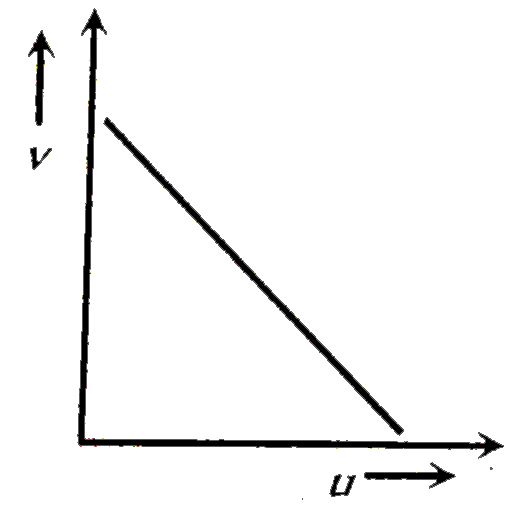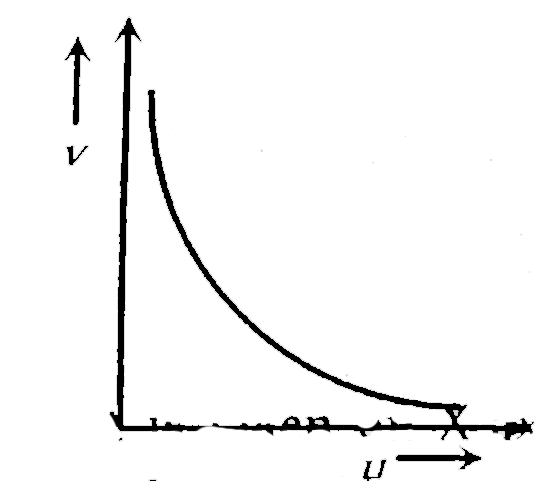Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 41801. |
Carefull measurement of the electric field at the surface of ablack box indicates that the net outwards flux through the surface of the box is 8.0xx10^(3) Nm^(2) //C What is the net charges inside the box? If the net outwardsflux through the surface of the were zero ,could you concide that there were no charges insidethe box? Why or why not? |
|
Answer» Solution :` because ` Netoutwards flux `phi _E =8.0xx 10^(3)NM^(2) //C ` From the mathematical expression of Gauss. theorem `phi_E=(q)/(in_0) , ` we find that Net charges insidethe box `q =phi _E. in _0=8.0 xx 10 ^(3)xx 8.55 xx 10^(-12) C ` ` =7.08 xx 10^(-8)C = 0.07 muC .` If the net outwards flux through the surfaceof the box were zero thanin ACCORDANCE with GAUS theorem we conclude that the net charge inside the box were zero. It means that either no charges we present in the box or charges were present inside the box but their ALGEBRAIC sum was zero. |
|
| 41802. |
In biprismexperiment, 10th dark band is observed at 2.09 mm from the centralbright point on the screenwith red light of wavelength6400 Å. By how muchwill fringe width change if blue lightof wavelength 4800Å is used with thesame setting ? |
|
Answer» Solution :In the biprism experiment, the `10^(th)`dark band isobserved.The distancebetween the`m^(th)`dark band with the central bright band is `x_(m) = (2m-1) (lambda D)/(2d)` Therefore, the DISTANCEFOR the `10^(th)`dark band is `x_(10) = ((2 xx 10)- 1) (lambdaD)/(2d) = (19lambdaD)/(2d)` Now, when red light is used, we have `(x_(10))_r = (19 lambda_(r)D)/(2d) "....."(i)` Similarly, for blue light, we have `(x_(10))_(b) = (19 lambdaD)/(2d) "....."(ii) ` Now, the fringewidth is `x = (lambdaD)/(d)` `:.` For red light, `x_(r) = (lambda_(r)D)/(d) "....."(iii)` `:.` For blue light, `x_(b) = (lambda_(b)D)/(d) "...."(IV)` From equations (i)and (iii), we get `(x_(10)) = (19x_(r))/(2) = 2.09mm` `:. x_(r) = (2 xx 2.09)/(19) = 0.22` mm Dividing equations (i) and (ii), we get `((x_(10))_(r))/((x_(10))_(b)) = ((19 lambda_(r)D)/(2d))/((19 lambda_(b)D)/(2d)) = (lambda_(r))/(lambda_(b))` `:. (x_(10))_(b) = (lambda_(b) xx (x_(10))_(r))/(lambda_(r))` `= (4800 xx 10^(-10) xx 2.09)/(6400 xx 10^(-10))` Now, from equations (ii) and (iv), we get `(x_(10))_(b) = (19x_(b))/(2) = 1.57 mm` `:. x_(b) = (2 xx 1.57)/(19) = 0.165 mm` Therefore, thechange in the fringe width when blue lightis used INSTEAD of red is `x_(r) - x_(b) = 0.22 - 0.165= 0.055 mm`. |
|
| 41803. |
X-rays of wavelength lambda fall onphotosensitive surface, emitting electrons. Assuming that the work function of the surface can be neglected, prove that the de-broglie wavelength of electrons emitted will be sqrt((hlambda)/(2mc)). |
| Answer» Solution :`E=(HC)/lambda=(P^2)/(2m) THEREFORE P=sqrt((2mnc)/(lambda)),lambda_e=h/Psqrt((hlambda)/(2MC))` | |
| 41804. |
Tension in the strings is 100 N mass per unit length of strings is 0.01 kg/m, velocity of sound in air is 320 m/s. Column I : gives situation. Column II : gives frequency of resonance. Column III: gives wavelength for corresponding resonating frequency. Choose the correct option corresponding to maximum wavelength. |
|
