Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 44351. |
In a permanent magnet at room temperature |
|
Answer» magnetic MOMENT of each MOLECULE is zero. |
|
| 44352. |
In a moving cool galvanometer, current 1 is proportional to what ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`THETA`ANGLE of DEFLECTION | |
| 44353. |
In question 28, imagine a battery of emf E between the points 0 and 1, with its positive terminal connected with O. |
|
Answer» The current entering at O is equally divided into three `"RESISTANCES"`. `R_(01), R_(02), and R_(03)` are in PARALLEL having same potential difference, so they will have same current. Also current at O is equally divided among three resistances. |
|
| 44354. |
Micro wave link repeaters are typically 50 km apart |
|
Answer» because of atmospheric ATTENUATION |
|
| 44355. |
Define the term 'drift velocity' of charge carriers in a conductor and write its relationship with the current flowing through it. |
|
Answer» Solution : Drift velocity of CHARGE carriers in a CONDUCTOR is defined as that average velocity with which chargecarriers drift in the presence of an external electric field. Current` I=n Aev_d` , where n=number density of CONDUCTION ELECTRONS, A=cross-section area of conductor and e=charge on an electron. |
|
| 44356. |
Which of the following is a projectile ? |
|
Answer» A self POWER rocket |
|
| 44357. |
What will be current through the 200 Omega resistor in the given circuit a long time after the switch 'K' is made on? |
|
Answer» zero ` R_(eq)= 200Omega+ 400omega= 600 omega ` `therefore`currentthrough`200Omega `  resistancewill be ` I_("steady ")+(6V )/( 600 Omega ) =10 mA ` |
|
| 44358. |
What for Hertz and Lenard's experimental study on photoelectric effect meant ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) It was discovered in 1887 by Heinrich HERTZ. (ii) It was meant for PRODUCTION of ELECTROMAGNETIC waves by mean of a spark discharge using ultraviolet LIGHT . |
|
| 44359. |
The Earth's magnetic field passes through a square tabletop with a magnitude of 4.95 xx 10^(-5) T and is directed at an angle of 165° relative to the normal of the tabletop. If the tabletop has 1.50 m sides, what is the magnitude of the magnetic flux through it? |
|
Answer» `1.08xx10^(-4)WB` |
|
| 44360. |
Draw a labelled schematic diagram of an a.c. generator. Explain briefly its principle and working. |
|
Answer» Solution :The labelled diagram of an a.c. generator is given in Fig. 6.55. Principle: Ana.c. generator is based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. If a rectangular armature coil rotates about its axis in a uniform magnetic field, the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes and an induced emf is set up in the coil. The direction of induced current is given by Fleming.s right hand rule. WORKING : When an armature coil of N turns and each turn enclosing area A is placed in a uniform magnetic field of strength B making an angle `theta` from normal to the direction of magnetic field, magnetic flux linked with the coil is `phi = N B Acostheta.` As the coil is rotated about its own axis with an angular speed `omega` then value of angle `theta = omegat` and hence, magnetic flux changes and an induced emf is developed across the ends of coil. As `phi = N BA COS omegat` `therefore` Induced emf `varepsilon = -(dphi)/dt =N B Aomegasin omegat = varepsilon_(0) sin omegat` where `varepsilon_(0) = N B A omega = "maximum (PEAK)"` value of induced emf. It is obvious that induced emf is sinusoidal in nature. 
