Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 7151. |
Two wooden blocks of masses M and m are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in figure. If a force P is applied to the system as shown in figure such that the mass m remains stationary with respect to block of mass M, then the magnitude of the force P is: |
|
Answer» `(M+m) G TAN BETA` |
|
| 7152. |
Which chemical of the egg attracts and holds sperm? |
|
Answer» Fertilizin |
|
| 7153. |
The ratio of absolute temperatures of two black bodies is 2 : 1. The ratio of their maximum radiation intensities will be |
|
Answer» ` 1:32` `(E_(m_1))/(E_(m_2))=((T_1)/(T_2))^5=((2)/(1))^5= 32/1` |
|
| 7154. |
If P(r) is the radial probability density for a hydrogen atom then the probability that the separation of the electron and proton is between r and r+ dr is |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7155. |
Types of impurities added to semiconductors are_____and_____. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7156. |
For what distance is ray optics a good approximation when the aperature is 3 mm wide and the wavelength 500 nm. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7157. |
The potential of the plate A of a parallel plate capacitor is zero and the its other plate B is maintained at a potential +V. How does the potential vary from point to point between these plates? Neglect the end effect. |
|
Answer» Solution :Let the POTENTIAL of a point at a distance x from the plate A be V' and intensity of the ELECTRIC field be E, then `E= (V')/(x)" or, "V' = Ex` The intensity of the electric field (E ) in the space between the two plates is a cosntant. `:. ""V' prop x` i.e., the potential V' increases UNIFORMLY with x. So, the graph of VARIATION of potentital with distance from A to B is a straight line passing through the origin. 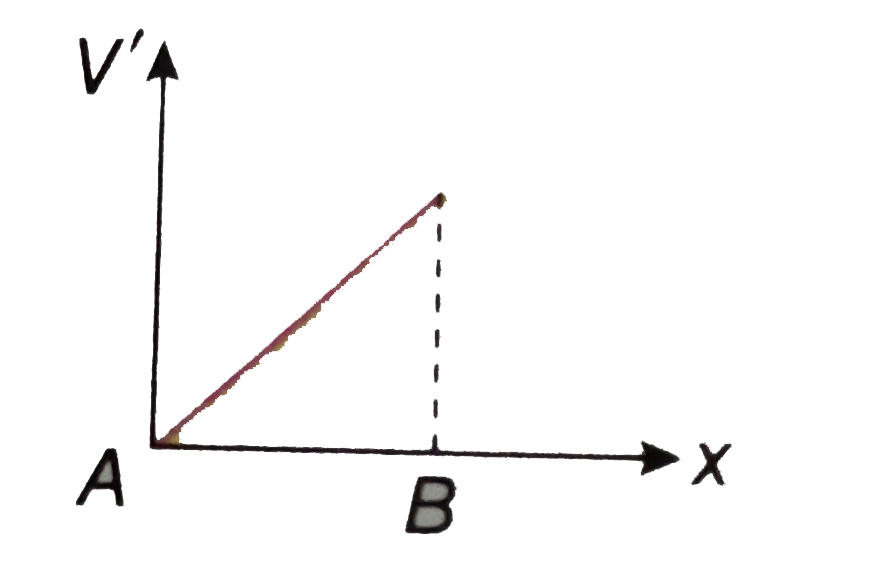
|
|
| 7158. |
(i) Draw a neat labelled ray diagram of a compound microscope. Explain briefly its working. (ii) Why must both the objective and the eye-piece of a compound microscope have short focal lengths ? |