Answer» <P>(I) (III) (P) |
|
| 41805. |
The refracting angle of a prism is 45^(@) and the refractive index of the material of the prism is 1.6. What should be the minimum angle of deviation of a ray on a face of the prism so that no internal reflection of the ray takes place on the second face at the time of emergence. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41806. |
A piece of wire of resistance 4Omega is bent through 180^(@) at its midpoint and the two halves are twisted together. Then the resistance is |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 41807. |
At particular instant a source of sound of frequency 1000 Hz is at (2m,1m) and an observer is at (5m,5m). The velocity of source and observer are 30(hati+hatj)m//s and 15(hati+sqrt(3)hatj)m//s respectively at this instant. The velocity of sound in air is 330 m/s. find the frequency and wavelength of sound received by the observer. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41808. |
f:NrarrN f(x)=x^2+x+1 is |
|
Answer» ONE-one and onto |
|
| 41809. |
The half life period of a radioactive sample depends upon |
|
Answer» TEMPERATURE |
|
| 41810. |
An aluminiumsphere is dipped into water. Which of the following is true? |
|
Answer» Buoyancy in water at `0^@`C will be same as that in water at `4^@`C |
|
| 41811. |
Tension in the strings is 100 N mass per unit length of strings is 0.01 kg/m, velocity of sound in air is 320 m/s. Column I : gives situation. Column II : gives frequency of resonance. Column III: gives wavelength for corresponding resonating frequency. Choose the correct option for a process in which system is vibration in 7 th harmonic. |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 41812. |
Tension in the strings is 100 N mass per unit length of strings is 0.01 kg/m, velocity of sound in air is 320 m/s. Column I : gives situation. Column II : gives frequency of resonance. Column III: gives wavelength for corresponding resonating frequency. Pick correct combination. |
|
Answer» <P>(III) (i) (S) |
|
| 41813. |
In a class of 60 students, 25 students play cricket and 20 students play tennis, and 10 students play both the games. Then, the number of students who play neither is? |
|
Answer» 0 |
|
| 41814. |
Determine the current drawn from a 12V supply with internal resistance 0.5Omegaby the infinite network shown in figure. Each resistor has 1 Omegaresistance. |
| Answer» Solution :LET X be the equivalent resistance of the INFINITE NETWORK. Clearly, `2+X//(X+1)= X` which gives , therefore the CURRENT is 3.7A | |
| 41815. |
If the mass of a body is M on the surface of the earth, the mass of the same body on the surface of the moon is |
|
Answer» M So correct choice is (a). |
|
| 41816. |
A radioactive element ""_(90)X^(238) decays into ""_(83)Y^(222). The number of beta-particular emitted are : |
|
Answer» 4 |
|
| 41817. |
A simple pendulum executing S.H.M. has period T and amplitude A. Its speed, when at a distance (A)/(4) is : |
|
Answer» `(piAsqrt(15))/(2T)` `=(2pi)/(T)sqrt((15)/(16)A^(2))=(PI sqrt(15)A)/(2T)` Hence correct choice is(a). |
|
| 41818. |
Consider the following nuclear decay: ""_(92)^(236)Uto""_(90)^(234)Th+X Determine the amount of energy released in this decay. Use the following atomic masses. ""_(92)^(236)=236.045562u, ""_(90)^(232)Th=232.038054u ""_(2)^(4)He=4.002603u, ""_(0)^(1)n=1.008665u and ""_(1)^(1)p=1.007277h Conversion factors 1u=931.5meV, 1eV=1.602xx10^(-19)J |