|
|
| 44361. |
Can the potential function have a maximum or minimum in free space ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :No, it is not POSSIBLE. | |
| 44362. |
A magnetic field in a certain region is given by vecB = (40hatî - 18 hatk)G. How much flux passesthrough a 5.0 "cm"^2 area of the loop, if the loop lies flat on the XY Plane ? 1G (gauss) =10^(-4) T. |
|
Answer» `-900` nWb `=(5.0 xx 10^(-4) HATK. 40 hati-18 hatk) G` `=-90xx10^(-4)` G `=-90xx10^(-4) xx 10^(-4)T [ because 1 T=10^4 G]` `=-900xx10^(-9)` Wb `THEREFORE phi`=-900 nWb |
|
| 44363. |
A man weighing60kg goes up a staircase 5 m high in 20 sec. Calculate the power in watts g=9.8m//s^2. |
|
Answer» 800 KW |
|
| 44364. |
A boy of mass M is applying a horizontal force to slide a box of mass M' on a rough horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the shoes of the boy and the floor is 4 and that between the box and the floor is mu. In which of the following cases, it is certainly not possible to slide the box? |
|
Answer» `MU LT mu ,M lt M'` |
|
| 44365. |
Why do Ge and Si behave as semiconductors? |
| Answer» Solution :The energy gaps in Ge and Si are of the order of 1 eV Electrons can be easily EXCITED from valence BAND to the CONDUCTION band to enable them to conduct: electricity. So, Ge and Si BEHAVE as SEMICONDUCTORS. | |
| 44366. |
The stopping potential in an experiment on photoelectric effect is 1.5 V. What is the maximum K.E. of the photoelectrons emitted ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`K_max = eV_0 = 1.6 xx 10^(-!9) C xx 1.5 V` = 2.4`xx 10^(-19)` J or 1.5 eV. |
|
| 44367. |
A degital circuit which works according to some logical relationship, what we call ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44368. |
If lamda_1,lamda_2 and lamda3 are the wavelengths of the wave giving resonance in the fundamental,first and second overtones respectively, within a pipe closed at one end, the ratio of the wavelengths lamda_1,lamda_2 and lamda_3 is , |
|
Answer» 0.21042824074074 |
|
| 44369. |
AB+ bar(AB )is always |
|
Answer» 0 |
|
| 44370. |
(A) : In an electromagnetic wave, the electric and magnetic fields oscillate in phase (R) : In an electromagnetic wave, the electric and magnetic fields oscillate out of phase. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are TRUE and 'R' is the CORRECT explanation of 'A'. |
|
| 44371. |
A body moving with uniform acceleration has velocities 20 ms and 30 ms when passing two points A and B. The velocity mid-way between A and B is: |
|
Answer» 25 `ms^(-1)` |
|
| 44372. |
What is the order of radiation pressure of visible light in Nm^(-2) ? |
|
Answer» `10^(-2)` |
|
| 44374. |
According to particle theory of light what is the velocity of light in a dense medium, compared to that in rare medium ? |
|
Answer» more in RARER MEDIUM and LESS in DENSER |
|
| 44375. |
The work function for the following metals is given: Na: 2.75 eV, K: 2.30 eV, Mo: 4.17 eV, Ni: 5.15 ev. Which of these metals will not give photoelectric emission for a radiation of wavelength 3300 Å from a He-Cd laser placed 1 m away from the photocell? What happens if the laser is brought nearer and placed 50 cm away ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :It is FOUND that the given incident frequency ν is greater than `ν_(0) (NA), and ν_(0) (K)`, but less than `ν_(0) (Mo), and ν_(0) (Ni)`. Therefore, Mo and Ni will not give photoelectric emission. If the laser is brought closer, INTENSITY of radiation increases, but this does not affect the result regarding Mo and Ni. However, photoelectric current from Na and K will increase in proportion to intensity. | |