Answer» Solution :(i) 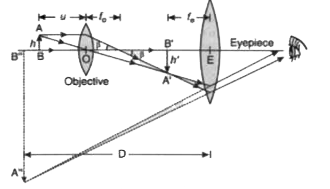 (ii) The objective forms a real, INVERTED MAGNIFIED image of the object. This serves as the object for the second lens, the eyepiece, which functions essentially like a simple microscope or magnifier, produces the final image, which is enlarged and virtual. To achieve a LARGE magnification of a small object, both the objective and the eyepiece should have small focal lengths. |
|
| 7159. |
The fastest mode of transfer of heat is |
|
Answer» conduction |
|
| 7160. |
An experiment is performed to obtain the value of acceleration due to gravity g by using a simple pendulum of length L. In this experi- ment time for 100 oscillations is measured by using a watch of 1 second least count and the value is 90.0 seconds. The length L is measured by using a meter scale of least count I mm and the value is 20.0 cm. The error in the determination of g would be: |
|
Answer» `1.7%` |
|
| 7161. |
Generally, core of transformer is made up of……... |
|
Answer» steel |
|
| 7162. |
A parallel resonance a.c circuit is called: |
|
Answer» an ACCEPTOR circuit |
|
| 7163. |
A power transmission line feeds input power at 2300 V to a stepdown transformer with its primary windings having 4000 turns. What should be the number of turns in the secondary in order to get output power at 230 V? |
|
Answer» Solution :Primary coil `RARR` 1 Secondary coil `rarr` 2 For ideal transformer, we have `( epsilon_(1))/( epsilon_(2)) = ( N_(1))/( N_(2))` `:. N_(2) = N_(1) ( epsilon_(2))/(epsilon_(1))` `= ( 4000 ) ( 2130)/( 2300)` `:. N_(2) = 400` |
|
| 7164. |
A moving charge is a source of……………………….as well as………….. . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7165. |
A parallel beam of white light falls on a thin film whose refractive index is 1.33. IF angle of incedence is 52^(@) then thickness of the film for the reflected light to be coloured yel,ow (lambda = 6000 Å) most intensively must be : |
|
Answer» `14(2N + 1) mu m` `therefore sin r = (sin i)/(mu) = 0.6` `therefore cos r = sqrt(1 - sin^(2) r )= 0.8` For CONSTRUCTIVE interference after reflection, `2 mu t cos r = (2n + 1) (lambda)/(2)` Solving `t = 0.14 (2n + 1)mu m`. |
|
| 7166. |