|
Answer» `3.5xx10^(-8J` |
|
| 41819. |
If coulomb's law were F=K(qQ)/(r^(3)), calculate the electric field due to a uniformly charged line charge at a distance d from it. The linear charge density on the line charge is lamda C/m, and it is of infinite length. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41820. |
A beam of alpha -particle passes without deflection through crossed electric and magnetic fields with E=6.6xx10^(6) N/C and B=12 N/Am. Their speed is : |
|
Answer» `1.8xx10^(5)MS^(-1)` |
|
| 41821. |
Three charges, 4muC each, are kept at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side 9 cm. Find magnitude of force on any charge. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41822. |
A 600 pF capacitor is charged by a 200 V supply. It is then disconnected from the supply and isconnected to another uncharged 600 pF capacitor. How much electrostatic energy is lost in theprocess ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `C_1 = C_2= 600 pF = 6 xx 10^(-10) F, V_1 = 200 V and V_2 = 0` Loss of electrostatic energy on sharing charges `Delta u = (C_1C_2(V_1-V_2)^2)/(2(C_1 + C_2)) = (6 xx 10^(-10) xx 6 xx 10^(-10) xx (200-0)^2)/(2 (6 xx 10^(-10) + 6 xx 10^(-10))` `=(6 xx 10^(-10) xx 6 xx 10^(-10) xx 200 xx 200)/(2 xx 12 xx 10^(-10)) =6 xx 10^(-6)J`. |
|
| 41823. |
You are given two spheres of same material and radii 10 cm and 20 cm. They are heated to the same temperature. They are placed in the same environment. The ratio of their rates of cooling will be: |
|
Answer» `1 : 2` `(dT)/(dt) = (e A SIGMA)/(mc) (T^(4) -T_(0)^(4))` `rArr (dT)/(dt) prop (A/(m) ` `prop (R^(3))/(r^(3))` `prop (1)/( r )` `rArr (((dT)/(dt))_(1))/((dT)/(dt))_(2) =(20)/(10) =(2)/(1)` |
|
| 41824. |
A man fixes outside his house one evening a two metre high insulating slab carrying on its top a large aluminium sheet of area 1 m^(2). Will he get an electric shock if he touches the metal sheet next morning ? |
| Answer» Solution :Yes, the man will get an electric shock if he touches the metal SLAB NEXT morning. The steady discharging current in the atmosphere charges up the aluminium sheet. Hence, its voltage rises gradually. The raise in the voltage depends on the capacitance of the capacitor formed by the aluminium slab and the GROUND. | |
| 41825. |
In a nuclear fission 0.1% of mass is converted into energy. The energy released by the fission of 1kg mass is |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 41826. |
Consider two solid dielectric spheres of radius a, separated by a distance R(R gt gt a). One of the spheres has a charge q, and the other is neutral (see figure). We double the distance between two sphere. How much charge should reside on the first sphere now so that the force between the spheres remains the same ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41827. |
Equations y=2 A cos^2 omega t and y = A ( sin omega t + sqrt3 cos omega t) represent the motion of two particles. |
|
Answer» Only ONE of these is S.H.M |
|
| 41828. |
