C(D) D |
| Answer» | |
| 10. |
Let S be a stack of size n ≥ 1. Starting with the empty stack, suppose we push the first n natural numbers in sequence, and then perform n pop operations. Assume that Push and pop operation take X seconds each, and Y seconds elapse between the end of one such stack operation and the start of the next operation. For m ≥ 1, define the stack-life of m as the time elapsed from the end of Push(m) to the start of the pop operation that removes m from S. The average stack-life of an element of this stack is(A) n (X + Y)(B) 3Y + 2X(C) n (X + Y) – X(D) Y + 2X |
| Answer» None | |
| 11. |
Consider the grammar shown below.S → C CC → c C | dThe grammar is(A) LL(1)(B) SLR(1) but not LL(1)(C) LALR(1) but not SLR(1)(D) LR(1) but not LALR(1) |
| Answer» | |
| 12. |
Consider the grammar shown belowS → i E t S S' | aS' → e S | εE → b In the predictive parse table. M, of this grammar, the entries M[S’, e] and M[S’, $] respectively are(A) {S’ → e S} and {S’ → e}(B) {S’ → e S} and {}(C) {S’ → ε} and {S’ → ε}(D) {S’ → e S, S’→ ε} and {S’ → ε} |
| Answer» | |
| 13. |
Which of the following suffices to convert an arbitrary CFG to an LL(1) grammar?(A) Removing left recursion alone(B) Factoring the grammar alone(C) Removing left recursion and factoring the grammar(D) None of these |
| Answer» | |
| 14. |
Assume that the SLR parser for a grammar G has n1 states and the LALR parser for G has n2 states. The relationship between n1 and n2 is:(A) n1 is necessarily less than n2(B) n1 is necessarily equal to n2(C) n1 is necessarily greater than n2(D) none of these |
| Answer» | |
| 15. |
In a bottom-up evaluation of a syntax directed definition, inherited attributes can(A) always be evaluated(B) be evaluated only if the definition is L-attributed(C) be evaluated only if the definition has synthesized attributes(D) never be evaluated |
| Answer» | |
| 16. |
Assuming all numbers are in 2’s complement representation, which of the following numbers is divisible by 11111011?(A) 11100111(B) 11100100(C) 11010111(D) 11011011 |
| Answer» | |
| 17. |
A 1-input, 2-output synchronous sequential circuit behaves as follows :Let zk, nk denote the number of 0’s and 1’s respectively in initial k bits of the input (zk + nk = k). The circuit outputs 00 until one of the following conditions holds. zk - nk = 2. In this case, the output at the k-th and all subsequent clock ticks is 10. nk - zk = 2. In this case, the output at the k-th and all subsequent clock ticks is 01.What is the minimum number of states required in the state transition graph of the above circuit?(A) 5(B) 6(C) 7(D) 8 |
| Answer» | |
| 18. |
Consider an array multiplier for multiplying two n bit numbers. If each gate in the circuit has a unit delay, the total delay of the multiplier is(A) Θ(1)(B) Θ(log n)(C) Θ(n)(D) Θ(n2) |
| Answer» None | |
| 19. |
The literal count of a boolean expression is the sum of the number of times each literal appears in the expression. For example, the literal count of (xy + xz’) is 4. What are the minimum possible literal counts of the product-of-sum and sum-of-product representations respectively of the function given by the following Karnaugh map ? Here, X denotes “don’t care”(A) (11, 9)(B) (9, 13)(C) (9, 10)(D) (11, 11) |
| Answer» | |
| 20. |
Which of the following scenarios may lead to an irrecoverable error in a database system ?(A) A transaction writes a data item after it is read by an uncommitted transaction(B) A transaction reads a data item after it is read by an uncommitted transaction(C) A transaction reads a data item after it is written by a committed transaction(D) A transaction reads a data item after it is written by an uncommitted transaction |
| Answer» | |
| 21. |
The following resolution rule is used in logic programming.Derive clause (P ∨ Q) from clauses (P ∨ R), (Q ∨ ¬R) Which of the following statements related to this rule is FALSE?(A) ((P ∨ R) ∧ (Q ∨ ¬R)) ⇒ (P ∨ Q) is logically valid(B) (P ∨ Q) ⇒ ((P ∨ R)) ∧ (Q ∨ ¬R)) is logically valid(C) (P ∨ Q) is satisfiable if and only if (P ∨ R) ∨ (Q ∨ ¬R) is satisfiable(D) (P ∨ Q) ⇒ FALSE if and only if both P and Q are unsatisfiable |
| Answer» | |
| 22. |
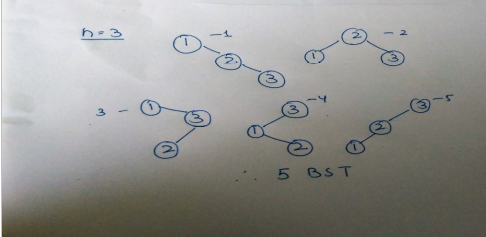
Let T(n) be the number of different binary search trees on n distinct elements.Then , where x is(A) n-k+1(B) n-k(C) n-k-1(D) n-k-2 |