In the given figure, the north pole of a magnet is brought towards a closed loop containing a condenser. Positive charge will be produced on |
|
Answer» PLATE A |
|
| 7167. |
The distance between charged parallel plates is d. An electron -proton is released somewhere in the gap between the plates and it is found that the proton reaches the negative plate at the same time as electron reaches the positive plate. At consider only electric force. The mass of electron is m_(e) and mass of proton is m_(p).The electric field between plates is E. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Let the pair be released at distance `x` from the NEGATIVE plate. Photon : `a_(p) = (eE)/(m_(p))` `s = ut + (1)/(2) at^(2)` `x = 0 + (1)/(2) (eE)/(m_(p)) t^(2)`….(i) Electron : `a_(e ) = (eE)/(m_(e))` `d -x = 0 + (1)/(2) (e E)/(m_(e)) t^(2)`....(II) Dividing (i) by (ii) , we get `(x)/( d - x) = (m_(e ))/(m_(p)) RARR m_(p) x = m_(e ) d - m_(e )x` `x = (m_(e )d)/(m_(e ) + m_(p))` 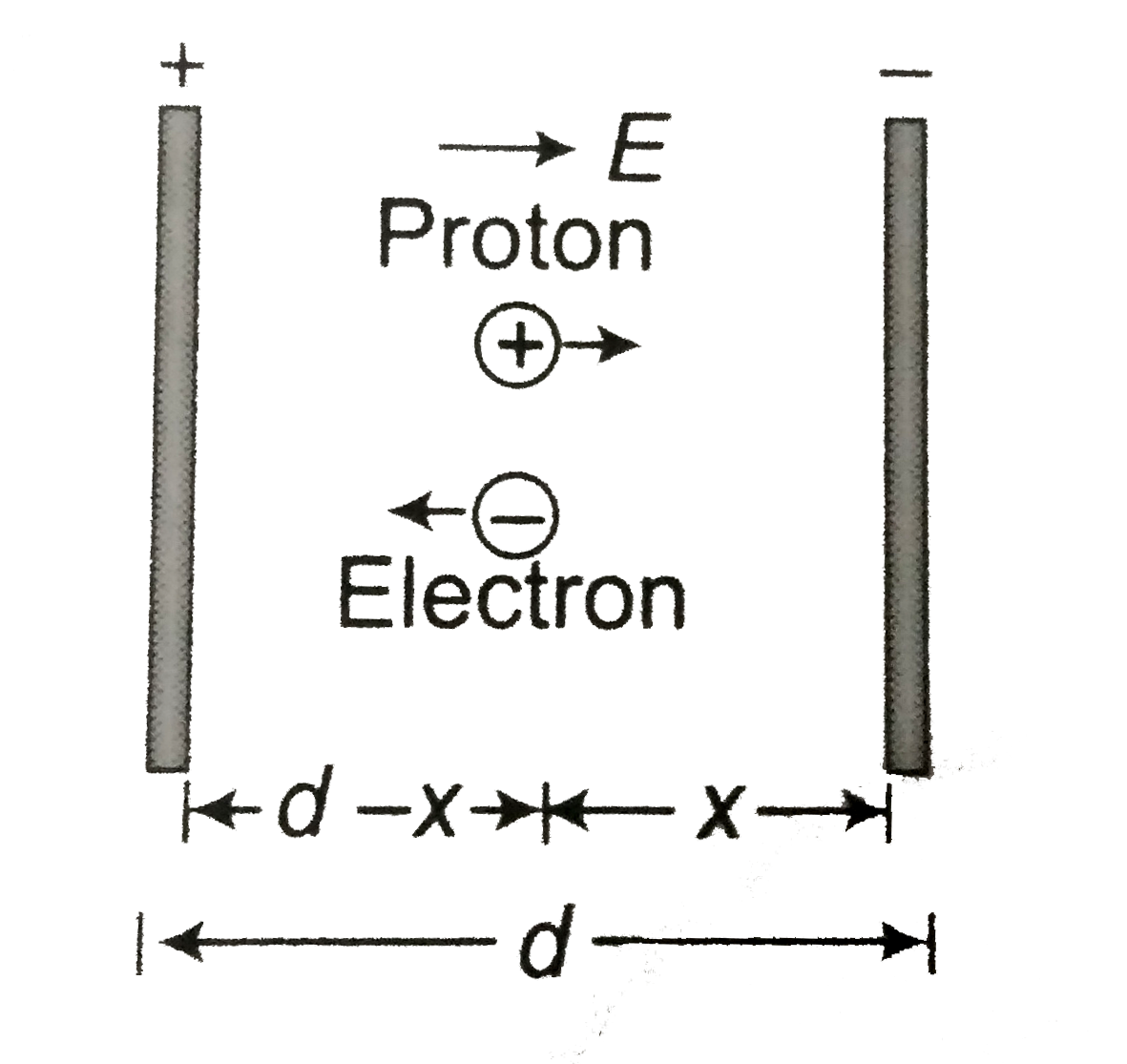
|
|
| 7168. |
Ohm's law is not applicable for |
|
Answer» INSULATORS |
|
| 7169. |
Whichof the followingrepresentforwardbias diode ? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 7170. |
The work function of potassium is 2.2 eV. UV light of wavelength 3000 Å and intensity 2 Wm^(-2) is incident on the potassium surface. (i) Determine the maximum kinetic energy of the photo electrons (ii) If 40% of incident photons produce photo electrons, how many electrons are emitted per second if the area of the potassium surface is 2 cm^(2) ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) The energy of the photon is `E = (hc)/(lambda) = (6.626 xx 10^(-34) xx 3 xx 10^(8))/(3000 xx 10^(-10))` `E = 6.626 xx 10^(-19)`J = 4.14 eV br> Maximum KE of the photoelectrons is `K_(MAX) = h upsilon - phi_(0) = 4.14 - 2.2 = 1.94` eV (ii) The number of photons reaching the surface PER second is `n_(P) = (P)/(E) xx A` `= (2)/(6.626 xx 10^(-19)) xx 2 xx 10^(-4) = 6.04 xx 10^(14)` photons/sec The rate of emission of photoelectrons is `= (0.40) n_(P) = 0.4 xx 6.04 xx 10^(14)` `= 2.415 xx 10^(14)` photoelectrons/sec |
|
| 7171. |
The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted from a surface when photons of energy 3 eV fall on it is 4 eV. The stopping potential, in volt, is……………….. |