A standing wavc is formed by two harmonic waves, y_1 = A sin (kx - omegat) and y_2= A sin(kx + omega t) travelling on a string in opposite directions. Mass density of the string is rho and area of cross - section is s. Find the total mechanical energy between two adjacent nodes on the string. |
|
Answer» Solution :The distance between two adjacent nodes is `lambda/2 or pi/k`. `:.` Volume of string between two nodes will be V =(area of cross-section) (distance between two nodes) `=(s) = (pi/k)`.Energy density (energy per unit volume) of a TRAVELLING wave is GIVEN `U = 1/2 rho A^2 omega^2`. A standing wave is FORMED by two idential waves travelling in oposite directions. Therefore, the energy stored between two nodes in a standing wave E = 2[energy stored in a distance of `pi/k` of travelling wave] = 2 (energy density) (volume) `=2(1/2 rhoA^2 omega^2) ((pi s)/k) or E =(rho A^2 omega^2 pis )/k` |
|
| 41829. |
Derive an expression for the induced emf and induced current produced by changing the area of a rectangular coil placed perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. |
Answer» Solution : CONSIDER a U-shaped conductor abcd LYING normal to a uniform magnetic field `vecB`. Let a conductor rod PQ is placed on frame abed and let it be moving with a uniform velocity `VECV`. As the rod MOVES by a small distance dx = v dt, the area enclosed changes from QcbP to Qʻcbp. CONSIDER a U-shaped conductor abcd LYING normal to a uniform magnetic field `vecB`. Let a conductor rod PQ is placed on frame abed and let it be moving with a uniform velocity `VECV`. As the rod MOVES by a small distance dx = v dt, the area enclosed changes from QcbP to Qʻcbp. Thus, change in magnetic FLUX `df_(B) = B(dA) = B [area QcbP to Q.cbP.]` = B (area Q.QPP.) = B l dx = B lvdt `therefore` magnitude for induced emf `|varepsilon| = (dphi_(B))/dt = (Blvdt)/dt = Blv` If R be the resistang of the loop then induced current `|I| = (|varepsilon|)/R = (Blv)/R.` |
|
| 41830. |
The Number of silicon atoms per m^(3) is 5 xx 10^(28) . This is doped simultaneously with5 xx 10^(22) atoms per m^(3) of Arsenic and 5 xx 10^(20)per m^(3) atoms of Indium. Calculate the number of electron and holes. Given that n_(i)= 1.5 xx 10^(16) m^(-3). Is the material n-type or p-type? |
|
Answer» Solution :We known that for each atomdoped of ARSENIC one free electron is received . Similarly , for each atom doped of indium a vacancyis created .So, the number of free electrons INTRODUCED by pantavalent impurity added. `n_( e) = N_( A s)= 5xx 10^(22) m^(3)`...(i) The number of holes introduced by trivalent impurity added. Now, `n_( e ) -n_(h) = 5 xx10^(22) - 5 xx 10^(20) =4.95 xx 10^(20)` ....(ii) So, ` ( n_( e ) +n_(h))^(2) = ( n_(e ) - n_(h))^(2) +4n_(e ) n_(h )` `n_( e ) + n_(h ) = sqrt((4.95xx10^(22))^(2)+( 4.15 xx 10^(16))^(2))`...(iii) AddingEqs (iii) and (ii) `2n_( e ) = 4.95 xx 10^(22)+ sqrt((4.95 xx10^(22))^(2) + 4( 1.5 xx 10^(10))^(2))` `n_(e ) = (1)/(2) ( 4.95 xx 10^(22) + sqrt(( 4.95 xx10^(22))^(2)))` `= n_( e ) = 4.95xx 10^(22) // m^(2) ` Now `n_(i) ^(2) = n_(h ) xx n _( e ) ` `n_( h ) =( n_(i)^(2))/( n_(e ))= ((1.5 xx 10^(16))^(2))/( 4.95 xx 10^(22))=4.54 xx 10^(9) //m^(3)` As number of electrons `n_(e )( = 4.95 xx 10^(22))` is greater than the number of holes `n_(h ) (=4.5 xx10^(9))` . So the MATERIAL is n-type semicoductor. |
|
| 41831. |