| 44376. |
What happens to the electrical capacitance of a capacitor, when a dielectrc medium is introduced? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The CAPACITANCE of a capacitor INCREASES with the INTRODUCTION of dielectric MEDIUM between the plates. | |
| 44377. |
A horizontal, homogeneous cylinder of mass M and radius R is pivoted about its axis of symmetry. A string is wrapped several times around the cylinder and tied to a body of mass m resting on a support positioned so that the string has no slack. The body of mass m is then lifted vertically to a distance h, and then released. (a) Evaluate the angular velocity omega_(0) of the cylinder, the speed v_(0) of the falling body of mass m, and the kinetic energy K_(0) of the system, just before the string becomes taut. (b) Evaluate the corresponding quantities, omega_(1),v_(1),andK_(1), for the instant just after the string becomes taut. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Since string is slack we can expect that the block will fall freely for distance l. Till this time tension in string will be zero. Calculation: Just before the string becomes taut, the cylinder is still at rest. Since the tension remained zero nothing has caused the cylinder to begin TURNING. That is, `omega_(0)=0`. Since the string has exerted no force on the body of MASS m, it has fallen freely with acceleration g thus `v_(0)=2gh`. Same result can be derived by writing 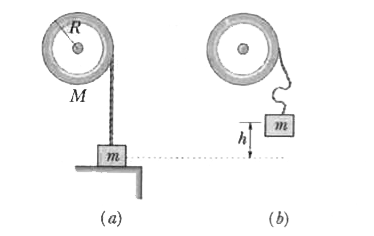 work-kinetic energy theorem for the system. The kinetic energy of the system is given by `K_(0)=1/2mv_(0)^(2)+1/2I_(C)omega_(0)^(2)=mgh` where `I_(c)` is the inertia of the cylinder. Putting `omega_(0)=0`, we get `v_(0)=sqrt(2gh)` (b) (1) The end attached to the block will be moving and it will pull the part of string touching the cylinder as the string becomes taut. (2) Thus, when string becomes tight an impulse/jerk will develop in the string. This jerk will start the motion of cylinder. There will be also an impulse due to axis of the cylinder. Here we can take cylinder, string and clock as our system. We will take axle of cylinder as the axis for writing ANGULAR momentum. Calculations: The impulse due to jerk in string will produce internal angular impulse, and the impulse due to the angular momentum will produce zero angular impulse about the axle. Further, the angular momentum of the system must be CONSERVED, since the impulse due to the snap of the string is of very short duration and the weight mg contributes negligibly in that time. The string is assumed to be inextensible, so `v_(1)=omega_(1)R`. Thus, we have `L_(1)=mv_(1)R+(1//2)MR^(2)omega_(1)=L_(0)`, where `L_(0)=mv_(0)R=msqrt(2gh)R`. SOLVING for the angular speed, we get `omega_(1)=v_(0)/(R[1+(M//2)m))=sqrt(2gh)/(R[1+((M//2)m)])` The corresponding speed is given by `v_(1)=omega_(1)R=v_(0)/(1+((M//2)m))=(sqrt(2gh))/([1+((M//2)m)])` The final kinetic energy `K_(1)` is given by `K_(1)=1/2mv_(1)^(2)+1/2I_(c)omega_(1)^(2)=mgh` = `1/2mv_(1)^(2)+1/2(1/2MR^(2))` `(v_(1)^(2)/R^(2))=1/2(m+M/2)v_(1)^(2)` = `1/2((mv_(0)^(2))/(1+((M//2)m)))` |
|
| 44378. |
(a) At what distance should the lens be held from the figure in Exercise 9.29 in order to view the squares distinctly with the maximum possible magnifying power? (b) What is the magnification in this case? (c) Is the magnification equal to the magnifying power in this case? Explain. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Maximum magnifying power is obtained when the image is at the NEAR POINT (25 cm) `u = - 7.14 cm.` (b) Magnitude of MAGNIFICATION `= (25// |u|) = 3.5.` (c) Magnifying power = 3.5 YES, the magnifying power (when the image is produced at 25 cm) is EQUAL to the magnitude of magnification. |