|
Answer» 2 |
|
| 7172. |
Consider a rubber ball freely falling from a height h = 4.9 m on to a horizontal elastic plate. Assume that the duration of collision is negligible and the collision with the plate is totally elastic. Then the velocity as a function of time and the height as a function of time will be : |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 7173. |
An electric technicain requires a capacitance fo 2 muF in a circuit across a potentialdifferences of 1 KV. A large numberof 1 muF capacitors are available to him, each of which can withstanda potentialdifference of not more than 400V. Suggesta possiblearrangement that requiresminimum numberof capacitors. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here. Total capacitance,`C = 2 mu F`, Potentialdifference, `V = 1 kV = 1000 vol t` Capacity of eachcapacitor, `C_(1) = 1 muF`, Maximum potentialdifferenceacross each. `V' = 400 vol t` Let n capacitorsfo `1 muF` each be connectedin series in a row and m suchrows be connectedin parallel as shown in FIG. As potentialdifferenceacorosseach row = 1000 volt `:.` Potential DIFFERENCE across each capacitors`= (1000)/(n) = V' = 400` `:. n = (1000)/(400) = 2.5` As n has to be a whole NUMBER(not less than 2.5), therefore , `n = 3`. Capacitanceof eachrow of 3 conderes of `11 muF` each, in series `= 1//3`. Total capacitance of m such rows in parallel `= (m)/(3) :. (m)/(3) = 2 (muF) or m = 6` `:.` total number capacitors `= n xx m = 3xx6 = 18` HENCE `1 muF` capacitors should beconnectedin six parallel rows, each row contaning three capacitors in series. 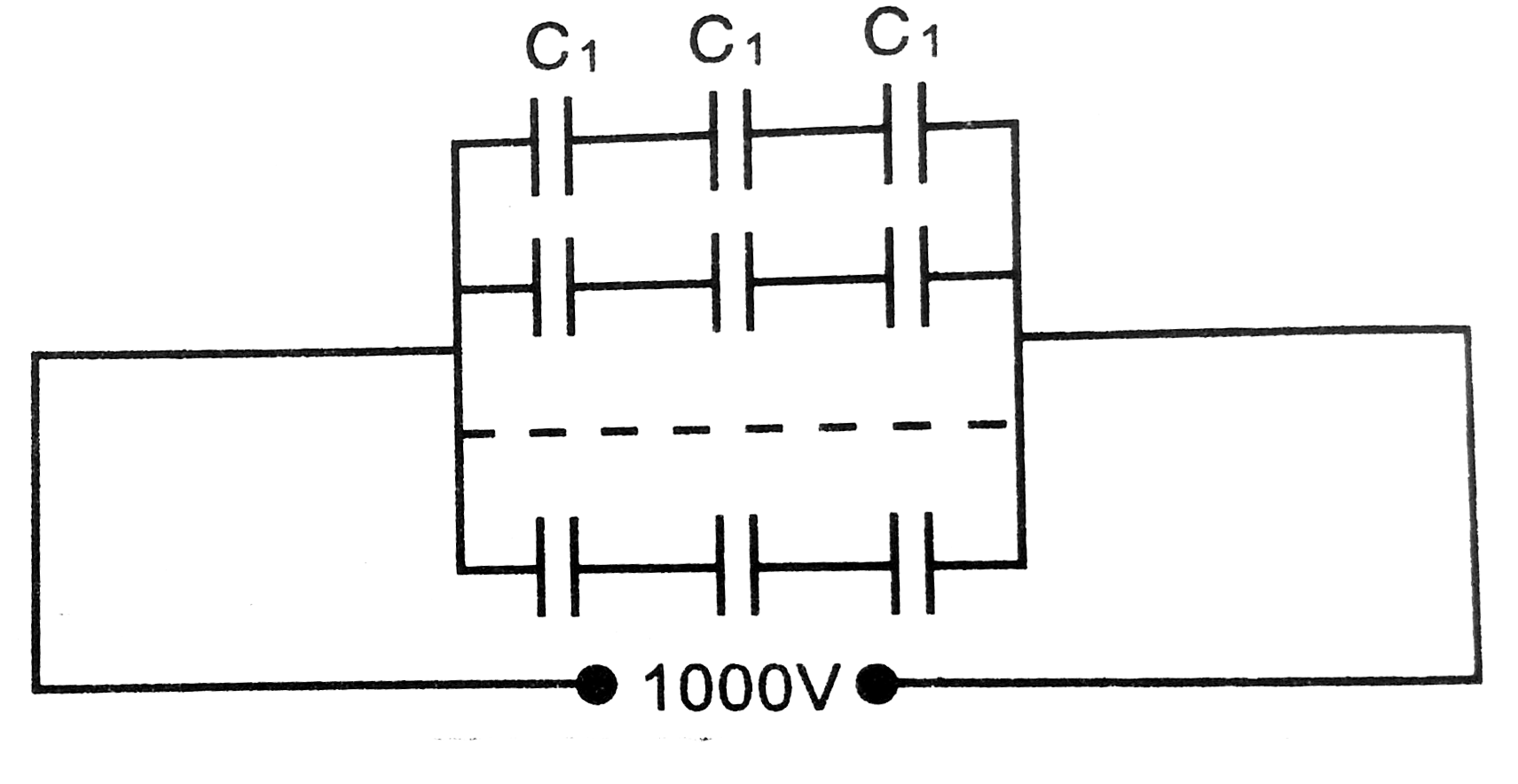
|
|
| 7174. |
After 300 days, the activity of a radioactive sample is 5000 dps (disintegrations per sec). The activity become 2500 dps after another 150 days. The initial activity of the sample in dps is |
|
Answer» 20000 |
|
| 7175. |
N divisions on the main scale of a vernier callipers coincide with (N+1) divisions of the vernier scale if each division of the main scale is 'a' units, then the least count of the instrument is |
|
Answer» a |
|
| 7176. |
