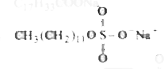Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 88851. |
(A): Magnetic moment of Mn^(+2) is 5.8 B.M (R): Mn^(+2) has five unpaired electrons |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are TRUE and (R) is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of (A) |
|
| 88852. |
A magnetic moment of 1.73BM will be shown by one among the following |
|
Answer» `TiCl_(4)` |
|
| 88853. |
A xerophytic plant among the following is |
|
Answer» `[Cu(NH_3)_4]^(2+)` |
|
| 88854. |
Find the magnetic moment of Cr^(3+) ion. |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 88855. |
A magnetic moment of 1.73 BM will be shown by one among the following : |
|
Answer» `[Cu(NH_(3))_(4)]^(2+)` `therefore 1.73=sqrt(n(n+2))` or n=1 So the complex containing one unpaired one unpaired ELECTRON is `[Cu(NH_(3))_(4)]^(2+)`. |
|
| 88856. |
A magnetic moment of 1.73 B.M. will be shown by a complex among the following |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 88857. |
A : Magnesium sulphate is heptahydrate where as calcium sulphate is dihydrate. R : Mg and Ca belongs to Group II. |
|
Answer» If both ASSERTION & Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanantion of the assertion, then mark (1). |
|
| 88858. |
A magnet will cause the greatest deflection of |
|
Answer» `GAMMA`-rays |
|
| 88859. |
A: Magnesium oxide is used for the lining in stoel making furnace . R: Magnesium oxides acts as flux |
|
Answer» If both Assertion & Reason are TRUE and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion, then mark (1). |
|
| 88860. |
(A): Magnesium metal can easily be extracted from sea water rather than sodium metal, (R): Mg(OH)_(2) is less soluble in water than NaOH. |
|
Answer» A and are true, R EXPLAINS A |
|
| 88861. |
A : Magnesium do not impact flame colourtion. R : The e^(-) in magnesium are too strongly bound to get excited by flame. |
|
Answer» If both Assertion & Reason are true and the reason is the CORRECT explanantion of the assertion, then MARK (1). |
|
| 88862. |
A : Magnesium and Cesium gives blue colour in flame colouration. R : Mgand Cs are of comparable size. |
|
Answer» If both ASSERTION & Reason are true and the reason is the CORRECT explanantion of the assertion, then mark (1). |
|
| 88863. |
(A) Magnesium can not be extracted by electrolysisof aqueous saltsolution (R)Magnesium reacts with water |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of (A) |
|
| 88864. |
A magenisum alkyl halide is known as: |
|
Answer» |
|
| 88865. |
A macromolecule of iron has molar mass 2800amu, it contains 8% iron by mass. The number of iron atom in one formula unit of the macromolecule is: |
|
Answer» `=(%)/(100)xx("Molecule mass")/("Atomic mass")=(8)/(100)xx(2800)/(56)=4` |
|
| 88866. |