|
| 44379. |
In interference experiment of Thomas young we got phase difference how many times of path difference . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 44380. |
An alternating electric field, of frequency v, is applied across the dees (radius = R) of a cyclotron that is being used to accelerate protons (mass = m). The operating magnetic field (B) used in the cyclotron and the kinetic energy (K) of the proton beam, produced by it, are given by |
|
Answer» `B=(MV)/E` and `K=2mpi^(2)V^(2)R^(2)` |
|
| 44381. |
The strength of the Earth's magnetic field is |
|
Answer» CONSTANT everywhere |
|
| 44382. |
i. If f = 0.5 m for a glass lens, what is the power of the lens ? ii. The radii of curvature of the faces of a double convex lens are 10cm and 15cm . Its focal length is 12cm. What is the refractive index of glass ? iii. A convec lens has 20 cm focal length in air. what is focal length in water ? (Refractive index of air-water = 1.33, refractive index for air-glass = 1.5) |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Power `= +2` dioptre. (ii) Here, we have `f = +12 cm, R1 = +10 cm, R2 = -15 cm`. REFRACTIVE index of air is TAKEN as unity. We use the lens formula of EQ. (9.22). The SIGN convention has to be applied for `f, R_(1) and R_(2)` . Substituting the values, we have `(1)/(12)=(n-1)((1)/(10)-(1)/(-15))` This gives `n=1.5`. (iii) For a glass lens in air, `n_(2)=1.5, n_(1)=1, f=+20cm`. Hence, the lens formula gives `(1)/(20)=0.5[(1)/(R_(1))-(1)/(R_(2))]` For the same glass lens in water, `n_(2)=1.5, n_(1)=1.33`. Therefore, `(1.33)/(f)=(1.5-1.33)[(1)/(R_(1))-(1)/(R_(2))]` Combining these two EQUATIONS, we find `f=+78.2cm`. |
|
| 44383. |
Classify the following molecules into Polar and non-polar. (H_2O, H_2, NH_3, N_2, CO_2, CO, HCI, O_2) b. Define polar and non-polar molecules. c. Whar is meant by dielectric polarization? |
|
Answer» Solution :Polar molecules `H_2O, NH_3, CO, HCl` Non-polar molecules : `H_2, N_2, CO_2, and O_2` b. Refer Section 2.10.1 C. Adielectric material, polar or non-polar, when placed in an ELECTRIC field `E_0` the dipoles get aligned parallel to the field. The dielectric material set up a secondary electric field `E_p` of its own in a direction opposite to the APPLIED field `E_0`. This PHENOMENON is known as dielectric polarization. The net field strength gets reduced and is given as `E=E_0-E_P` Definition: The alignment of dipole moment of PERMANENT or induced dipoles of a dielectric in an external electric field is called dielectric polarization. |
|
| 44384. |
An electron and proton are possessing same amount of kinetic energy. Which of the two has greater de Broglie wavelength ? |
| Answer» Solution :de Brogile WAVELENGTH `LAMBDA = h/sqrt(2mE)` where E is the kinetic energy of a particle of mass m. Given that E is same for electron and proton. So, `lambda prop 1/sqrtm`. HENCE,`lambda` will be GREATER for smaller mass. Thus, de Broglie wavelength is greater for an electron. | |
| 44385. |
As shown in Fig. 6.26, a rectangular loop and a circular loop are moving out of a uniform magnetic field region to a field free region with a constant velocity v. In which loop do you expect the induced emf to be constant during the passage out of the field region ? The field is normal to the loops. |
