Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 7101. |
Derive an expression for the work done in rotating an electric dipole of dipole moment 'p' in a uniform electric field 'E' from an orientation theta_1" to " theta_2. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Consider an ELECTRIC dipole of dipole MOMENT `vecp` placed in a uniform electric field `vecE` oriented at an angle `theta` with the direction of electric field. The torque acting on the dipole is `tau = pE sin theta` Elementary work done in rotating the dipole further through a small angle `d theta` against the torque is `dW = tau d theta = pE sin theta d theta` `:.`TOTAL work done in rotating the dipole from orientation `theta_1 " to " theta_2` will be `W = underset(theta_1)overset(theta_2)int pE sin theta d theta= pE [ -costheta]_(theta_1)^(theta_2)=pE[cos theta_1 - costheta_2]` |
|
| 7102. |
In case of suoerposition of two light waves, if the intensity is maximum , we call it ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :CONSTRUCTIVE INTERFERENCE | |
| 7103. |
Ideal fluid flows along a flat tube of constant cross-section, located in a horizontal plane and bent as shown in figure. (top view). The flow is steady. Are the presssures and velocities of the fluid equal at points 1 and 2? What is the shape of the streamlines? |
|
Answer» Solution :Between 1 and 2 FLUID particles are in nearly circular motion and therefore have centripetal acceleration. The force for this acceleration, like for any other situation in an ideal fluid, can only come from the pressure variation along the line joining 1 and 2. This requires that pressure at 1 should be greater than the pressure at 2 i.e. `p_1gtp_2` so that the fluid particles can have required acceleration. If there is no turbulence, the motion can be taken as irrotational. Then by considering `oint vecv.dvecl=0` along the circuit shown we INFER that `v_2gtv_1` (The portion of the circuit near 1 and 2 are streamlines while the other two arms are at right angle to streamlines) In an INCOMPRESSIBLE liquid we also have div `vecv=0` By electrostatic analogy we then FIND that the density of streamlines is proportional to the velocity at that POINT. 
|
|
| 7104. |
Referring to the previous illustration, if the boy releases the ball from rest, what will be the radius of curvature of the path at the instant of its release? |
|
Answer» Solution :The radius of curvature, `r=(V^(2))/(gostheta_(0))` `theta_(0)`=angle between v & HORIZONTAL = 0, when the ball is released. It STARTS moving horizontally with a SPEED y = speed of the train `10 m//sec`. `rArr r=(v^(2))/(gcostheta^(@))=((10)^(2))/(g)=10m` `thetA_(0)`=angle between V & horizontal = 0 |
|
| 7105. |
A convex mirror gives the image of an object 30 cm from it at the same point as plane mirror at a distance of 5.0 cm from the convex mirror and 25.0 cm from the object. Find the radius of curvature of convex mirror. |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 7106. |
The reverse biasing in a p-n junction diode |
|
Answer» decreases the potential BARRIER. |
|
| 7107. |