(A) Lucas reagent is used to distinguish 1^@ , 2^@ and 36@alcohols(R) The role of anhyd. ZnCl_2in the Lucas reagent is to weaken the bond between C-O by accepting electron pair from oxygen atom of alcohol |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are TRUE and (R) is the correct EXPLANATION of (A) |
|
| 88867. |
A lump of coal burns slowly in air while coal dust burns explosively . This is because of : |
|
Answer» less mass of powdered coal |
|
| 88868. |
A: Lower Aliphatic amines are soluble in water.R: Lower Aliphatic amines are gases. |
|
Answer» If both Assertion & Reason are TRUE and the reason is the CORRECT explanation of the assertion, then mark (1). |
|
| 88869. |
A low melting metal can be refined by |
|
Answer» distillation |
|
| 88870. |
A lot of scum formation was observed during washing with hard water. The washing powder could be |
|
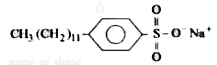
Answer» `C_(17)H_(33)COONa` `2C_(17)H_(33)COONa(aq) + Ca^(2+) + (aq)` (Hard water) to`(C_(17)H_(33)COO)_(2) Ca(s) + 2Na^(+) (aq.) ` |
|
| 88871. |
A long rectangular box is filled with chlorine (at. w : 35.45) which is known to contain only ""^(35)Cl" and "^(37)Cl. If the box could be dvided by a partition and the two types of chlorine molecules put in the two compartments respectively, calcutate where should the partition be made if the pressure on both sides dre to be equal. is this pressure the same as the original pressure ? |
|
Answer» Solution :3.44:1 Since the pressures on both the SIDES of the partion is equal, the PRESSURE before and after partition will be same (no of MOLES unit VOLUME being same.) |
|
| 88872. |
A long rectangular box is filled with CI_(2) (at wt 35.45) which is known to contain only CI^(35) and CI^(37) if the box could be divided by a partition and the two type of chlorine molecules put into the two compartments respectively calculate where should partition be made if the pressure on both sides are to be equal Is this pressure the same as original pressure ? . |
|
Answer» Solution :Since 34/45 is the average atomic weight of `""^(35)Cl` (at. wt. = 35)and `""^(37)Cl` (at. wt. = 37) we have, `(35 n_(1) + 37 n_(2))/(n_(1) + n_(2)) = 35.45`, where `n_(1)` and `n_(2)` are the number of molesof `""^(35)Cl` and `""^(27)Cl` respectively. `therefore (n_(1))/(n_(2)) = 3.44, n_(1) : n_(2) = 3.44 :1`. `therefore` ratio of LENGTHS is 3.44 : 1. Since the pressure on both the SIDES of the partition is EQUAL, the pressure before and after partition will be same (no. of moles PER unit volume being same). |
|
| 88873. |
A long iron rod is partially dipped in common salt solution. What happens ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The part of iron rod dipped in salt solution has less ACCESS to atmospheric oxygen. The concentration of oxygen is less on that part of METAL. The IMMERSED part is corroded and the PROCESS is called anodic dissolution. |
|
| 88874. |
A long iron rod is partially dipped in common salt solution. What happens? |