|
Answer» Answer: (B) Explanation: The idea is to make a key root, put (k-1) keys in one subtree and remaining n-k keys in other subtree. A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a tree in which all the nodes follow the below-mentioned properties −
Now construction binary search trees from n distinct number- If n=3 We have 5 possibilities. Keeping each number first as root and then arranging the remaining 2 numbers as in case of n=2. |
|
| 23. |
How many perfect matchings are there in a complete graph of 6 vertices ?(A) 15(B) 24(C) 30(D) 60 |
| Answer» | |
| 24. |
A graph G = (V, E) satisfies |E| ≤ 3 |V| – 6. The min-degree of G is defined as . Therefore, min-degree of G cannot be(A) 3(B) 4(C) 5(D) 6 |
| Answer» | |
| 25. |
Let G be an arbitrary graph with n nodes and k components. If a vertex is removed from G, the number of components in the resultant graph must necessarily lie between(A) k and n(B) k – 1 and k + 1(C) k – 1 and n – 1(D) k + 1 and n – k |
| Answer» | |
| 26. |
Consider the translation scheme shown belowS → T RR → + T {print ('+');} R | εT → num {print (num.val);} Here num is a token that represents an integer and num.val represents the corresponding integer value. For an input string ‘9 + 5 + 2’, this translation scheme will print(A) 9 + 5 + 2(B) 9 5 + 2 +(C) 9 5 2 + +(D) + + 9 5 2 |
| Answer» None | |
| 27. |
Consider the syntax directed definition shown below.S → id : = E {gen (id.place = E.place;);}E → E1 + E2 {t = newtemp ( ); gen (t = El.place + E2.place;); E.place = t}E → id {E.place = id.place;} Here, gen is a function that generates the output code, and newtemp is a function that returns the name of a new temporary variable on every call. Assume that ti’s are the temporary variable names generated by newtemp.For the statement ‘X: = Y + Z’, the 3-address code sequence generated by this definition is(A) X = Y + Z(B) t1 = Y + Z; X = t1(C) t1 =Y; t2 = t1 + Z; X = t2(D) t1 = Y; t2 = Z; t3 = t1 + t2; X = t3 |
| Answer» | |
| 28. |
A program consists of two modules executed sequentially. Let f1(t) and f2(t) respectively denote the probability density functions of time taken to execute the two modules. The probability density function of the overall time taken to execute the program is given by : A) B) C) D) (A) A(B) B(C) C(D) D |
| Answer» | |
| 29. |
Consider the following class definitions in a hypothetical Object Oriented language that supports inheritance and uses dynamic binding. The language should not be assumed to be either Java or C++, though the syntax is similar.Class P{ void f(int i) { print(i); }}Class Q subclass of P{ void f(int i) { print(2*i); }}Now consider the following program fragment:P x = new Q();Q y = new Q();P z = new Q();x.f(1); ((P)y).f(1); z.f(1); Here ((P)y) denotes a typecast of y to P. The output produced by executing the above program fragment will be(A) 1 2 1(B) 2 1 1(C) 2 1 2(D) 2 2 2 |
| Answer» | |
| 30. |
A processor uses 2-level page tables for virtual to physical address translation. Page tables for both levels are stored in the main memory. Virtual and physical addresses are both 32 bits wide. The memory is byte addressable. For virtual to physical address translation, the 10 most significant bits of the virtual address are used as index into the first level page table while the next 10 bits are used as index into the second level page table. The 12 least significant bits of the virtual address are used as offset within the page. Assume that the page table entries in both levels of page tables are 4 bytes wide. Further, the processor has a translation look-aside buffer (TLB), with a hit rate of 96%. The TLB caches recently used virtual page numbers and the corresponding physical page numbers. The processor also has a physically addressed cache with a hit rate of 90%. Main memory access time is 10 ns, cache access time is 1 ns, and TLB access time is also 1 ns.Suppose a process has only the following pages in its virtual address space: two contiguous code pages starting at virtual address 0x00000000, two contiguous data pages starting at virtual address 0×00400000, and a stack page starting at virtual address 0×FFFFF000. The amount of memory required for storing the page tables of this process is:(A) 8 KB(B) 12 KB(C) 16 KB(D) 20 KB |
| Answer» None | |