The polariser and analyser are inclined to each other at 60^(@). If I/2 is the intensity of the polarised light emergent from analyser .Then the intensity of the unpolarised light incident on the polariser is |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 7108. |
A transistor is used in the common emitter mode as an amplifier then :– (A) the input signal is connected in series with the voltage applied to bias the base collector junction (B) the base emitter junction is reverse baised (C) the input signal is connected in series with the voltage applied to bias the base emitter junction (D) the input signal is connected in series with the voltage applied to bias the base collector junction |
|
Answer» A, B |
|
| 7109. |
Young's duble slit experiment is set up in a liquid.The 10th bright fringe in the liquid lies where the 6th dark fringe lies in vacuum. The refractive index of the liquid is approximately : |
|
Answer» `1.8` `beta. = lambda. (D)/(d)` In LIQUID `lambda. gt lambda`(in AIR), so `beta. ` is REDUCED. `10 beta. = (5.5) beta` `10lambda.((D)/(d)) = (5.5)(lambdaD)/(d)` `(lambda)/(lambda). = (10)/(5.5) = mu` `mu = 1.8` |
|
| 7110. |
A driver can be see the sunset at an angle of |
|
Answer» `SIN^(-1) (4//3)` `._(w)mu_(a) = (1)/(._(a)mu_(w)) = sin c` `:. sin c = (1)/((4)/(3)) = (3)/(4)` `c = sin^(-1)((3)/(4))`. |
|
| 7111. |
A hole is |
|
Answer» A positively charge electron |
|
| 7112. |
The amplitude of the sinusoidally oscillating electric field of a plane is vm^(-1). Then the amplitude of magnetic field is: |
|
Answer» `2XX10^7T` |
|
| 7113. |
A point charge causes an electric field of -1.0xx10^3Nm^2//Cto pass through a spherical Gaussian surface of 10.0 cm radius centred on the charge If the radius’ of the Gaussian surface were doubled, how much flux would pass through the surface ? |
| Answer» Solution :The CHARGE inside the Gaussian SURFACE REMAINS .CONSTANT. So the flux passing through the surface will not change EVEN if the radius is doubled.Flux=-1.0xx10^3Nm^2//C | |
| 7114. |
In a a.c. circuit, the instantaneous current is maximum when the instantaneous voltage is maximum. The circuit element connected to the source is a : |
|
Answer» PURE INDUCTOR |
|
| 7115. |
Applying an external battery across two ends of a diode what we call ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7116. |
The frequency of the first overtone of a closed pipe of length l_(1)is equal to that of the first overtone of an open pipe of length l_(1) . The ratio of their lengths (l_(1) : l_(2)) is |
|
Answer» `2:3` `v_( c) =(3v)/(4l_(1))` Where v is the velocity of sound in air. The frequency of the first overtone of an open pipe of length `l_(2)` is `v_(O) =(2v)/(2l_(2)) =v/l_(2)` As per QUESTION, `v_( C) =v_(0)` `therefore 3/4 v/l_(1) = v/l_(2)` or `l_(1)/l_(2) = 3/4` |
|
| 7117. |
Statement - I : It is hotter above the top of a fire than at some distance on the sides. Statement - II : Airsorrounding the fire conducts more heat upwards. |
|
Answer» STATEMENT - I is true, Statement - II is true and Statement - I is CORRECT EXPLANATION for Statement - II. So correct CHOICE is (c ). |
|
| 7118. |