| Answer» Solution :The part of iron rod dipped in salt solution has less access to ATMOSPHERIC oxygen. The concentration of oxygen is less on that part of METAL. The immersed part is corroded and the process is called anodic DISSOLUTION. | |
| 88875. |
(a) (i) Explain the formation of water with copper catalyst by intermediate compound formation theory. (ii) O-nitro phenol is slightly soluble in water where as P-nitro phenol is more soluble, Give reason. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) (i) Formation of WATER due to the relation of `H_(2)` and `O_(2)` in the PRESENCE of Cu can be given as `underset("catalyst")(2Cu) + underset("Reactant")(1/2 O_(2)) to underset("Intermediate compound")(Cu_(2)O)` `Cu_(2)O + underset("Reactant")(H_(2)) to underset("Product")(H_(2)O) + underset("Catalyst")(2Cu)` (ii) O-nitro phenol is slightly soluble in water and more VOLATILE due to intra molecular hydrogen bonding, whereas P-nitro phenol is more soluble in water and less volatile due to INTERMOLECULAR hydrogen bonding. |
|
| 88876. |
A lone pair of electrons in an atom implies |
|
Answer» a pair of VALENCE electrons not involved in BONDING |
|
| 88877. |
i) Explain Hoffmann bromamide degradation for the preparation of aniline. ii) Give the IUPAC name of CH_(3)-NH-CH_(2)-CH_(3). |
|
Answer» Solution :a) i) When amides are heated with bromine and NaOH/KOH (alcoholic/aqueous) Hoffmann.s bromamide degradation takes PLACE leading to the formation of AMINES containing one carbon atom less than the respective amide. `underset("Amide")(R-overset(O)overset(||)C-NH_(2))+Br_(2)+4NaOH rarr underset("AMINE")(R-NH_(2))+Na_(2)CO_(3)+2NaBr+2H_(2)O` ii) The IUPAC NAME is N-methylethánaminie. |
|
| 88878. |
A littlewater is there on the inner surface of a conical flask. Can this water be removed by making with ether? Answer with reason. |
| Answer» Solution :No, because water does not DISSOLVE in ether. Instead alcohol cann be used to remove water SINCE water dissolves in alcohol. | |
| 88879. |
i) Explain the preparation of phenol from cumene. ii) Complete the reaction : |
Answer» SOLUTION :a) i) 
|
|
| 88880. |
A litre of solution is saturated with AgCl. To this solution if 1.0 xx 10^(-4) mole of solid NaCl is added, what will be the [Ag^(+)], assuming no volume change |
|
Answer» More After NaCl is added `K_(sp) = x xx (x +1 xx 10^(-4))` That is why `Ag^(+)` will be less. |
|
| 88881. |
p-dichlorobenzene has higher melting point than those of ortho and meta isomers. Give reason. |
|
Answer» Solution : When methyl bromide undergoes hydrolysis with aqueoous potassium hydroxide , Methyl alcohol is formed . `CH_3-Br+ KOH to CH_3-OH +KBr` This mechanism involves only ONE step .  The NUCLEOPHILE OH- attack from the REAR side of the leaving group . A transition atate with partial formtion of C-OH bond and partial breaking f C+Br bond TAKES place simultaneously . The rate of the reaction depends both on the concentration of nucleophile as well as alkyl halide Hence , It is a second order reaction . In `S_n^2` reaction , complete inversion of configuration takes place . `R-OH+ SOCl_2 to R-Cl +SO_2 +HCl` Swart.s Reaction Due to SYMMETRY of para - isomers |