A bulb of resistance 10 Omega , connected to an inductor of inductance L, is in series with an a.c. source marked 100 V, 50 Hz. If the phase angle between the voltage and current is pi/4. calculate the value of inductance. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7177. |
A physical quantity of the dimensions of length that can be formed out of c, G and (e^(2))/(4pi in_(0)) is [c is velocity of light G is universal constant of gravitation and e is charge : ]: |
|
Answer» `(1)/(C)G(e^(2))/(4piin_(0))` |
|
| 7178. |
Calcualte the increase in mass when a body of rest mass 1 kg is lifted up through 1 m near the earth's surface. |
|
Answer» Solution :The increase in energy = MGH ` = (1kg) (9.8 m s ^(-2) ) (1 m) = 9.8 J. ` The increase in MASS `= 9.8 J / c^(2) ` = 1.11 XX 10^(-16)kg`. |
|
| 7179. |
An aeroplane flies along a straight line from A to B with a speed v_0 and back again with the same speed v_0 . A steady wind v is blowing . If AB = 1 then (a) total time for the trips is (2v_0 1)/(v_0^2 - v^1) if wind blows along the line AB (b) total time for the trip is (21)/(sqrt(v_0^2- v^2)), if wind blows perpendicular to the line AB (c )total time for the trip decrease because of the presence of wind (d) total time for the trip increase because of the presence of wind |
|
Answer» a,B,d are CORRECT |
|
| 7180. |
In the above problem the angular width of the central maximum is |
|
Answer» `30^(@)` |
|
| 7181. |
What is positive health ? |
|
Answer» When our BODY and MIND is POSITIVE and healthy |
|
| 7182. |
In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the lowest orbit corresponds to |
|
Answer» INFINITE energy |
|
| 7183. |
An alternating current passes through a coil. When current in coil decreases from maximum to zero, then |
|
Answer» Energy is absorbed from SOURCE |
|
| 7184. |
A mobile phone lies along the principal axis of a concave mirror longitudinaly. Explain why the magnification is not uniform. |
Answer» Solution :The ray diagram for the formation of image of the PHONE is SHOWN in FIGURE. The image of the part which is on the plane perpendicular to principal axis will be on the same plane. It will be the SAMESIZE i.e., B'C = BC. 