Here are two vectors: veca = (4.0m) hati - (3.0m)hatj and vecb = (6.0m)hati + (8.0m)hatj. What are (a) the magnitude and (b) the angle (relative to hati) of veca? What are (c ) the magnitude and (d) the angle of vecb ? What are(e) the magnitude and(f) the angle veca + vecb, of (g) teh magnitude and (h) the angle of veca =- vecb, and (i) the magnitude and (i) the angle of veca - vecband veca - vecb ? |
| Answer» Solution :`(a) 5.0-m, (b) - 37 ^(@)` (clockwise), `©10m, (d) 53^(@),(e) 11m,(f) 27 ^(@) ,(g) 11m, (h) 80^(@) , (i) 11m, (J) 260^(@),(K) 180^(@)` | |
| 7119. |
(a) state briefly the processes involved in the formation ofp-nhow the depletion region is formed (b) using the necessary ciruitdiagrams showp-n jucntion are obtained in (i) forward biasing (ii) reverse biasing how these characteiistics are made use of in recitifcation |
Answer» SOLUTION :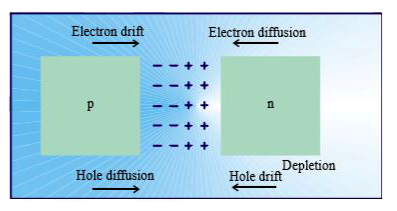 Two PROCESSES occur during the formation of a p-n junction are diffusion and drift. Due to the concentration gradient across p and n-sides of the junction, holes diffuse from p-side to n-side (p `to` n) and electrons diffuse from n-side to p-side (n `to` p). This movement of CHARGE carriers leaves behind ionised acceptors (negative charge `phi` - immobile) on the p-side and donors (positive charge immobile) on the n-side of the junction. This SPACE charge region on EITHER side of the junction together is known as depletion region. |
|
| 7120. |
Obtain the expression of electric field by thin spherical shell with uniform charge distribution at a point inside it. |
Answer» Solution :As shown in FIGURE, surface charge density on spherical SHELL of radius R is `sigma` 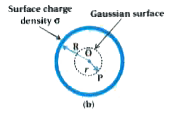 The point P is inside the shell. The Gaussian surface is a SPHERE through P centered at O of radius r. The FLUX through the Gaussian surface, calculated as before is `E xx 4pir^(2)`. In this case, the Gaussian surface encloses no charge. Gauss.s law gives, `E xx 4pir^(2) =0 , (therefore q/epsilon_(0) =0 "as" q=0)` `therefore E =0, (r LT R)` Thus, the field due to a uniformly charged thin shell is zero at all points inside the shell. |
|
| 7121. |
In the above problem find the work done is shifting of mass 1kg from origin (0,0) to a point (5 ,4) (In J) . |
|
Answer» `-180` |
|
| 7122. |
If the electron drift speed is small, and the electron's charge is small, how can we still obtain large amounts of current in a conductor ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Because FREE electron NUMBER density is very large in the metal approximately`10^(29)`per `1 m^(3)` , it contributes majority in producing large current in the metallic wires. | |
| 7123. |
What happens if an iron bar magnet is melted ? Does it retain its magnetism? |
| Answer» Solution :MOLTEN iron does not retain its magnetism because in the process it is heated up even beyond the Curie temperature and LOSES its FERROMAGNETIC character. | |
| 7124. |
A thin horizontal circular disc is rotating about a vertical axis passing through its centre. An insect is at rest at a point near the rim of the disc. The insect now moves along a diameter of the disc to reach its other end. During the journey of the insect, the angular speed of the disc : |
|
Answer» continuously decreases |