|
| 88882. |
A litre of public water contains 5 mg of chlorine. The concentration of chlorine in ppm is |
|
Answer» `5xx10^(-4)` `10^(6)` parts contain chlorine `=(5xx10^(-3))/(10^(3))xx10^(6)` `=5` PPM |
|
| 88883. |
(a) (i) Discuss the manufactures of chlorine. (ii) What is inert pair effect? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) (i) Electrolytic process: When a solution of brine (NaCl) is electrolysed, `Na^(+)` ions are formed. `Na^(+)` ions reacts with `OH^(-)` ions of water and forms sodium hydroxide. Hydrogen and chlorine are liberated as gases. `{:(NaCl to Na^(+) + Cl^(-), "At Cathode", "At the cathode"),(H_(2)O to H^(+) + OH^(-), H^(+) + e^(-) to H, Cl^(-) to Cl + e^(-)),(Na^(+) + OH^(-) to NaOH, H + H to H_(2), Cl +Cl to Cl_(2)):}` Deacon.s process: In this process a mixture of air and hydrochloric acid is passed up a chamber containing a NUMBER of shelves, pumice stones SOAKED in cuprous chloride are placed. Hot gases at about 723 K are passed through a jacket that surrounds the chamber. `4HCl + O_(2) overset(400^(@)C) underset(Cu_(2)Cl_(2)) to 2H_(2)O + Cl_(2) uarr` The chlorine obtained by this method is dilute and is EMPLOYED for the MANUFACTURE of bleaching POWDER. The catalysed reaction is given below, `2Cu_(2)Cl_(2) + O_(2) to underset("Cuprous oxy chloride") (2Cu_(2)OCl_(2))` `Cu_(2)OCl_(2) + 2HCl to underset("Cupric chloride") (2CuCl_(2) + H_(2)O)` `2CuCl_(2) to underset("Cuprous Chloride")(Cu_(2)Cl_(2) + Cl_(2))` (ii) In p-block elements, as we go down the group, two electrons present in the valence s-orbital become inert and are not available for bonding (only p-orbital involves chemical bonding). This is called inert pair effect. |
|
| 88884. |
A litre of air weighs 1.293 grams at NTP. At what temperature will a litre of air weigh 1 gram, the pressure being 72 cm ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 88885. |
(a) (i) Calculate the number of atoms in a fcc unit cell. (ii) How do nature of the reactant influence rate of reaction? |
Answer» Solution :(a) (i) Number of atoms in a fcc unit cell. 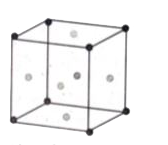 `N_(c )/8 + N_(f)/2` `=8/8 + 6/2 = 1+3=4` (ii) Nature and state of the reactant: We know that a chemical reaction involves breaking of certain existing bonds of the reactant and forming new bonds which LEAD to the product. The net energy involved in this process is dependent on the nature of the reactant and HENCE the rates are different for different reactants. Let us compare the following two reactions that we carried out in volumetric analysis. 1. Redox reaction between ferrous ammonium sulphate (FAS) and `KMnO_(4)` 2. Redox reaction between oxalic acid and `KMnO_(4)`.  