|
|
| 7185. |
Whichof thefollowingcompoundswill notyieldiodoform on heating with iodineanddiluteNaOH? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 7186. |
The relative strengths of gravitational, coulomb.s and nuclear forces of protons are in the ratio (nearly) |
|
Answer» `1:1:1` |
|
| 7187. |
An electric dipole is along a uniform electric field. If it is deflected by 60^(@), work done by agent is 2 xx 10^(-19)J. Then the work done by an agent if it is deflected by 30^(@) further is |
|
Answer» `2.5 xx 10^(-19)J` |
|
| 7188. |
Three small spheres each carrying a positive charge Q are placed on the circumference of a circle of radius to form an equilateral triangle. The electric field intenstiy at the centre of the circle will be. |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 7189. |
In the figure shown 'PQRS' is a fixed resistanceless conducting frame is a uniform and constant magnetic field of strength B. A rod 'EF' of mass 'm' length 'l' and resistance R can smoothly move on this frame. A capacitor charged to a potential difference 'V_(0)' initially is connected as shown in the figure. Find the velocity of the rod as function of time 't' if it is released at t=0 from rest. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7190. |
(a)a conductor a witha cavitygiven a charge Q show that the entire charge must appear on the outer surface of theconductor (b) another condluctor B with charge q is sensitive instrument is to be shielded from the strong electrosatitic fields in its environmentsuggest a possible way |
| Answer» Solution :THEFORCE is `10^(-2)`in the negativez direction that is in the direction of decreasing electric fieldyoucan check that this is also theenergy of the dipole torque is ZERO | |
| 7191. |
A point charge 50 mu Cis located at a point 2hati + 3hatj . Find the electric field vector vec(E) at a point with position vector 8hati - 5hatj, when the position vectors are expressed in metre. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `q = 50 XX 10^(-6) C ` `vec(r ) = (vec(r_2)- vec(r_1)) = (8 hati - 5hatj) = (2 hati + 3hatj) = (6hati - 8hatj)` `bar(E ) = 1/(4 pi epsilon_0) q/(r^3) vecr implies (9 xx 10^(9) xx 50 xx 10^(-6))/(1000) xx (6 hati - 8 hatj)` then `bar(E) = 450 (6 hati - 8 hatj) NC^(-1) = 900 (3hati - 4hatj) NC^(-1)`. |
|
| 7192. |
The V-I characteristic of a silicon diode is shown in the Fig. Calculate the resistance of the diode at a) I_(D)=15mA and (b) V_(D)=-10V |
|
Answer» Solution :Considering the diode characteristics as a straight line between I = 10 mA to I = 20 mA passing through the origin, we can calculate the RESISTANCE using Ohm.s LAW. a) From the curve, at `I=20A, V=0.8V`, `I=10mA, V=0.7V` `r_("fb")=DeltaV//DeltaI=0.1V//10mA=10Omega` b) From the curve at `V=-10V.I=-1muA`. THEREFORE, `r_("RB")=10V//1muA=1.0xx10^(7)Omega` |
|
| 7193. |
In a uniform electric field, the potential is 10 V at the origin of coordinates and 8V at each of the points (1,0,0), (0,0,1) and (0,0,1). Then potential at the point (1,1,1) will be |
|
Answer» 0 |
|
| 7194. |
A laser has lambda= 7xx 10^(-7)m and aperature 10^(-3)m sends a beam to Moon which is at a distance of 4xx 10^(8)m from the Earth. Deduce the angular spread of the beam and the areal spread as it reaches Moon. |
|
Answer» Solution :We are given that `lambda= 7xx 10^(-7)m, a= 10^(-3)m, D= 4xx 10^(8)m` CLEARLY, angular SPREAD, `theta= (lambda/a)= (7xx 10^(-7)m)/(10^(-3)m)= 7xx 10^(-4)rad` Linear spread, `X= D theta` `=(4XX10^(-8)m)(7xx 10^(-4))= 28xx 10^(4)m` Areal spread `x^(2)= (28xx 10^(4)m)^(2)= 7.84xx 10^(10) m^(2)`. |
|
| 7195. |
A moving coil galvanometer is a sensitive device which can be used as a detector to check if a curretn is flowing in a circuit. A galvanometer works on the principle that a current carrying coil placed in a radial magnetic field experiences a deflecting torque whose magnitudes is directly proportional to the electric current passing through it. The deflection phi is indicated by a pointer and is give as phi = (NAB)/k cdot I. A galvonometer can be used to measure electric current flowing througha circuit direcly in ampere and its submultiples. For this purpose we join a small resistance 'r_s' in parallel to the galvonometer. Such a shunted galvonometer is called an ammeter. If a galvanomter, having a resistance R_G, givens full scale deflection for a current I_g and we want to measure a current ranging from 0 - I_g A, then the value of shunt resistance will be r_s = (R_G cdot I_g)/(I - I_g) There is a moving coil galvonometer in which there are 30 divisions on either side of central zero mark. It gives full scale deflection for a current of 600 mu A. What is its current sensitivity ? |