|
| 7125. |
A nuclear event is shown in the diagram. a. Name the nuclear phenomenon. b. What happens to the residual nucleus? Explain. c. Compare the binding energy per nucleon of the daughter and the parent. d. At what time the h upsilon is emitted ? Explain. |
|
Answer» Solution :a. Radiactivity . B. It rebounds (or recoils): DUE to momentum conservation principle. c. The BE per nucleon increases by the ACTIVITY. d. There is no SPECIFIC time. It is spontaneous `gamma`- emission can be independent or followed by `alpha`- DECAY. |
|
| 7126. |
A particle of mass m and charge q has an initial velocity vecv =v_(0)hatj. If an electric field E = E_(0)hatiand B = B_(0)hatimagnetic field act on the particle, its speed will double after a time |
|
Answer» `t=(sqrt(3)mv_(0))/(qE)` 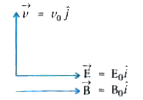 Magnitude of VELOCITY doesn.t change in Y-Z plane. `(2v_(0))^(2) =v_(0)^(2) +v_(x)^(2)` `therefore v_(x) = sqrt(3)v_(0)` `therefore` From equation of motion, `v_(x) =v_(0x) + a_(0x)t` `therefore sqrt(3)v_(0) =(qE)/MT, therefore t=(sqrt(3)mv_(0))/(qE)` |
|
| 7127. |
What is called "to speak in a soft voice and romantically"? |
|
Answer» Murmur |
|
| 7128. |
A rectangular glass slab of thickness 3 cm and of refractive index 1.5 is placed in front of a concave mirror, perpendicular to its principal axis. The radius of curvature of the mirror is 10 cm. Where is an object to be placed onthe principal axis so that its image will be formed on the object? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The rectangular GLASS slab is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of the CONCAVE mirror `M_(1)M_(2)` [Fig. 2.58]. SUPPOSE that if an OBJECT is placed at O on the principal axis, its image will be formed at O. `OABM_(1)` is the path of the ray. The ray after reflection at `M_(1)` retraces the path and forms image at O. So the ray `BM_(1)` must be incident on the mirror at `M_(1)` perpendicular. If `M_(1)B "its produced backward it intersects the principal axis at O. . So O. is the centre of curvature of the concave of the concave mirror."` `therefore "" PO. = 10cm` `Now, "" O O.= t(1-(1)/(mu)) = 3(1- (1)/(1.5))` = 3 - 2 = 1cm So, the distance of O from the concave mirror PO. + O O. = 10 + 1 = 11cm 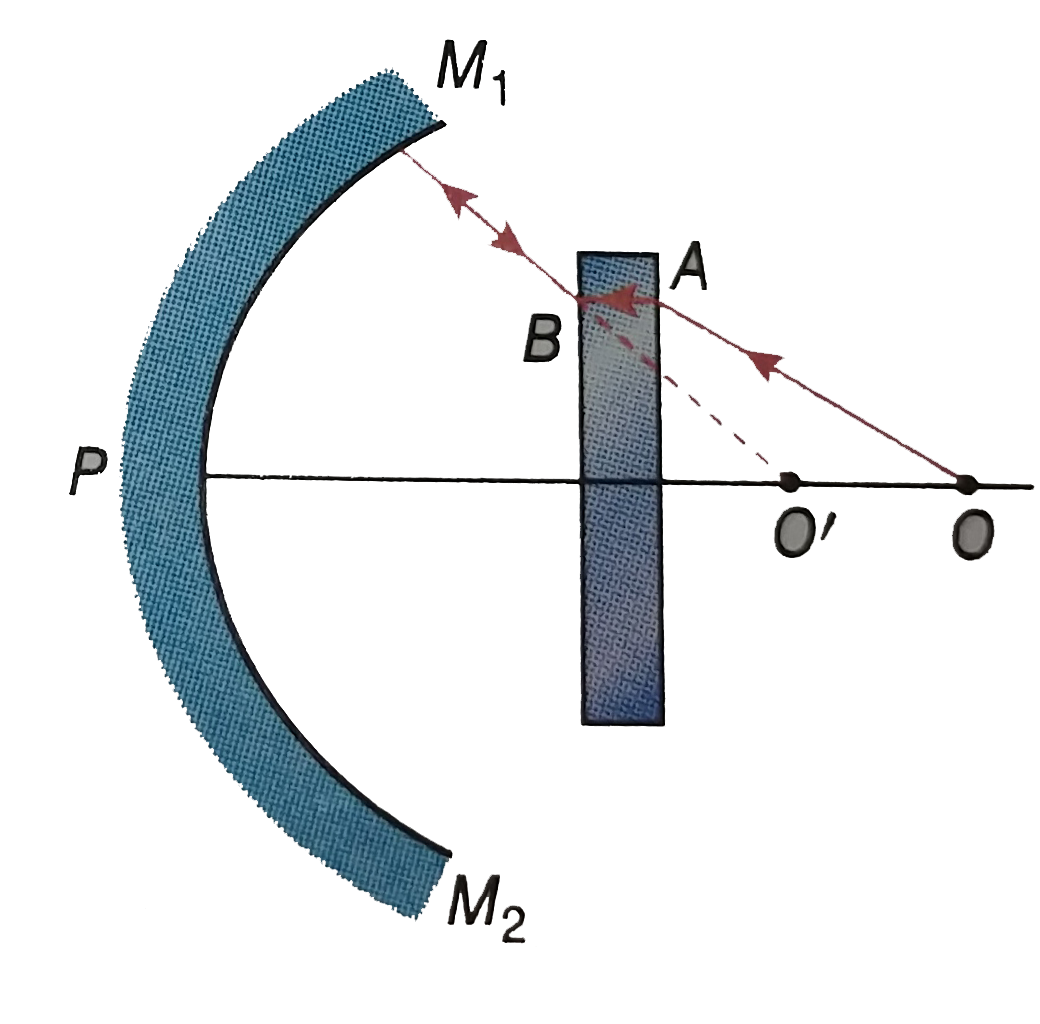
|
|
| 7129. |
The error in the measurement of length of a simple pendulum is 0.1 % and error in the time period is 2% . The possible maximum error in the quantity having dimensional formula LT^(-2) is |
|
Answer» `1.1 %` |
|
| 7130. |
If a disc of mass m and radius r is reshaped into a ring of radius 2r, the mass remaining the same, the radius of gyration goes up by a factor of : |
|
Answer» 4 For RING `m(2R)^(2)=mk_(2)^(2)""k_(2)""2r` `therefore (k_(2))/(k_(1))=(2r)/(sqrt((1)/(2)r))=2sqrt(2)` |
|
| 7131. |
A thermos bottle containing coffee is vigorouslyshaken. Consider coffee as a system: Has its internal energy changed ? |
| Answer» Solution :`DeltaQ=DeltaU+Delta` But `DeltaQ=0,thereforeDeltaU=-DeltaW`, here `DeltaW`is negative because WORK is done on the SYSTEM. Now A [7 is positive, HENCE internal . ENERGY of the system increases | |
| 7132. |