The oxidation of oxalate ion by`KMnO_(4)`is relatively slow compared to the reaction between `KMnO_(4)`and `Fe^(2+)`.In fact heating is required for the reaction between `KMnO_(4)` , and Oxalate ion and is carried out at around 60°C. The physical state of the reactant also plays an important ROLE to influence the rate of reactions. Gas phase reactions are faster as compared to the reactions involving solid or liquid reactants. For example, reaction of sodium metal with iodine vapours is faster than the reaction between solid sodium and solid iodine. Let us consider another example that we carried out in inorganic qualitative analysis of lead salts. If we mix the aqueous solution of colorless potassium IODIDE with the colorless solution of lead nitrate, precipitation of YELLOW lead iodide take place instantaneously, whereas if we mix the solid lead nitrate with solid potassium iodide, yellow coloration will appear slowly. |
|
| 88886. |
A litre of gas is measured at 27^(@)C . What volume will it occupy at -23^(@)C ? |
|
Answer» 1200ml or `V_(2) = ( V_(1) T_(2))/( T_(1))` `= 100 xx (250)/( 300) = 833 ml` |
|
| 88887. |
(a) (i) An aromatic compound 'A' of molecular formula C_(7)H_(7)ON undergoes a series of reactions as shown below. Write the structures of A, B,C,D and E in the following reactions. underset((A))(C_(7)H_(7)ON) overset(Br_(2) + KOH)rarr underset(underset((D))(darr CHCl_(3) + NaOH))(C_(6)H_(5)NH_(2)) underset(273K)overset(NaNO_(2) + HCl)rarr underset(underset(E)(darr KI))((B)) overset(CH_(3)CH_(2)OH)rarr (C) |
Answer» SOLUTION :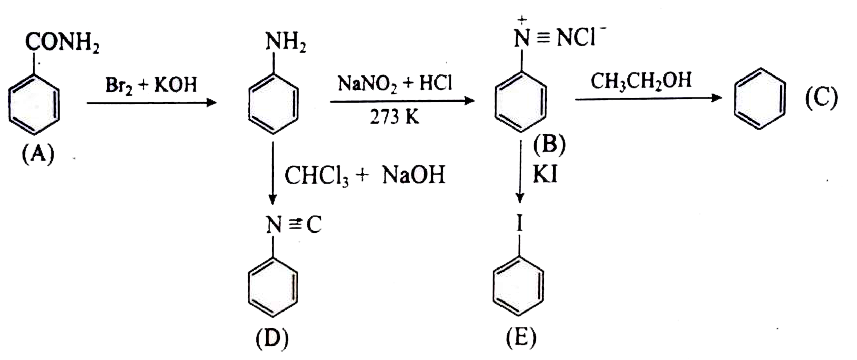
|
|
| 88888. |
A : Lithium is less reactive but the strogest reducing agent in aqueous solution. R : Lithium shows positive reduction potential. |
|
Answer» If both ASSERTION & Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanantion of the assertion, then mark (1). |
|
| 88889. |
(a) (i) A solution of [Co(NH_(3))_(4)I_(2)]Cl_(2) when treated with AgNO_(3) gives a white precipitate. What should be the formula of isomer of the dissolved complex that gives yellow precipitate with AgNO_(3). What are the above isomers called? (ii) Write the following in the complex [Cr("en")_(3)] [CrF_(6)] (i) Type of complex (ii) Ligands (iii) central metal (iv) Oxidation state of central metal (v) IUPAC name |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) (i) 1 A solution of `[Co(NH_(3))_(4)I_(2)]Cl` when treated with `AgNO_(3)` gives a white precipitate. Because `Cl^(-)` ION is COUNTER ion. 2. Formula of isomer of the dissolved complex that give YELLOW precipitate with `AgNO_(3) " is " [Co(NH_(3))_(4)Cl] I` because `I^(ө)` is counter ion 3. `[Co(NH_(3))_(4) I_(2)] Cl and [Co(NH_(3))_(4)Cl I]` I both are ionisation isomers (ii) 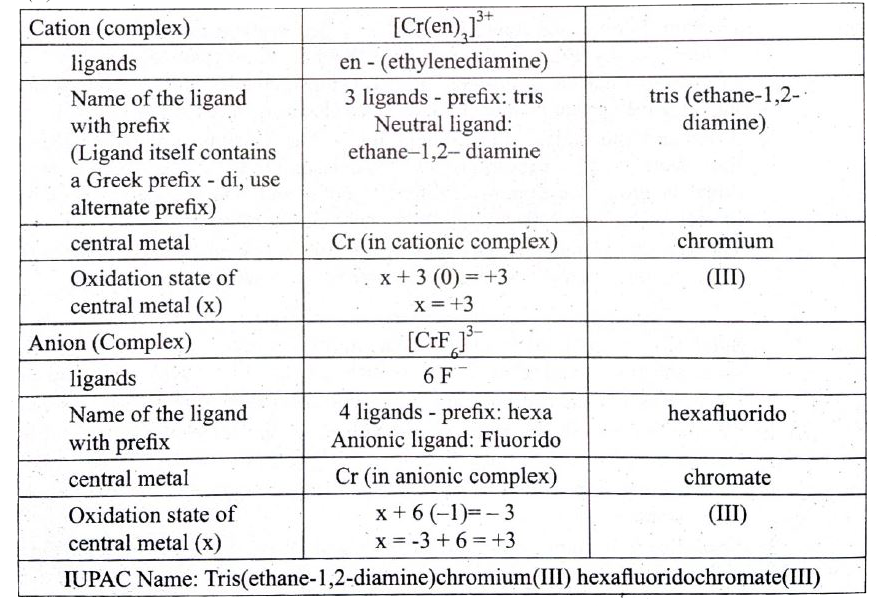
|
|
| 88890. |
(A) : Lithium has less electrode potential than caesium (R) : Hydration energy of lithium ion is high. |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are TRUE and (R) is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of (A) |