A particle starts from point A moves along a straight line path with an aceleration given by a=p-qx where p,q are constants and x is distance from point A. The particle stops at point B. The maximum velocity of the paticle is |
|
Answer» `p/q` |
|
| 41833. |
(A): It is desirable to slow down fast moving neutrons to sustain controlled chain reactions. (R): Slow moving neutrons efficiently collides with U^(235) |
|
Answer» Both .A. and .R. are true and .R. is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of .A. |
|
| 41834. |
(A): ""_(27)^(60)C_(0)is a source of gamma radiation. (R) : Gamma emission is due to nuclear decay |
|
Answer» Both .A. and .R. are true and .R. is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of .A. |
|
| 41835. |
Draw the graph to show variation of binding energy per nucleon with mass number of different atomic nuclei. Calculate binding energy per nucleon of " "_(20)^(40)Ca nucleus. Given : mass of " "_(20)^(40)Ca = 39.962589 u, mass of proton=1.007825 u, mass of neutron=1.008665 u and 1 u=931 MeV/c^(2). |
|
Answer» Solution : Binding ENERGY of `" "_(20)^(40)Ca` nucleus `E_(b) =[20m_(p) + 20m_(n)-m (" "_(20)^(40)Ca)] xc^(2)= [20 XX 1.007825 + 20 xx 1.008665 - 39.962589] u xx c^(2)= 0.367211 u xx c^(2) = 0.367211 xx 931 MeV = 341.8 MeV`. `THEREFORE` Binding energy per nucleon `E_(bn) =341.8/40= 8.545 MeV` /nucleon. |
|
| 41836. |
What sort of arrangement is to be taken so that an object cannot be visible even in light? Or, why is a place of glass immersed in glycerine not visible? |
|
Answer» Solution :An object having nearly the same refractive index as the medium will not be VISIBLE in that medium. SINCE the refractive indices of both of them are nearly the same, reflection or refraction of visible RAY almost does not take place at their surface of separation and light will travel almost undeviated through them. Then in cannot be understood that light in traveling from one medium to another. It seems as if light is moving in the same medium. As a result, the surface of separation is not visible. So a medium VANISHES in the other medium. The refractive indices of glycerine and glass are almost equal. So when a PIECE of glass is immersed in glycerine kept in a vessel, the piece of glass in not visible. |
|
| 41837. |
A : In Young.s double slit experiment, we observe an interference pattern on the screen if both the slits are illuminated by two bulbs of same power. R : The interference pattern is obserbed only when source are monochromatic. |
|
Answer» Both A and R are TRUE and R is the correct explanation of A |
|
| 41838. |
At what temperature will the rms speed of air molecules be double that of NTP? |
|
Answer» `519^(@)C` But at TEMPERATURE T, `v_(rms)=2xxsqrt((3RT_(0))/(M))` `implies sqrt((3RT)/(M))=2sqrt((3RT_(0))/(M))impliesT=4T_(0)` `T=4xx273K=1092KthereforeT=819^(@)C` |
|
| 41839. |
Which physical quantity remains unchanged in a transformer ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The FREQUENCY of ALTERNATING VOLTAGE. | |
| 41840. |
Infrared radiation was discovered in 1800 by |
|
Answer» William Wollaston |
|
| 41841. |
Charge in LC oscillations, |
|
Answer» DECREASES continuously. |
|
| 41842. |
A fuse wire is a wire of |
|
Answer» LOW RESISTANCE and low MELTING point |
|
| 41843. |