A metallic piece gets hot when surrounded by a coil carrying high frequency alternatingcurrent. Why ? |
| Answer» Solution :DUE to the heating EFFECT of eddy currents set up in the METALLIC PIECE. | |
| 7133. |
The two surfaces of a biconvex lens has same radii of curvatures. This lens is made of glass of refractive index 1.5 and has a focal length 10 cm in air. The lens is cut into two equal halves along a plane perpendicular to its principal axis to yield two plano-convex lenses. The two pieces are glued such that the convex surfaces touch each other. If this combination lens is immersed in water of refractive index 4/3 its focal length (in cm) is |
|
Answer» 5 |
|
| 7134. |
A gaseous mixture enclosed in a vessel consists of one g mole ofa gas A with gamma=(5/3)and some amount of gas B with gamma=7/5 ata temperature T .The gases A and B do not react with each other and are assumed to be ideal . Find the number of g moles of the gas B if gamma for the gaseous mixture is (19/13) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7135. |
A radioactive isotope X decays simultaneously by two ways alpha and beta decay. The decay constants of alpha and beta decays are lambda_(1) and lambda_(2) and the products formed are Y and Z respectivley. Both Y and Z are stable. Initially. there was no presence of Y and Z in the sample. The process of alpha decay stops fater time t_(0). Find the ratio of mass of Y to mass of Z in the sample at time 2t_(0) the molar masses of Y and Z are M_(y) and M_(z) respectively. |
| Answer» | |
| 7136. |
The frequency changes by 10% as a sound source approaches a stationary observer with constant speed v . What would be the percentage change in frequency as the source recedes the observer with the same speed. Given that v_(s) lt v . (v = speed of sound in air) |
|
Answer» 0.143 |
|
| 7137. |
If the radius of communication satellite were to reduce to half, then its time period would be- |
|
Answer» a)`2"times"` |
|
| 7138. |
If the wavelength of K_(alpha) radiation emitted an atom of atomic number Z = 41 is lambda , then the atomic number for an atom that emits K_(alpha) radiation with the wavelength 4lambda, is |
|
Answer» 21 |
|
| 7139. |
Nuclei of a radioactive element A are being produced at a constant rate alpha. The element has a decay constant lambda. At time t=0, there are N_0 nuclei of the element. (a) Calculate the number N of nuclei of A at time t. (b) If alpha=2N_0lambda, calculate the number of nuclei of A after one half-life of A, and also the limiting value of N as trarroo. |
|
Answer» `1/LAMBDA[alpha + (alpha -N_0lambda)e^(-lambdat)]` Decay constant of element =` lambda` At t=0, nuclei of the element present =`N_0` Number N of nuclei of A at time t : NET rate of FORMATION of nuclei of element A =`"dN"/"dt"` `therefore "dN"/"dt"=alpha -lambdaN` or `(dN)/(alpha - lambdaN)=dt` or `underset(N_0)oversetNint (dN)/(alpha - lambdaN) = underset0oversett INT dt` or `-1/lambda [ In (alpha - lambdaN)]_(N_0)^N=t` or In` ((alpha-lambdaN)/(alpha - lambdaN_0))=-lambdat` or `(alpha - lambdaN)/(alpha - N_0lambda)=e^(-lambdat)` or `alpha -lambdaN=e^(-lambdat)(alpha - lambdaN_0)` or `N=1/lambda[alpha - (alpha -N_0lambda)e^(-lambdat)]` |