|
| 88891. |
A hypothetical reaction, A_(2)+B_(2)to2 AB, follows the mechanism as given below : A_(2)iff A+A""("Fast") A+B_(2)to AB+B""("Slow") A+BtoAB""("Fast") The overall order of reaction is |
|
Answer» zero Rate `= k[A][B_(2)]` for the equilibrium, `iff 2A , K_(c) = ([A]^(2))/([A_(2)])` or `[A]=sqrt(K_(c)[A_(2)])` ` therefore` Rate `=k K_(c)^(1//2) [A_(2)]^(1//2)[B_(2)] = k'[A_(2)]^(1//2)[B_(2)]` Hence, order `= (1)/(2) + 1 = 1""(1)/(2).` |
|
| 88892. |
(a) List the factors on which the rate of a chemical reaction depends. (b) The half-life for the decay of radioactive ""^(14)C is 5730 years. An archaeological artifact containing wood has only 80% of the ""^(14)C activity as found in living trees. Calculate the age of the artifact. |
| Answer» Solution :`"["(B)t=(2.303)/((0.693//5730))log""(100)/(80)=1845" YEARS""]"` | |
| 88893. |
A hypothetical reaction, A_2+B_2rarr2AB follows the mechanism as given below ,A2rarrA+A........(fast) A+B2rarrAB+B.......(slow)A+BrarrAB.......(fast) The order of the reaction is : |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 88894. |
(a) List the following species in order or decreasing nucleophilicity in aqueous medium. (b) Indicate which of the following solvent is protic or aprotic . , (C)Identify the strongest nucleophile in each pair of anions. (i)Br^(Theta) " and " CI^(Theta) " in " H_(2)O (ii) .^(Theta)SH " and " F^(Theta) " in " CH_(3)OH (iii) ,^(Theta)OH " and " CI^(Theta) " in " DMF |
Answer» Solution :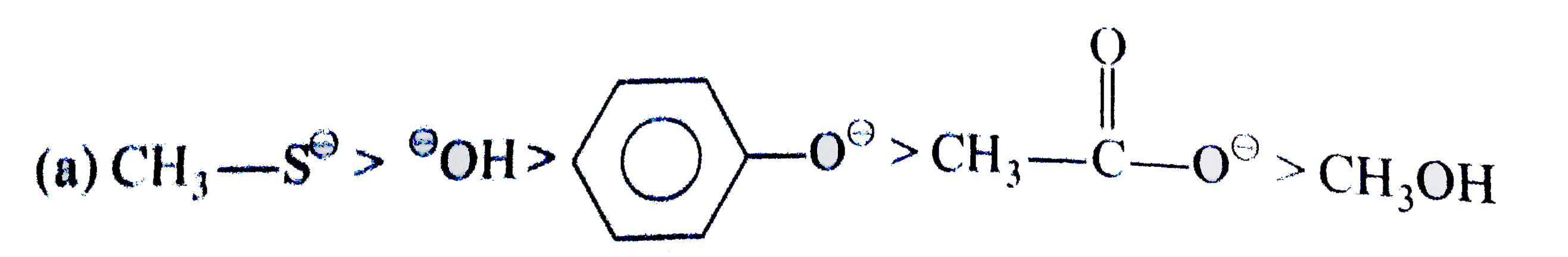 <BR> `(b) "PROTIC - (i) ,(iii) ,(v)` <BR> `(b) "PROTIC - (i) ,(iii) ,(v)` `"Aprotic" -(ii),(iv),(VI)` `(C) (i) Br^(THETA) (ii).^(Theta)SH (iii) .^(Theta)OH` |
|
| 88895. |
A hypothetical reaction, A_2+B_2rarr2AB follows the mechanism as given below ,A2---->A+A........(fast) A+B2----->AB+B.......(slow)A+BrarrAB.......(fast) The order of the reaction is : |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 88896. |
A list of solids are given below : Quartz, glass, iodine, ice. From this, identify crystal (s) which is/are isotropic |
|
Answer» |
|
| 88897. |
A reaction A_(2)+B_(2)to2ABoccurs by the following mechanism: A_(2)hArr A+A…………(fast) A+B_(2)toAB+B……….(slow) A+BtoAB…………..(fast) Its order would be: |
|
Answer» 2 |
|
| 88898. |
A list of solids are given below: Quartz, glass, iodine, ice. From this identify crystal (s), having sharp melting point. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :QUARTZ,IODINE,ICE | |
| 88899. |
A hypothetical reaction A_2 + B_2 to 2ABfollows the mechanism as given below:A_2 iff A + A (fast)A + B_2 to AB + B (slow)A+B to AB (fast) The order of the over all reaction is : |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 88900. |
A list of solids are given below : Quartz, glass, iodine, ice. From this, identify crystal (s) having sharp melting point. |
|
Answer» |
|