| Answer» Solution :The induced emí is expected to be constant in case of RECTANGULAR LOOP only. Induced emf depends upon RATE of CHANGE of magnetic flux, which in present case is proportional to change in area of the loop. For a rectangular loop the rate of change in area is constant, hence induced emf is expected to be constant. However, for a circular loop, the rate of change of area of the loop during its passage out of the field region is not constant. Hence, induced emf will also VARY accordingly. | |
| 44386. |
A carrier wave of 1000 W is subjected to 100% modulation. Calculate (i) Power of modulated wave, (ii) Power in USB, (iii) Power in LSB. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Total power of modulated WAVE `P_(tau)=P_(C)(1+(m^(2))/(2))=1000(1+(1^(2))/(2))=1500` watt (ii) Power in USB `=1/2P_("SB")` where power carried by side bands is given by Amplitude Modulation and Detection `P_("SB")=P_(C)((m^(2))/(2))=1000((1^(2))/(2))=500` watt `P_("USB")=1/2P_("SB")=1.2xx500=250` watt (iii) Since power in LSB = Power in USB `P_("LSB")=P_("USB")=250` watt |
|
| 44387. |
The relative permeability of a diamagnetic material is |
|
Answer» GREATER than unity |
|
| 44388. |
A man is watching two trains one leaving and other approaching with equal velocities of 4 ms^(-1). If they sound their whistles each of natural frequency 240 hz, the number of beats heard per seceond by the mas will be (velocity of sound in air 320 ms^(-1) ) : |
|
Answer» 6 and `v_(2) = ((320)/(320 + 4)) 240 = 237 Hz. `, `THEREFORE` beat frequency , b = `v_(1) - v_(2)` = 243 - 237 = 6 Hz. Hence the correct choice is (a). |
|
| 44389. |
A) Tangent galvanometer is a moving magnet type galvanometer B) Tangent galvanometer works on tangent law |
|
Answer» A is true, B is false |
|
| 44390. |
What is microscope? |
| Answer» Solution :An INSTRUMENT which FORMS a magnified IMAGE of small object closed to the EYE. | |
| 44391. |
Coffee cools faster in saucer than in cup because of |
|
Answer» the emissive POWER of SAUCER is LESS than cup |
|
| 44392. |
The electric mains in the house are marked 220 V, 50 Hz. Write down the equation for instantaneous voltage. |
| Answer» Solution : Equation for instantaneous voltage is `V = 220 XX SQRT(2) SIN 2PI(50)t = 311 sin 314 t`. | |
| 44393. |
Velocity of efflux in torricelli's theorem is given by v=sqrt(2gh), here h is the height of hole from the top surface, after that, motion of liquid can be treated as projectile motion. Liquid is filled in a vessel of square base (2mxx2m) upto a height of 2m as shown in figure (i). in figure (ii) the vessel is tilted from horizontal at 30^(@) what is the velocity of efflux in this case ? Liquid does not spills out? |
|
Answer» 3.29m/s Hence, `2xx2xx2=2xx(1)/(2)[x+x+(2)/(sqrt(3))]xx2` `thereforexapprox1.42m` now, `h=xsin60^(@)=1.23m` `thereforev=sqrt(2gh)=sqrt(2xx10xx1.23)=4.96m//s` |
|
| 44394. |
Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than an a-particle. Consider the following decay processes: ""_(88)^(223)Ra to ""(82)^(209)Pb + ""_(6)^(14)C. ""_(88)^(223)Ra to ""_(86)^(219)Rn + ""_(2)^(4)He Calculate the Q-values for these decays and determine that both are energetically allowed. |
|
Answer» Solution :For `""_(6)^(14)C` emission `Q=[m(N)(""_(88)^(223)RA)-m(N)(""_(82)^(209)Pb)-m(N)(""_(6)^(14)C)]c^(2)` `=[m(""_(88)^(223)Ra)-m(""_(82)^(209)Pb)-m(""_(6)^(14)C)]c^(2)=31.85MeV` For `""_(2)^(4)He" emission, "Q-[m(""_(86)^(223)Ra)-m(""_(86)^(219)Rn)-m(""_(2)^(4)He)]c^(2)=5.98MeV` |
|
| 44395. |
State and explain Kirchhoff's rules. |