|
| 7140. |
A soap bubble of radius 1/sqrtpi cm is expanded to have double the radius. If S.T. is 30 dyne/cm then the work done is |
|
Answer» 180 ergs |
|
| 7141. |
Draw parallel and crossed polaroids neatly. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 7142. |
Do all photons have same mass ? If not , why ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Mass of a photon = E/`c^2` = `(he)/c^2`. DIFFERENT RADIATIONS have different frequencies. So, their photons have different masses. | |
| 7143. |
In the circuit as shown in the figure, the heat produced by 6 ohm resistance due to current flowing in it is 60 calorie per second. The heat generated across 3 ohm resistance per second will be |
|
Answer» 30 calorie/sec |
|
| 7144. |
The figure shows five pairs of plates : A, B and D are charged plastic plates and C is an electrically neutral copper plate. The electrostatic forces between the pairs of plates are shown for three of the pairs. For the remaining two pairs, do the plates repel or attract each other ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :C and D ATTRACT, B and D attract | |
| 7145. |
Match the items mentioned in the lists I and II belowLIST - I(a) Static friction(b) Limiting friction(c ) Kinetic friction(d) Rolling frictionLIST - II (e ) constant for a given pair of surfaces(f) Independent of area of contact(g) Self adjusting(h) Has the least magnitude for a given normal reaction |
|
Answer» a-e, b-f, C-g, d-h |
|
| 7146. |
When a glass lens with mu = 1.47 is immersed in a troug of liquid, it looks to be disappeared. The liquid in the trough could be |
|
Answer» water |
|
| 7147. |
A conducting sphere of radius a has charge Q on it. It is enchosed by a neutral coorducting concentric spherical shell having inner radius 2a and other radius 3a. Find self energy of outer shell |
|
Answer» `(5)/(12)(KQ^(2))/(a)` |
|
| 7148. |
If I_(0) is the intensity of principal maxima in single slit diffraction pattern, then what is intensity, if slit width is doubled? |
|
Answer» `(I_(0))/(2)` |
|
| 7149. |
Find the quality factorof a circuit with capacitance C=2.0 mu F and inductance L=5.0 mH if the maintenance of undamped oscillations in the circuit with the voltage amplitude across the capacitor being equal to V_(m)=1.0 Vrequires a power ( :P: )=0.10m W.The damping of oscillations is sufficiently low |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :Given `V=V_(m) E^(-BETAT)sin omegat, omega~= omega_(0) betaTlt lt 1`Power loss `=(" Energy loss per cylcle")/(T)` `~=(1)/(2) CV_(m)^(2)xx2 beta` `(` energy decreasesas `W_(0) e^(-2betat) ` so loss per cycle is `W_(0)xx2 betaT)` Thus `lt P gt =(1)/(2)CV_(m)^(2)xx(R)/(L)` or `R=(2lt P gt)/( V_(m)^(2))(L)/(C)` HENCE`Q=(1)/(R) sqrt((L)/(C))=sqrt((C)/(L))(V_(m)^(2))/(2lt P gt)=100`on putting the vales. |
|
| 7150. |
Light of wavelength 5000Åand intensity 39.8Wm^(-1) is incident on a metal surface. If only 1% photons of incident light emit photoelectrons, then the number of electrons emitted per second per unit area from the surface will be nearly : |
|
Answer» `10^(18)` `rArr n=(E lambda)/(hc)` But `n=(n)/(100)=(E lambda)/(100 hc)=10^(18)` |
|