| Answer» Solution :Current SENSITIVITY = `(PHI)/I = (30 "div")/(600 mu A) = 5 xx 10^(4) "div"//A` | |
| 7196. |
If current is not obtained from secondary coil of an ideal transformer, then the power factor of primary coil of transformer is ......... |
|
Answer» 0 `lt P gt =V_(rms) I_(rms) cos delta` but power is not obtained in secondary coil `therefore` In 0 = `V_(rms) I_(rms) cos delta, V_(rms) ne 0 , I_(rms) ne 0` `therefore cos delta=0` `therefore delta=pi/2` and power REMAIN same in an ideal transformer . `therefore cos delta=0`, which is power factor. |
|
| 7197. |
A moving coil galvanometer is a sensitive device which can be used as a detector to check if a curretn is flowing in a circuit. A galvanometer works on the principle that a current carrying coil placed in a radial magnetic field experiences a deflecting torque whose magnitudes is directly proportional to the electric current passing through it. The deflection phi is indicated by a pointer and is give as phi = (NAB)/k cdot I. A galvonometer can be used to measure electric current flowing througha circuit direcly in ampere and its submultiples. For this purpose we join a small resistance 'r_s' in parallel to the galvonometer. Such a shunted galvonometer is called an ammeter. If a galvanomter, having a resistance R_G, givens full scale deflection for a current I_g and we want to measure a current ranging from 0 - I_g A, then the value of shunt resistance will be r_s = (R_G cdot I_g)/(I - I_g) How is a radial magnetic field obtained? |
| Answer» Solution :To make the FIELD radial the POLE PIECES of magnet USED to produce magnetic field B are given a concave shape and a cylindrical soft iron core is fixed in free space between the POLES. | |
| 7198. |
Sketch the electric lines of force due to a point charge q. If i) q0 |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 7199. |
A square loop of side 12 cm with its sides parallel to X and Y axes is moved with a velocity of 8 cm s^(-1) in the positive x-direction in an environment containing a magnetic field in the positive z-direction. The field is neither uniform in space nor constant in time. It has a gradient of 10^(-3) T cm^(-1) along the negative x-direction (that is it increases by 10^(-3) T cm^(-1) as one moves in the negative x-direction), and it is decreasing in time at the rate of 10^(-3)T s^(-1). Determine the direction and magnitude of the induced current in the loop if its resistance is 4.50 mOmega. |
|
Answer» Solution :Rate of change of flux due to explicit time variation in B `= 144 xx 10^(-4) m^2 xx 10^(-3) T s^(-1)` `= 1.44 xx 10^(-5) Wbs^(-1)` Rate of change of flux due to motion of the loop in a non-uniform B `=144 xx 10^(-4) m^2 xx 10^(-3) T cm^(-1) xx 8 cm s^(-1)` `= 11.52 xx 10^(5) Wb s^(-1)` The two effects ADD up since both CAUSE a decrease in flux along the positive z-direction. Therefore, INDUCED emf `= 12.96 ×x 10^(-5) V`, induced current = `2.88 x× 10^(-2)` A. The direction of induced current is such as to increase the flux through the loop along positive z-direction. If for the observer the loop moves to the right, the current will be seen to be anti-clockwise. A proper proof of the procedure above is as follows: `Phi (t) = int_0^a aB (x,t)dx` `(dPhi)/(dt) = a int_(0)^a dx (dB(x,t))/(dt)` using, `(dB)/(dt) = (deltaB)/(deltat) + (deltaB)/(deltax) (dx)/(dt)` `=[(deltaB)/(deltat) + v(deltaB)/(deltax)]` we get, `(dPhi)/(dt) = a int_(0)^a dx [(deltaB(x,t))/(deltat) + v(deltaB(x,t))/(deltax)]` `=A [(deltaB)/(deltat) + v(deltaB)/(deltax)]` where A= `a^2` The last STEP follows because `((deltaB)/(deltat)) , ((deltaB)/(deltax))` and v are given to beconstants in the problem. Even if you do not understand this formal proof (which requires good familiarity with calculus), you will still appreciate that flux change can occur both due to the motion of the loop as well as time variations in the magnetic FIELD. |
|
| 7200. |
Heavy stable nuclei have more neutrons than protons. This is because of the fact that |
|
Answer» NEUTRONS are heavier than PROTONS. |
|