Answer» Solution :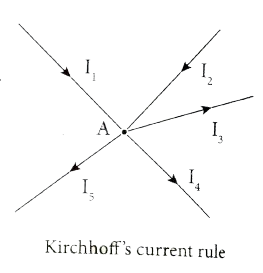 Kirchhoff.s FIRST rule (current rule or junction rule): Statement: It states that the algebraic sum of the currents at any junction of a circuit is zero. It is a statement of conservation of electric charge. Explanation: All charges that enter a given junction in a circuit must leave that junction since charge cannot build up or disappear at a junction. Current entering the junction is TAKEN as positive and current leaving the junction is taken negative. Applying this law to the junction A, `I_(1)+I_(2)-I_(3)-I_(4)-I_(5)=0` or`I_(1)+I_(2)=I_(3)+I_(4)+I_(5)` Kirchhoff.s SECOND rule (voltage rule or loop rule) Statement: It states that in a closed circuit the algebraic sum of the products of the current and resistance of each part of the circuit is equal to the total emf included in the circuit. This rule follows from the law of conservation of energy for an isolated system. (The energy supplied by the emf sources is equal to the sum of the energy delivered to all resistors). Explanation: The product of current and resistance is taken as positive when the direction of the current is followed. Suppose if the direction of current is opposite to the direction of the loop, then product of current and voltage across the resistor is negative. It is shown in Fig. (a) and (b). The emf is considered positive when proceeding from the negative to the positive terminal of the cell. It is shown in Fig. (C ) and (d).   Kirchhoff voltage rule has to be applied only when all currents in the circuit reach a steady state condition (the current in various branches are constant). |
|
| 44396. |
An object of height h_(0)=1 cm is moved along principal axis of a convex lens of focal length f=10 cm. Figure shows variation of magnitudeof height of image with image distance (v) . Find v_(2)-v_(1) in cm . |
|
Answer» `|h_(i)|=(v)/(f)h_(0)-h_(0)flevle-infty` So `h_(2)=h_(2)=1 cm` From second eq. `v_(2)=2f` Or When `vrarr0,urarr0&h_(i)rarrh_(0)soh_(2)=h_(0)=1 cm` image of same height is obtained when `v=2f` so `v_(2)=2f` |
|
| 44397. |
Two circular coils are made from a uniform copper wire. Radii of circular coils is in the ratio 3:4 and number of turns in the ratio 3:5. If they are connected in series across a battery. Statement (A) : Ratio between magnetic field inductions at their centers is 4 : 5 Statement (B) : Ratio between effective magnetic moments of the two coils is 16 : 15 |
|
Answer» Both STATEMENTS are wrong |
|
| 44398. |
A bar made of material whose Young's modulus is equal to E and Poisson's ratio to mu is subjected to the hydrostatic pressure p. Find: (a) the fractional decrement of its volume, (b) the relationship between the compressibility beta and the elastic constants E and mu. Show that Poisson's ratio mu cannot exceed 1//2. |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider a cube of unit length before pressure is applied. The pressure acts on each FACE. The pressure on the OPPOSITE faces constitute a TENSILE stress producing longitudinal compression and lateral extension. The COMPRESSIONS is `p/E` and the lateral extension is `mup/E` The net result is a compression `p/E(1-2mu)` in each side. Hence `(DeltaV)/(V)=-(3p)/(E)(1-2mu)` because from symmetry `(DeltaV)/(V)=3(Deltal)/(l)` (b) Let us consider a cube under an equal compressive stress `sigma`, acting on all its faces. Then, VOLUME strain `=-(DeltaV)/(V)=(sigma)/(k)`, (1) where k is the bulk modulus of elasticity. So `sigma/k=(3sigma)/(E)(1-2mu)` or, `E=3k(1-2mu)=3/beta(1-2mu)` (as `k=1/beta`) `mule1/2` if E and `beta` are both to remain positive. |
|
| 44399. |
What is conductance: Give its unit. |
| Answer» Solution :The RECIPROCAL of RESISTANCE is called conductance. It.s S.I. unit is `"ohm"^(-1)`. | |
| 44400. |
An object is placed at a distance x from the principal focus of a spherical mirror of focal length f. Calculate the magnification of the image. |
|
Answer» |
|