If 10% of a substance decays in 10 days, then approximate percentage of substance left after 24 days |
|
Answer» 78 `(X)/(100)=(1/2)^(24//T)` TAKING logs, we get `log"" (9)/(100)=(10)/T log"" 1/2 & log ""(X)/(100)=(24)/(T) log""1/2` Dividin, we get `(log X)/(log 100) "/" log (90)/(100) =((24)/(T) log 1//2)/((10)/(T) log 1//2)=2.4` Then, X=77.8 |
|
| 41844. |
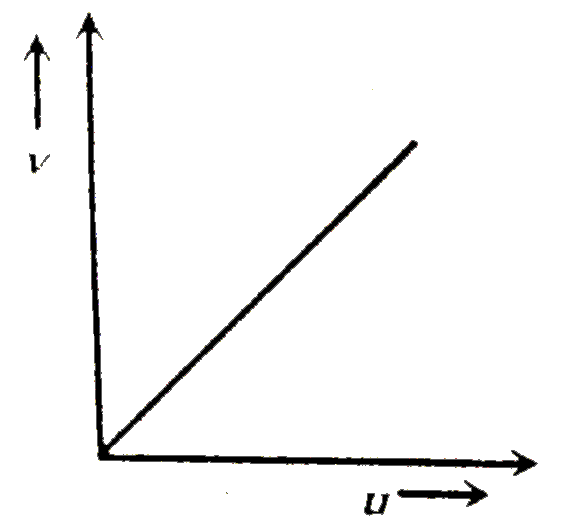
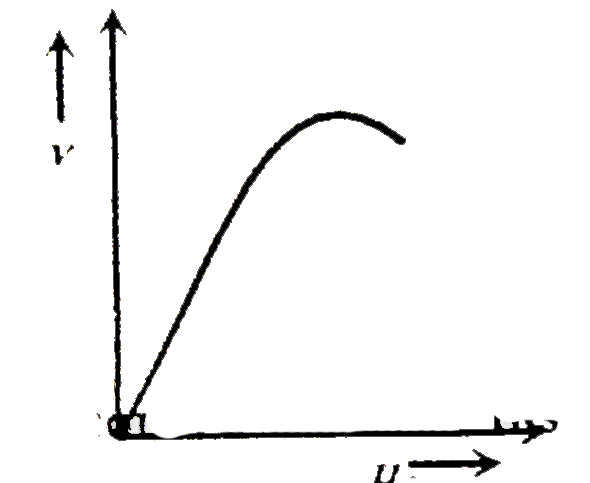
The distance v of the real image formed by a convex lens is measured for various object distance u . A graph is plotted between v and u , which one of the following graphs is correct |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 41845. |
Value of dielectric constant of metal is....... |
|
Answer» infinite |
|
| 41846. |
The number of turns in the primary coil of a transformer is 1000A. A power of 2kW is fed to it by a current of 0.1A. The number of turns in the secondary coil in order to produce a voltage of 200V in it, will be |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 41847. |
What is atomic mass ? |
| Answer» Solution :It is defined as the TOTAL MASS of PROTONS, NEUTRONS and electrons EXPRESSED in a.m.u. | |
| 41848. |
A step down transformer has _____ gt_____ and _____gt _____ . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`E_S` and `E_P, I_S` and `I_P` | |
| 41849. |
(a) Write Einstein's photoelectric equation. State clearly how this equation is obtained using the photon picture of electromagnetic radiation. (b) Write the three salient features observed in photoelectric effect which can be explained using this equation. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) To Explain photoelectric emission, Einstein assumed that emission of a photoelectron was the result of interaction of a single incident photon with a stationary ELECTRON PRESENT in metal surface, in which photon is completely absorbed by the electron. we know that to remove the electron, a minimum energy `phi_(0)` (known as work function of given metal) is REQUIRED. thus, when a photon of energy E=hv is absorbed by an electron, an energy `phi_(0)` (PROVIDED that `hvgt phi_(0)`) is used up in liberating the electron and balance energy appears as kinetic energy `K_(max)` of ejected photo electron. `therefore hv=phi_(0)+K_(max)` . . (i) If we go on reducing v then for a certain frequency`v_(0)` (known as THRESHOLD frequency) `K_(max)` becomes just equal to zero. then `hv_(0)=phi_(0)` Combining the two results, we obtain `hv=hv_(0)+K_(max)`. `implies h(v-v_(0))=K_(max)=(1)/(2)mv_(max)^(2)`. . (ii) if `V_(0)` be the stopping potential, then `K_(max)=eV_(0)` and hence, we have `h(v-v_(0))=eV_(0)` Equation written either as (i) or (ii) or (iii) is known as Einstein.s photoelectric equation. |
|
| 41850. |
In the diode-based rectifier circuit given below, if V_(s) =V_(m)sin omega t and the diode is ideal, then the average value of V_(L) is |
|
Answer» `(R_(L))/((R_(L) + R_(S))) (V_(m))/(PI)` 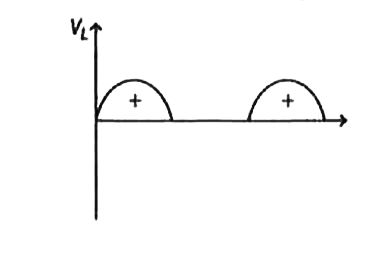 Average voltage,` V _(av) = (V_(m))/(pi)` average current `I _(av) = (V_(av))/(R)` Toal resistance, `R = R_(s) + R_(L)` `L _(av )=(V_(m))/((R_(S) + R_(L))pi)` Now, voltage across `R_(L),` `V_(L) =I_(av) . R_(L)` `V_(L) = (R_(L))/(R_(S) + R _(L)). (V_(m))/(pi)` |
|